40 KiB
在数据持久层,数据源和事务是两个非常重要的组件,对数据持久层的影响很大,在实际开发中,一般会使用 Mybatis 集成第三方数据源组件,如:c3p0、Druid,另外,Mybatis 也提供了自己的数据库连接池实现,本文会通过 Mybatis 的源码实现来了解数据库连接池的设计。而事务方面,一般使用 Spring 进行事务的管理,这里不做详细分析。下面我们看一下 Mybatis 是如何对这两部分进行封装的。
1 DataSource
常见的数据源都会实现 javax.sql.DataSource接口,Mybatis 中提供了两个该接口的实现类,分别是:PooledDataSource 和 UnpooledDataSource,并使用不同的工厂类分别管理这两个类的对象。
1.1 DataSourceFactory
DataSourceFactory系列类 的设计比较简单,DataSourceFactory 作为顶级接口,UnpooledDataSourceFactory 实现了该接口,PooledDataSourceFactory 又继承了 UnpooledDataSourceFactory。
public interface DataSourceFactory {
// 设置 DataSource 的属性,一般紧跟在 DataSource 初始化之后
void setProperties(Properties props);
// 获取 DataSource对象
DataSource getDataSource();
}
public class UnpooledDataSourceFactory implements DataSourceFactory {
private static final String DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX = "driver.";
private static final int DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX_LENGTH = DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX.length();
protected DataSource dataSource;
// 在实例化该工厂时,就完成了 DataSource 的实例化
public UnpooledDataSourceFactory() {
this.dataSource = new UnpooledDataSource();
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
Properties driverProperties = new Properties();
// 创建 dataSource 对应的 MetaObject
MetaObject metaDataSource = SystemMetaObject.forObject(dataSource);
// 处理 properties 中配置的数据源信息
for (Object key : properties.keySet()) {
String propertyName = (String) key;
if (propertyName.startsWith(DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX)) {
// 以 "driver." 开头的配置项是对 DataSource 的配置,将其记录到 driverProperties 中
String value = properties.getProperty(propertyName);
driverProperties.setProperty(propertyName.substring(DRIVER_PROPERTY_PREFIX_LENGTH), value);
} else if (metaDataSource.hasSetter(propertyName)) {
String value = (String) properties.get(propertyName);
Object convertedValue = convertValue(metaDataSource, propertyName, value);
metaDataSource.setValue(propertyName, convertedValue);
} else {
throw new DataSourceException("Unknown DataSource property: " + propertyName);
}
}
if (driverProperties.size() > 0) {
// 设置数据源 UnpooledDataSource 的 driverProperties属性,
// PooledDataSource 中持有 UnpooledDataSource对象
metaDataSource.setValue("driverProperties", driverProperties);
}
}
@Override
public DataSource getDataSource() {
return dataSource;
}
}
public class PooledDataSourceFactory extends UnpooledDataSourceFactory {
// 与 UnpooledDataSourceFactory 的不同之处是,其初始化的 DataSource 为 PooledDataSource
public PooledDataSourceFactory() {
this.dataSource = new PooledDataSource();
}
}
1.2 UnpooledDataSource
本实现类实现了 DataSource接口 中的 getConnection() 及其重载方法,用于获取数据库连接。其中的主要属性及方法如下:
public class UnpooledDataSource implements DataSource {
// 加载 Driver驱动类 的类加载器
private ClassLoader driverClassLoader;
// 数据库连接驱动的相关配置,通过 UnpooledDataSourceFactory 的 setProperties()方法 设置进来的
private Properties driverProperties;
// 缓存所有已注册的 数据库连接驱动Driver
private static Map<String, Driver> registeredDrivers = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// 数据库连接驱动名称
private String driver;
// 数据库url
private String url;
// 用户名
private String username;
// 密码
private String password;
// 是否自动提交事务
private Boolean autoCommit;
// 默认的事务隔离级别
private Integer defaultTransactionIsolationLevel;
// 默认的网络连接超时时间
private Integer defaultNetworkTimeout;
/**
* UnpooledDataSource 被加载时,会通过该静态代码块将已经在 DriverManager
* 中注册的 JDBC Driver 注册到 registeredDrivers 中
*/
static {
Enumeration<Driver> drivers = DriverManager.getDrivers();
while (drivers.hasMoreElements()) {
Driver driver = drivers.nextElement();
registeredDrivers.put(driver.getClass().getName(), driver);
}
}
// getConnection() 及其重载方法、doGetConnection(String username, String password)方法
// 最终都会调用本方法
private Connection doGetConnection(Properties properties) throws SQLException {
// 初始化数据库驱动,该方法会创建配置中指定的 Driver对象,
// 并将其注册到 DriverManager 和 registeredDrivers 中
initializeDriver();
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, properties);
// 配置数据库连接属性,如:连接超时时间、是否自动提交事务、事务隔离级别
configureConnection(connection);
return connection;
}
private synchronized void initializeDriver() throws SQLException {
// 判断驱动是否已注册
if (!registeredDrivers.containsKey(driver)) {
Class<?> driverType;
try {
if (driverClassLoader != null) {
// 注册驱动
driverType = Class.forName(driver, true, driverClassLoader);
} else {
driverType = Resources.classForName(driver);
}
// 通过反射获取 Driver实例对象
Driver driverInstance = (Driver)driverType.newInstance();
// 注册驱动到 DriverManager,DriverProxy 是 UnpooledDataSource 的内部类
// 也是 Driver 的静态代理类
DriverManager.registerDriver(new DriverProxy(driverInstance));
// 将 driver 缓存到 registeredDrivers
registeredDrivers.put(driver, driverInstance);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new SQLException("Error setting driver on UnpooledDataSource. Cause: " + e);
}
}
}
private void configureConnection(Connection conn) throws SQLException {
// 连接超时时间
if (defaultNetworkTimeout != null) {
conn.setNetworkTimeout(Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(), defaultNetworkTimeout);
}
// 是否自动提交事务
if (autoCommit != null && autoCommit != conn.getAutoCommit()) {
conn.setAutoCommit(autoCommit);
}
// 事务隔离级别
if (defaultTransactionIsolationLevel != null) {
conn.setTransactionIsolation(defaultTransactionIsolationLevel);
}
}
}
1.3 PooledDataSource
数据库建立连接是非常耗时的,且并发的连接数也非常有限。而数据库连接池可以实现数据库的重用、提高响应速度、防止数据库因连接过多而假死等。 数据库连接池的设计思路一般为:
- 连接池初始化时创建一定数量的连接,并添加到连接池中备用;
- 当程序需要使用数据库连接时,从连接池中请求,用完后会将其返还给连接池,而不是直接关闭;
- 连接池会控制总连接上限及空闲连接上线,如果连接池中的连接总数已达上限,且都被占用,后续的连接请求会短暂阻塞后重新尝试获取连接,如此循环,直到有连接可用;
- 如果连接池中空闲连接较多,已达到空闲连接上限,则返回的连接会被关闭掉,以降低系统开销。
PooledDataSource 实现了简易的数据库连接池功能,其创建数据库连接的功能依赖了上面的 UnpooledDataSource。
1.3.1 PooledConnection
PooledDataSource 通过管理 PooledConnection 来实现对 java.sql.Connection 的管理。PooledConnection 封装了 java.sql.Connection数据库连接对象 及其代理对象(JDK动态代理生成的)。PooledConnection 继承了 JDK动态代理 的 InvocationHandler接口。
class PooledConnection implements InvocationHandler {
// 记录当前 PooledConnection对象 所属的 PooledDataSource对象
// 当调用 close()方法 时会将 PooledConnection 放回该 PooledDataSource
private final PooledDataSource dataSource;
// 真正的数据库连接对象
private final Connection realConnection;
// 代理连接对象
private final Connection proxyConnection;
// 从连接池中取出该连接时的时间戳
private long checkoutTimestamp;
// 创建该连接时的时间戳
private long createdTimestamp;
// 最后一次使用的 时间戳
private long lastUsedTimestamp;
// 由 数据库URL、用户名、密码 计算出来的 hash值,可用于标识该连接所在的连接池
private int connectionTypeCode;
// 检测当前 PooledConnection连接池连接对象 是否有效,主要用于 防止程序通过 close()方法 将
// 连接还给连接池之后,依然通过该连接操作数据库
private boolean valid;
/**
* invoke()方法 是本类的重点实现,也是 proxyConnection代理连接对象 的代理逻辑实现
* 它会对 close()方法 的调用进行处理,并在调用 realConnection对象 的方法之前进行校验
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
// 如果调用的是 close()方法,则将其放进连接池,而不是真的关闭连接
if (CLOSE.hashCode() == methodName.hashCode() && CLOSE.equals(methodName)) {
dataSource.pushConnection(this);
return null;
}
try {
if (!Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// 通过上面的 valid字段 校验连接是否有效
checkConnection();
}
// 调用 realConnection对象 的对应方法
return method.invoke(realConnection, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
private void checkConnection() throws SQLException {
if (!valid) {
throw new SQLException("Error accessing PooledConnection. Connection is invalid.");
}
}
}
1.3.2 PoolState
PoolState 主要用于管理 PooledConnection 对象状态,其通过持有两个 List<PooledConnection>集合 分别管理空闲状态的连接 和 活跃状态的连接。另外,PoolState 还定义了一系列用于统计的字段。
public class PoolState {
// 所属的连接池对象
protected PooledDataSource dataSource;
// 空闲的连接
protected final List<PooledConnection> idleConnections = new ArrayList<>();
// 活跃的连接
protected final List<PooledConnection> activeConnections = new ArrayList<>();
// 请求数据库连接的次数
protected long requestCount = 0;
// 获取连接的累计时间(accumulate累计)
protected long accumulatedRequestTime = 0;
// CheckoutTime = 记录 应用从连接池取出连接到归还连接的时长
// accumulatedCheckoutTime = 所有连接累计的CheckoutTime
protected long accumulatedCheckoutTime = 0;
// 超时连接的个数(当连接长时间未归还给连接池时,会被认为连接超时)
protected long claimedOverdueConnectionCount = 0;
// 累计超时时间
protected long accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections = 0;
// 累计等待时间
protected long accumulatedWaitTime = 0;
// 等待次数
protected long hadToWaitCount = 0;
// 无效的连接数
protected long badConnectionCount = 0;
public PoolState(PooledDataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
public synchronized long getRequestCount() {
return requestCount;
}
public synchronized long getAverageRequestTime() {
return requestCount == 0 ? 0 : accumulatedRequestTime / requestCount;
}
public synchronized long getAverageWaitTime() {
return hadToWaitCount == 0 ? 0 : accumulatedWaitTime / hadToWaitCount;
}
public synchronized long getHadToWaitCount() {
return hadToWaitCount;
}
public synchronized long getBadConnectionCount() {
return badConnectionCount;
}
public synchronized long getClaimedOverdueConnectionCount() {
return claimedOverdueConnectionCount;
}
public synchronized long getAverageOverdueCheckoutTime() {
return claimedOverdueConnectionCount == 0 ? 0 : accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections / claimedOverdueConnectionCount;
}
public synchronized long getAverageCheckoutTime() {
return requestCount == 0 ? 0 : accumulatedCheckoutTime / requestCount;
}
public synchronized int getIdleConnectionCount() {
return idleConnections.size();
}
public synchronized int getActiveConnectionCount() {
return activeConnections.size();
}
@Override
public synchronized String toString() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
builder.append("\n===CONFINGURATION==============================================");
builder.append("\n jdbcDriver ").append(dataSource.getDriver());
builder.append("\n jdbcUrl ").append(dataSource.getUrl());
builder.append("\n jdbcUsername ").append(dataSource.getUsername());
builder.append("\n jdbcPassword ").append(dataSource.getPassword() == null ? "NULL" : "************");
builder.append("\n poolMaxActiveConnections ").append(dataSource.poolMaximumActiveConnections);
builder.append("\n poolMaxIdleConnections ").append(dataSource.poolMaximumIdleConnections);
builder.append("\n poolMaxCheckoutTime ").append(dataSource.poolMaximumCheckoutTime);
builder.append("\n poolTimeToWait ").append(dataSource.poolTimeToWait);
builder.append("\n poolPingEnabled ").append(dataSource.poolPingEnabled);
builder.append("\n poolPingQuery ").append(dataSource.poolPingQuery);
builder.append("\n poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor ").append(dataSource.poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor);
builder.append("\n ---STATUS-----------------------------------------------------");
builder.append("\n activeConnections ").append(getActiveConnectionCount());
builder.append("\n idleConnections ").append(getIdleConnectionCount());
builder.append("\n requestCount ").append(getRequestCount());
builder.append("\n averageRequestTime ").append(getAverageRequestTime());
builder.append("\n averageCheckoutTime ").append(getAverageCheckoutTime());
builder.append("\n claimedOverdue ").append(getClaimedOverdueConnectionCount());
builder.append("\n averageOverdueCheckoutTime ").append(getAverageOverdueCheckoutTime());
builder.append("\n hadToWait ").append(getHadToWaitCount());
builder.append("\n averageWaitTime ").append(getAverageWaitTime());
builder.append("\n badConnectionCount ").append(getBadConnectionCount());
builder.append("\n===============================================================");
return builder.toString();
}
}
1.3.3 PooledDataSource
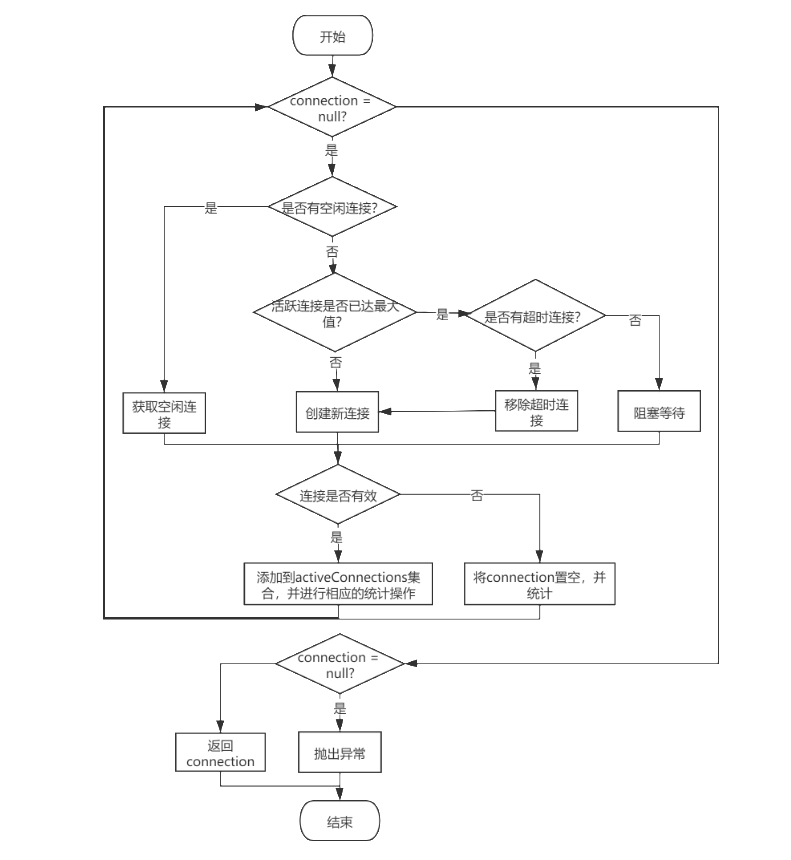
PooledDataSource 管理的数据库连接对象 是由其持有的 UnpooledDataSource对象 创建的,并由 PoolState 管理所有连接的状态。 PooledDataSource 的 getConnection()方法 会首先调用 popConnection()方法 获取 PooledConnection对象,然后通过 PooledConnection 的 getProxyConnection()方法 获取数据库连接的代理对象。popConnection()方法 是 PooledDataSource 的核心逻辑之一,其整体的逻辑关系如下图:
public class PooledDataSource implements DataSource {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(PooledDataSource.class);
// 管理连接池状态 并统计连接信息
private final PoolState state = new PoolState(this);
// 该对象用于生成真正的数据库连接对象,构造函数中会初始化该字段
private final UnpooledDataSource dataSource;
// 最大活跃连接数
protected int poolMaximumActiveConnections = 10;
// 最大空闲连接数
protected int poolMaximumIdleConnections = 5;
// 最大Checkout时长
protected int poolMaximumCheckoutTime = 20000;
// 在无法获取连接时,线程需要等待的时间
protected int poolTimeToWait = 20000;
// 本地坏连接最大数
protected int poolMaximumLocalBadConnectionTolerance = 3;
// 检测数据库连接是否可用时,给数据库发送的sql语句
protected String poolPingQuery = "NO PING QUERY SET";
// 是否允许发送上述语句
protected boolean poolPingEnabled;
// 当连接超过poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor毫秒未使用,
// 就发送一次上述sql,检测连接连接是否正常
protected int poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor;
// 根据数据库URL、用户名、密码 生成的一个hash值,
// 该hash值用于标记当前的连接池,在构造函数中初始化
private int expectedConnectionTypeCode;
/**
* 下面的两个 getConnection()方法 都会调用 popConnection()
* 获取 PooledConnection对象,然后调用该对象的 getProxyConnection()方法
* 获取数据库连接的代理对象
*/
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return popConnection(dataSource.getUsername(), dataSource.getPassword()).getProxyConnection();
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return popConnection(username, password).getProxyConnection();
}
/**
* 本方法实现了连接池获取连接对象的具体逻辑,是 PooledDataSource 的核心逻辑之一
*/
private PooledConnection popConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
boolean countedWait = false;
PooledConnection conn = null;
long t = System.currentTimeMillis();
int localBadConnectionCount = 0;
// 循环获取数据库连接对象,直到获取成功
while (conn == null) {
// 连接池的连接是公共资源,要对线程加锁
synchronized (state) {
// 如果连接池中有空闲的 数据库连接对象,就取出一个
if (!state.idleConnections.isEmpty()) {
conn = state.idleConnections.remove(0);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Checked out connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " from pool.");
}
} else {
// 没有空闲的连接对象,就判断一下 活跃的连接数是否已达 设定的峰值
if (state.activeConnections.size() < poolMaximumActiveConnections) {
// 还没达到峰值 就创建一个新的连接
conn = new PooledConnection(dataSource.getConnection(), this);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Created connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {
// 如果活跃的连接已达上限,就取出最老的活跃连接对象,判断其是否超时
PooledConnection oldestActiveConnection = state.activeConnections.get(0);
long longestCheckoutTime = oldestActiveConnection.getCheckoutTime();
if (longestCheckoutTime > poolMaximumCheckoutTime) {
// 如果最老的连接超时了,就在 PoolState 中记录一下相关信息,然后将该连接对象释放掉
state.claimedOverdueConnectionCount++;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTimeOfOverdueConnections += longestCheckoutTime;
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += longestCheckoutTime;
state.activeConnections.remove(oldestActiveConnection);
// 如果最老的连接不是 自动提交事务的,就将事务回滚掉
if (!oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
try {
oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection().rollback();
} catch (SQLException e) {
/*
Just log a message for debug and continue to execute the following
statement like nothing happened.
Wrap the bad connection with a new PooledConnection, this will help
to not interrupt current executing thread and give current thread a
chance to join the next competition for another valid/good database
connection. At the end of this loop, bad {@link @conn} will be set as null.
*/
log.debug("Bad connection. Could not roll back");
}
}
// 从最老连接中取出真正的 数据库连接对象及相关信息,用来构建新的 PooledConnection对象
conn = new PooledConnection(oldestActiveConnection.getRealConnection(), this);
conn.setCreatedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getCreatedTimestamp());
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(oldestActiveConnection.getLastUsedTimestamp());
// 将最老活跃连接设为无效
oldestActiveConnection.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Claimed overdue connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
} else {
// 如果最老的连接对象也没超时,则进入阻塞等待,
// 等待时间 poolTimeToWait 可自行设置
try {
if (!countedWait) {
// 等待次数加一
state.hadToWaitCount++;
countedWait = true;
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Waiting as long as " + poolTimeToWait + " milliseconds for connection.");
}
long wt = System.currentTimeMillis();
// native方法,使执行到这里的线程阻塞等待 poolTimeToWait毫秒
state.wait(poolTimeToWait);
// 统计累计等待的时间
state.accumulatedWaitTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - wt;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
break;
}
}
}
}
// 到了这里 基本上就获取到连接对象咯,但我们还要确认一下该连接对象是否是有效的 可用的
if (conn != null) {
// ping一下数据库服务器,确认该连接对象是否有效
if (conn.isValid()) {
// 如果事务提交配置为手动的,则先让该连接回滚一下事务,防止脏数据的出现
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
// 设置 由数据库URL、用户名、密码 计算出来的hash值,可用于标识该连接所在的连接池
conn.setConnectionTypeCode(assembleConnectionTypeCode(dataSource.getUrl(), username, password));
// 设置 从连接池中取出该连接时的时间戳
conn.setCheckoutTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
// 设置 最后一次使用的时间戳
conn.setLastUsedTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
// 将该连接加入活跃的连接对象列表
state.activeConnections.add(conn);
// 请求数据库连接的次数加一
state.requestCount++;
// 计算 获取连接的累计时间(accumulate累计)
state.accumulatedRequestTime += System.currentTimeMillis() - t;
// 如果获取到的连接无效
} else {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") was returned from the pool, getting another connection.");
}
// 对无效连接进行统计
state.badConnectionCount++;
localBadConnectionCount++;
conn = null;
// 如果无效连接超出 阈值,则抛出异常
if (localBadConnectionCount > (poolMaximumIdleConnections + poolMaximumLocalBadConnectionTolerance)) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Could not get a good connection to the database.");
}
}
}
}
}
// 如果到了这里 连接还为空,则抛出一个未知的服务异常
if (conn == null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
throw new SQLException("PooledDataSource: Unknown severe error condition. The connection pool returned a null connection.");
}
// 返回数据库连接对象
return conn;
}
/**
* 看一下之前讲过的 PooledConnection 中的 动态代理方法invoke(),可以发现
* 当调用数据库连接代理对象的 close()方法 时,并未关闭真正的数据库连接,
* 而是调用了本方法,将连接对象归还给连接池,方便后续使用,本方法也是 PooledDataSource 的核心逻辑之一
*/
protected void pushConnection(PooledConnection conn) throws SQLException {
// 国际惯例,操作公共资源先上个锁
synchronized (state) {
// 先将该连接从活跃的连接对象列表中剔除
state.activeConnections.remove(conn);
// 如果该连接有效
if (conn.isValid()) {
// 如果连接池中的空闲连接数未达到阈值 且 该连接确实属于
// 本连接池(通过之前获取的 expectedConnectionTypeCode 进行校验)
if (state.idleConnections.size() < poolMaximumIdleConnections && conn.getConnectionTypeCode() == expectedConnectionTypeCode) {
// CheckoutTime = 应用从连接池取出连接到归还连接的时长
// accumulatedCheckoutTime = 所有连接累计的CheckoutTime
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
// 不是自动提交事务的连接 先回滚一波
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
// 从 conn 中取出真正的 数据库连接对象,重新封装成 PooledConnection
PooledConnection newConn = new PooledConnection(conn.getRealConnection(), this);
// 将 newConn 放进空闲连接对象列表
state.idleConnections.add(newConn);
// 设置 newConn 的相关属性
newConn.setCreatedTimestamp(conn.getCreatedTimestamp());
newConn.setLastUsedTimestamp(conn.getLastUsedTimestamp());
// 将原本的 conn 作废
conn.invalidate();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Returned connection " + newConn.getRealHashCode() + " to pool.");
}
// 唤醒阻塞等待的线程
state.notifyAll();
} else {
// 如果空闲连接已达阈值 或 该连接对象不属于本连接池,则做好统计数据
// 回滚连接的事务,关闭真正的连接,最后作废 该conn
state.accumulatedCheckoutTime += conn.getCheckoutTime();
if (!conn.getRealConnection().getAutoCommit()) {
conn.getRealConnection().rollback();
}
conn.getRealConnection().close();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closed connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + ".");
}
conn.invalidate();
}
// 如果该连接是无效的,则记录一下无效的连接数
} else {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("A bad connection (" + conn.getRealHashCode() + ") attempted to return to the pool, discarding connection.");
}
state.badConnectionCount++;
}
}
}
/**
* 关闭连接池中 所有活跃的 及 空闲的连接
* 当修改连接池的配置(如:用户名、密码、URL等),都会调用本方法
*/
public void forceCloseAll() {
// 日常上锁
synchronized (state) {
// 更新当前连接池的标识
expectedConnectionTypeCode = assembleConnectionTypeCode(dataSource.getUrl(), dataSource.getUsername(), dataSource.getPassword());
// 依次关闭活跃的连接对象
for (int i = state.activeConnections.size(); i > 0; i--) {
try {
PooledConnection conn = state.activeConnections.remove(i - 1);
conn.invalidate();
Connection realConn = conn.getRealConnection();
if (!realConn.getAutoCommit()) {
realConn.rollback();
}
realConn.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// ignore
}
}
// 依次关闭空闲的连接对象
for (int i = state.idleConnections.size(); i > 0; i--) {
try {
PooledConnection conn = state.idleConnections.remove(i - 1);
conn.invalidate();
Connection realConn = conn.getRealConnection();
if (!realConn.getAutoCommit()) {
realConn.rollback();
}
realConn.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// ignore
}
}
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("PooledDataSource forcefully closed/removed all connections.");
}
}
}
最后,我们来看一下 popConnection() 和 pushConnection() 都调用了的 isValid()方法,该方法除了检测 PooledConnection 中的 valid字段 外 还还会调用 PooledDataSource 中的 pingConnection()方法,让数据库连接对象 执行指定的 sql语句,检测连接是否正常。
class PooledConnection implements InvocationHandler {
/**
* 检测 PooledConnection对象 的有效性
*/
public boolean isValid() {
return valid && realConnection != null && dataSource.pingConnection(this);
}
}
public class PooledDataSource implements DataSource {
/**
* ping 一下数据库,检测数据库连接是否正常
*/
protected boolean pingConnection(PooledConnection conn) {
boolean result = true;
try {
result = !conn.getRealConnection().isClosed();
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " is BAD: " + e.getMessage());
}
result = false;
}
if (result) {
// 是否允许发送检测语句,检测数据库连接是否正常,poolPingEnabled 可自行配置
// 该检测会牺牲一定的系统资源,以提高安全性
if (poolPingEnabled) {
// 超过 poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor毫秒 未使用的连接 才会检测其连接状态
if (poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor >= 0 && conn.getTimeElapsedSinceLastUse() > poolPingConnectionsNotUsedFor) {
try {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Testing connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " ...");
}
// 获取真正的连接对象,执行 poolPingQuery = "NO PING QUERY SET" sql语句
Connection realConn = conn.getRealConnection();
try (Statement statement = realConn.createStatement()) {
statement.executeQuery(poolPingQuery).close();
}
if (!realConn.getAutoCommit()) {
realConn.rollback();
}
result = true;
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " is GOOD!");
}
// 如果上面这段代码抛出异常,则说明数据库连接有问题,将该连接关闭,返回false
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("Execution of ping query '" + poolPingQuery + "' failed: " + e.getMessage());
try {
conn.getRealConnection().close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
//ignore
}
result = false;
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Connection " + conn.getRealHashCode() + " is BAD: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
2 Transaction
遵循 “接口-实现类” 的设计原则,Mybatis 也是先使用 Transaction接口 对数据库事务做了抽象,而实现类则只提供了两个,即:JdbcTransaction 和 ManagedTransaction。这两种对象的获取,使用了两个对应的工厂类 JdbcTransactionFactory 和 ManagedTransactionFactory。 不过一般我们并不会使用 Mybatis 管理事务,而是将 Mybatis 集成到 Spring,由 Spring 进行事务的管理。细节部分会在后面的文章中详细讲解。
public interface Transaction {
/**
* 获取连接对象
*/
Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;
/**
* 提交事务
*/
void commit() throws SQLException;
/**
* 回滚事务
*/
void rollback() throws SQLException;
/**
* 关闭数据库连接
*/
void close() throws SQLException;
/**
* 获取配置的事务超时时间
*/
Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException;
}
public class JdbcTransaction implements Transaction {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(JdbcTransaction.class);
// 当前事务对应的数据库连接
protected Connection connection;
// 当前事务对应的数据源
protected DataSource dataSource;
// 事务隔离级别
protected TransactionIsolationLevel level;
// 是否自动提交
protected boolean autoCommit;
public JdbcTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel desiredLevel, boolean desiredAutoCommit) {
dataSource = ds;
level = desiredLevel;
autoCommit = desiredAutoCommit;
}
public JdbcTransaction(Connection connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (connection == null) {
openConnection();
}
return connection;
}
// 提交、回滚、关闭等操作的代码都比较简单,只对原生的 JDBC操作 做了简单封装
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Committing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.commit();
}
}
@Override
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Rolling back JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.rollback();
}
}
@Override
public void close() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null) {
resetAutoCommit();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.close();
}
}
protected void setDesiredAutoCommit(boolean desiredAutoCommit) {
try {
if (connection.getAutoCommit() != desiredAutoCommit) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Setting autocommit to " + desiredAutoCommit + " on JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.setAutoCommit(desiredAutoCommit);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// Only a very poorly implemented driver would fail here,
// and there's not much we can do about that.
throw new TransactionException("Error configuring AutoCommit. "
+ "Your driver may not support getAutoCommit() or setAutoCommit(). "
+ "Requested setting: " + desiredAutoCommit + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
protected void resetAutoCommit() {
try {
if (!connection.getAutoCommit()) {
// MyBatis does not call commit/rollback on a connection if just selects were performed.
// Some databases start transactions with select statements
// and they mandate a commit/rollback before closing the connection.
// A workaround is setting the autocommit to true before closing the connection.
// Sybase throws an exception here.
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Resetting autocommit to true on JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.setAutoCommit(true);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Error resetting autocommit to true "
+ "before closing the connection. Cause: " + e);
}
}
}
protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
}
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
if (level != null) {
connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel());
}
setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommit);
}
@Override
public Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
}
public class ManagedTransaction implements Transaction {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(ManagedTransaction.class);
// 数据源
private DataSource dataSource;
// 事务隔离级别
private TransactionIsolationLevel level;
// 对应的数据库连接
private Connection connection;
// 控制是否关闭持有的连接,在 close()方法 中用其判断是否真的关闭连接
private final boolean closeConnection;
// 本类的实现也很简单,commit()、rollback()方法 都是空实现
public ManagedTransaction(Connection connection, boolean closeConnection) {
this.connection = connection;
this.closeConnection = closeConnection;
}
public ManagedTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean closeConnection) {
this.dataSource = ds;
this.level = level;
this.closeConnection = closeConnection;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (this.connection == null) {
openConnection();
}
return this.connection;
}
@Override
public void commit() throws SQLException {
// Does nothing
}
@Override
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
// Does nothing
}
@Override
public void close() throws SQLException {
if (this.closeConnection && this.connection != null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closing JDBC Connection [" + this.connection + "]");
}
this.connection.close();
}
}
protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
}
this.connection = this.dataSource.getConnection();
if (this.level != null) {
this.connection.setTransactionIsolation(this.level.getLevel());
}
}
@Override
public Integer getTimeout() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
}
public interface TransactionFactory {
/**
* 配置 TransactionFactory对象,一般会在完成 TransactionFactory对象
* 初始化之后 就进行自定义属性配置
*/
default void setProperties(Properties props) {
// NOP
}
/**
* 在指定的数据库连接上创建 Transaction事务对象
*/
Transaction newTransaction(Connection conn);
/**
* 从指定数据源获取数据库连接,并在此连接上创建 Transaction对象
*/
Transaction newTransaction(DataSource dataSource, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit);
}
public class JdbcTransactionFactory implements TransactionFactory {
@Override
public Transaction newTransaction(Connection conn) {
return new JdbcTransaction(conn);
}
@Override
public Transaction newTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
return new JdbcTransaction(ds, level, autoCommit);
}
}
public class ManagedTransactionFactory implements TransactionFactory {
private boolean closeConnection = true;
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties props) {
if (props != null) {
String closeConnectionProperty = props.getProperty("closeConnection");
if (closeConnectionProperty != null) {
closeConnection = Boolean.valueOf(closeConnectionProperty);
}
}
}
@Override
public Transaction newTransaction(Connection conn) {
return new ManagedTransaction(conn, closeConnection);
}
@Override
public Transaction newTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
// Silently ignores autocommit and isolation level, as managed transactions are entirely
// controlled by an external manager. It's silently ignored so that
// code remains portable between managed and unmanaged configurations.
return new ManagedTransaction(ds, level, closeConnection);
}
}