8.3 KiB
Deploying
The following guides are based on some shared assumptions:
- You are placing your docs inside the
docsdirectory of your project; - You are using the default build output location (
.vitepress/dist); - VitePress is installed as a local dependency in your project, and you have setup the following npm scripts:
{
"scripts": {
"docs:build": "vitepress build docs",
"docs:serve": "vitepress serve docs"
}
}
Build and test locally
You may run yarn docs:build command to build the docs.
$ yarn docs:build
By default, the build output will be placed at .vitepress/dist. You may deploy this dist folder to any of your preferred platforms.
Once you've built the docs, you may test them locally by running yarn docs:serve command.
$ yarn docs:build
$ yarn docs:serve
The serve command will boot up local static web server that serves the files from .vitepress/dist at http://localhost:5000. It's an easy way to check if the production build looks OK in your local environment.
You may configure the port of the server by passing --port flag as an argument.
{
"scripts": {
"docs:serve": "vitepress serve docs --port 8080"
}
}
Now the docs:serve method will launch the server at http://localhost:8080.
GitHub Pages
-
Set the correct
baseindocs/.vitepress/config.js.If you are deploying to
https://<USERNAME>.github.io/, you can omitbaseas it defaults to'/'.If you are deploying to
https://<USERNAME>.github.io/<REPO>/, for example your repository is athttps://github.com/<USERNAME>/<REPO>, then setbaseto'/<REPO>/'. -
Inside your project, create
deploy.shwith the following content (with highlighted lines uncommented appropriately), and run it to deploy:
#!/usr/bin/env sh
# abort on errors
set -e
# build
npm run docs:build
# navigate into the build output directory
cd docs/.vitepress/dist
# if you are deploying to a custom domain
# echo 'www.example.com' > CNAME
git init
git add -A
git commit -m 'deploy'
# if you are deploying to https://<USERNAME>.github.io
# git push -f git@github.com:<USERNAME>/<USERNAME>.github.io.git main
# if you are deploying to https://<USERNAME>.github.io/<REPO>
# git push -f git@github.com:<USERNAME>/<REPO>.git main:gh-pages
cd -
::: tip You can also run the above script in your CI setup to enable automatic deployment on each push. :::
GitHub Pages and Travis CI
-
Set the correct
baseindocs/.vitepress/config.js.If you are deploying to
https://<USERNAME or GROUP>.github.io/, you can omitbaseas it defaults to'/'.If you are deploying to
https://<USERNAME or GROUP>.github.io/<REPO>/, for example your repository is athttps://github.com/<USERNAME>/<REPO>, then setbaseto'/<REPO>/'. -
Create a file named
.travis.ymlin the root of your project. -
Run
yarnornpm installlocally and commit the generated lockfile (that isyarn.lockorpackage-lock.json). -
Use the GitHub Pages deploy provider template, and follow the Travis CI documentation.
language: node_js
node_js:
- lts/*
install:
- yarn install # npm ci
script:
- yarn docs:build # npm run docs:build
deploy:
provider: pages
skip_cleanup: true
local_dir: docs/.vitepress/dist
# A token generated on GitHub allowing Travis to push code on you repository.
# Set in the Travis settings page of your repository, as a secure variable.
github_token: $GITHUB_TOKEN
keep_history: true
on:
branch: main
GitLab Pages and GitLab CI
-
Set the correct
baseindocs/.vitepress/config.js.If you are deploying to
https://<USERNAME or GROUP>.gitlab.io/, you can omitbaseas it defaults to'/'.If you are deploying to
https://<USERNAME or GROUP>.gitlab.io/<REPO>/, for example your repository is athttps://gitlab.com/<USERNAME>/<REPO>, then setbaseto'/<REPO>/'. -
Set
outDirin.vitepress/config.jsto../public. -
Create a file called
.gitlab-ci.ymlin the root of your project with the content below. This will build and deploy your site whenever you make changes to your content:
image: node:16
pages:
cache:
paths:
- node_modules/
script:
- yarn install # npm install
- yarn docs:build # npm run docs:build
artifacts:
paths:
- public
only:
- main
Netlify
- On Netlify, setup up a new project from GitHub with the following settings:
- Build Command:
vitepress build docsoryarn docs:buildornpm run docs:build - Publish directory:
docs/.vitepress/dist
- Hit the deploy button.
Google Firebase
-
Make sure you have firebase-tools installed.
-
Create
firebase.jsonand.firebasercat the root of your project with the following content:
firebase.json:
{
"hosting": {
"public": "./docs/.vitepress/dist",
"ignore": []
}
}
.firebaserc:
{
"projects": {
"default": "<YOUR_FIREBASE_ID>"
}
}
- After running
yarn docs:buildornpm run docs:build, deploy using the commandfirebase deploy.
Surge
-
First install surge, if you haven’t already.
-
Run
yarn docs:buildornpm run docs:build. -
Deploy to surge by typing
surge docs/.vitepress/dist.
You can also deploy to a custom domain by adding surge docs/.vitepress/dist yourdomain.com.
Heroku
-
Install Heroku CLI.
-
Create a Heroku account by signing up.
-
Run
heroku loginand fill in your Heroku credentials:
$ heroku login
- Create a file called
static.jsonin the root of your project with the below content:
static.json:
{
"root": "./docs/.vitepress/dist"
}
This is the configuration of your site; read more at heroku-buildpack-static.
- Set up your Heroku git remote:
# version change
$ git init
$ git add .
$ git commit -m "My site ready for deployment."
# creates a new app with a specified name
$ heroku apps:create example
# set buildpack for static sites
$ heroku buildpacks:set https://github.com/heroku/heroku-buildpack-static.git
- Deploy your site:
# publish site
$ git push heroku main
# opens a browser to view the Dashboard version of Heroku CI
$ heroku open
Vercel
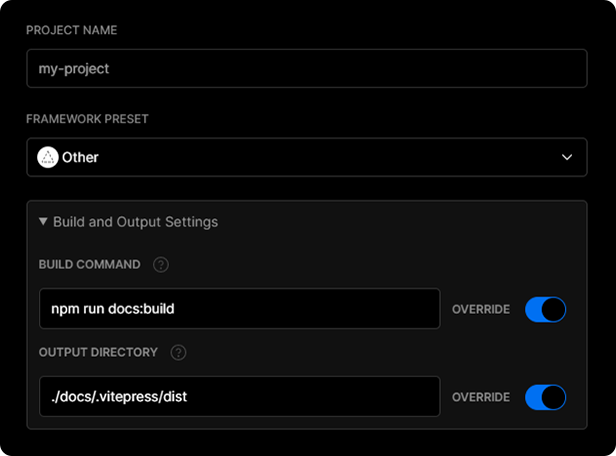
To deploy your VitePress app with a Vercel for Git, make sure it has been pushed to a Git repository.
Go to https://vercel.com/new and import the project into Vercel using your Git of choice (GitHub, GitLab or BitBucket). Follow the wizard to select the project root with the project's package.json and override the build step using yarn docs:build or npm run docs:build and the output dir to be ./docs/.vitepress/dist
After your project has been imported, all subsequent pushes to branches will generate Preview Deployments, and all changes made to the Production Branch (commonly "main") will result in a Production Deployment.
Once deployed, you will get a URL to see your app live, such as the following: https://vitepress.vercel.app
Layer0
See Creating and Deploying a VitePress App with Layer0.
Cloudflare Pages
- Go to Cloudflare dashboard > Account Home > Pages and selecting Create a project.
- You will see three options, just select first Connect to a git provider.
- Click Connect GitHub or Connect GitLab. Then select the repo you want to deploy.
- Set up build docs command, like
npm run buildornpm run docs:build. - Now deploy, you will get a domain like
my-project.pages.dev.
::: warning Do not Auto Minify HTML If you want or are using Cloudflare's Auto minify feature, you should not check the html box.
With Auto Minify, Cloudflare will automatically remove the comments in the html file, however, html comments for Vue has meanings. For example, it works as a placeholder for v-if.
If it gets removed, then you will probably see a hydration mismatch error. :::