14 KiB
Architecture Learning Journey
In this learning journey you will learn about the Now in Android app architecture: its layers, key classes and the interactions between them.
Goals and requirements
The goals for the app architecture are:
- Follow the official architecture guidance as closely as possible.
- Easy for developers to understand, nothing too experimental.
- Support multiple developers working on the same codebase.
- Facilitate local and instrumented tests, both on the developer’s machine and using Continuous Integration (CI).
- Minimize build times.
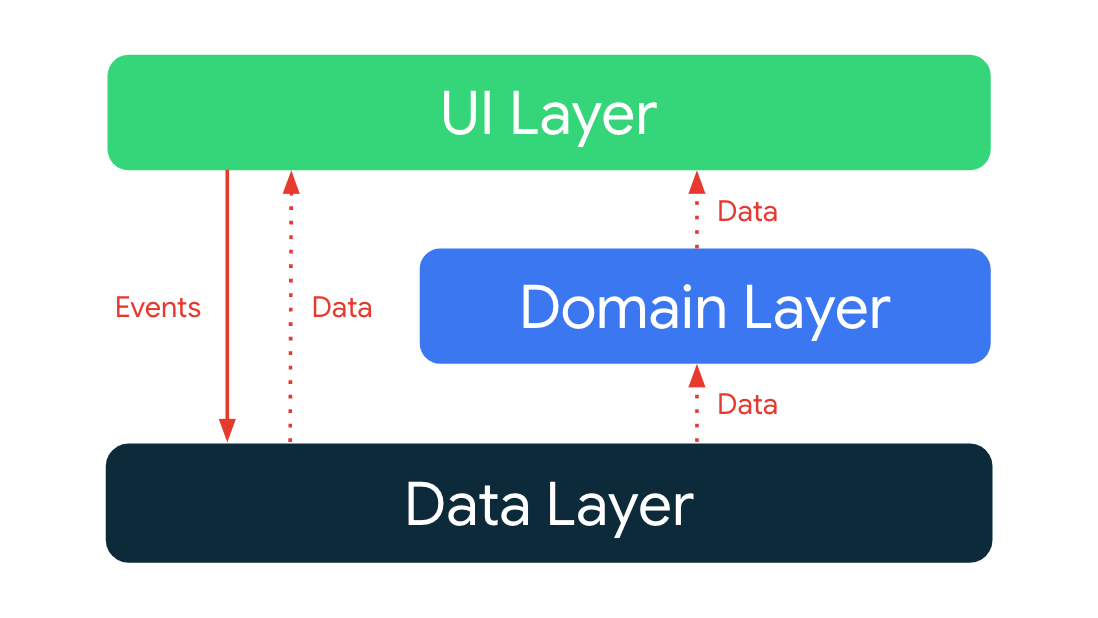
Architecture overview
The app architecture has three layers: a data layer, a domain layer and a UI layer.
[!NOTE]
The official Android architecture is different from other architectures, such as "Clean Architecture". Concepts from other architectures may not apply here, or be applied in different ways. More discussion here.
The architecture follows a reactive programming model with unidirectional data flow. With the data layer at the bottom, the key concepts are:
- Higher layers react to changes in lower layers.
- Events flow down.
- Data flows up.
The data flow is achieved using streams, implemented using Kotlin Flows.
Example: Displaying news on the For You screen
When the app is first run it will attempt to load a list of news resources from a remote server (when the prod build flavor is selected, demo builds will use local data). Once loaded, these are shown to the user based on the interests they choose.
The following diagram shows the events which occur and how data flows from the relevant objects to achieve this.
Here's what's happening in each step. The easiest way to find the associated code is to load the project into Android Studio and search for the text in the Code column (handy shortcut: tap ⇧ SHIFT twice).
| Step | Description | Code |
| 1 | On app startup, a WorkManager job to sync all repositories is enqueued. | Sync.initialize
|
| 2 | The ForYouViewModel calls GetUserNewsResourcesUseCase to obtain a stream of news resources with their bookmarked/saved state. No items will be emitted into this stream until both the user and news repositories emit an item. While waiting, the feed state is set to Loading.
|
Search for usages of NewsFeedUiState.Loading
|
| 3 | The user data repository obtains a stream of UserData objects from a local data source backed by Proto DataStore.
|
NiaPreferencesDataSource.userData
|
| 4 | WorkManager executes the sync job which calls OfflineFirstNewsRepository to start synchronizing data with the remote data source.
|
SyncWorker.doWork
|
| 5 | OfflineFirstNewsRepository calls RetrofitNiaNetwork to execute the actual API request using Retrofit.
|
OfflineFirstNewsRepository.syncWith
|
| 6 | RetrofitNiaNetwork calls the REST API on the remote server.
|
RetrofitNiaNetwork.getNewsResources
|
| 7 | RetrofitNiaNetwork receives the network response from the remote server.
|
RetrofitNiaNetwork.getNewsResources
|
| 8 | OfflineFirstNewsRepository syncs the remote data with NewsResourceDao by inserting, updating or deleting data in a local Room database.
|
OfflineFirstNewsRepository.syncWith
|
| 9 | When data changes in NewsResourceDao it is emitted into the news resources data stream (which is a Flow).
|
NewsResourceDao.getNewsResources
|
| 10 | OfflineFirstNewsRepository acts as an intermediate operator on this stream, transforming the incoming PopulatedNewsResource (a database model, internal to the data layer) to the public NewsResource model which is consumed by other layers.
|
OfflineFirstNewsRepository.getNewsResources
|
| 11 | GetUserNewsResourcesUseCase combines the list of news resources with the user data to emit a list of UserNewsResources.
|
GetUserNewsResourcesUseCase.invoke
|
| 12 | When ForYouViewModel receives the saveable news resources it updates the feed state to Success.
|
Search for instances of NewsFeedUiState.Success
|
Data layer
The data layer is implemented as an offline-first source of app data and business logic. It is the source of truth for all data in the app.
Each repository has its own models. For example, the TopicsRepository has a Topic model and the NewsRepository has a NewsResource model.
Repositories are the public API for other layers, they provide the only way to access the app data. The repositories typically offer one or more methods for reading and writing data.
Reading data
Data is exposed as data streams. This means each client of the repository must be prepared to react to data changes. Data is not exposed as a snapshot (e.g. getModel) because there's no guarantee that it will still be valid by the time it is used.
Reads are performed from local storage as the source of truth, therefore errors are not expected when reading from Repository instances. However, errors may occur when trying to reconcile data in local storage with remote sources. For more on error reconciliation, check the data synchronization section below.
Example: Read a list of topics
A list of Topics can be obtained by subscribing to TopicsRepository::getTopics flow which emits List<Topic>.
Whenever the list of topics changes (for example, when a new topic is added), the updated List<Topic> is emitted into the stream.
Writing data
To write data, the repository provides suspend functions. It is up to the caller to ensure that their execution is suitably scoped.
Example: Follow a topic
Simply call UserDataRepository.toggleFollowedTopicId with the ID of the topic the user wishes to follow and followed=true to indicate that the topic should be followed (use false to unfollow a topic).
Data sources
A repository may depend on one or more data sources. For example, the OfflineFirstTopicsRepository depends on the following data sources:
| Name | Backed by | Purpose |
| TopicsDao | Room/SQLite | Persistent relational data associated with Topics |
| NiaPreferencesDataSource | Proto DataStore | Persistent unstructured data associated with user preferences, specifically which Topics the user is interested in. This is defined and modeled in a .proto file, using the protobuf syntax. |
| NiaNetworkDataSource | Remote API accessed using Retrofit | Data for topics, provided through REST API endpoints as JSON. |
Data synchronization
Repositories are responsible for reconciling data in local storage with remote sources. Once data is obtained from a remote data source it is immediately written to local storage. The updated data is emitted from local storage (Room) into the relevant data stream and received by any listening clients.
This approach ensures that the read and write concerns of the app are separate and do not interfere with each other.
In the case of errors during data synchronization, an exponential backoff strategy is employed. This is delegated to WorkManager via the SyncWorker, an implementation of the Synchronizer interface.
See the OfflineFirstNewsRepository.syncWith for an example of data synchronization.
Domain layer
The domain layer contains use cases. These are classes which have a single invocable method (operator fun invoke) containing business logic.
These use cases are used to simplify and remove duplicate logic from ViewModels. They typically combine and transform data from repositories.
For example, GetUserNewsResourcesUseCase combines a stream (implemented using Flow) of NewsResources from a NewsRepository with a stream of UserData objects from a UserDataRepository to create a stream of UserNewsResources. This stream is used by various ViewModels to display news resources on screen with their bookmarked state.
Notably, the domain layer in Now in Android does not (for now) contain any use cases for event handling. Events are handled by the UI layer calling methods on repositories directly.
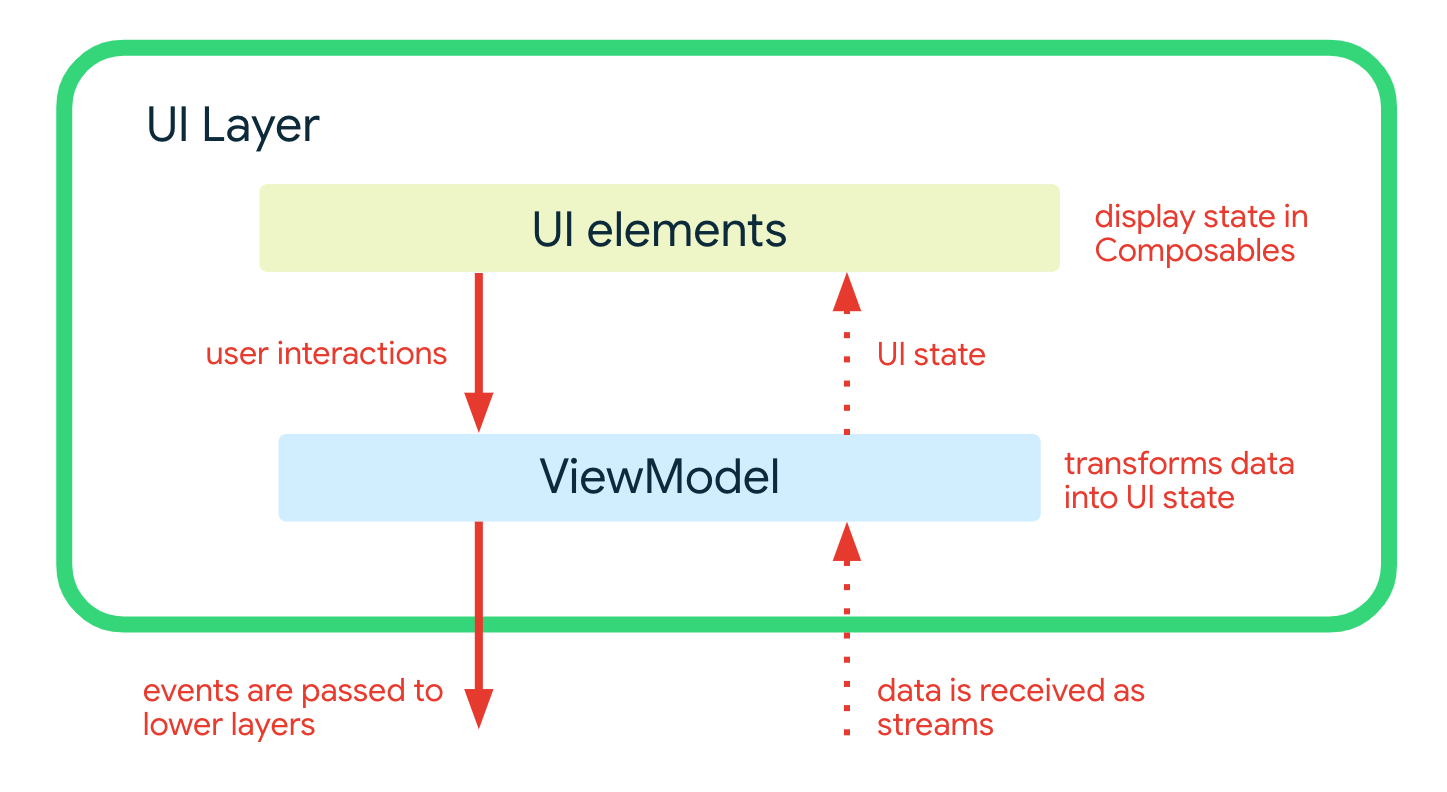
UI Layer
The UI layer comprises:
- UI elements built using Jetpack Compose
- Android ViewModels
The ViewModels receive streams of data from use cases and repositories, and transforms them into UI state. The UI elements reflect this state, and provide ways for the user to interact with the app. These interactions are passed as events to the ViewModel where they are processed.
Modeling UI state
UI state is modeled as a sealed hierarchy using interfaces and immutable data classes. State objects are only ever emitted through the transform of data streams. This approach ensures that:
- the UI state always represents the underlying app data - the app data is the source-of-truth.
- the UI elements handle all possible states.
Example: News feed on For You screen
The feed (a list) of news resources on the For You screen is modeled using NewsFeedUiState. This is a sealed interface which creates a hierarchy of two possible states:
Loadingindicates that the data is loadingSuccessindicates that the data was loaded successfully. The Success state contains the list of news resources.
The feedState is passed to the ForYouScreen composable, which handles both of these states.
Transforming streams into UI state
ViewModels receive streams of data as cold flows from one or more use cases or repositories. These are combined together, or simply mapped, to produce a single flow of UI state. This single flow is then converted to a hot flow using stateIn. The conversion to a state flow enables UI elements to read the last known state from the flow.
Example: Displaying followed topics
The InterestsViewModel exposes uiState as a StateFlow<InterestsUiState>. This hot flow is created by obtaining the cold flow of List<FollowableTopic> provided by GetFollowableTopicsUseCase. Each time a new list is emitted, it is converted into an InterestsUiState.Interests state which is exposed to the UI.
Processing user interactions
User actions are communicated from UI elements to ViewModels using regular method invocations. These methods are passed to the UI elements as lambda expressions.
Example: Following a topic
The InterestsScreen takes a lambda expression named followTopic which is supplied from InterestsViewModel.followTopic. Each time the user taps on a topic to follow this method is called. The ViewModel then processes this action by informing the user data repository.