8.9 KiB
JavaScript Basics: Making Decisions
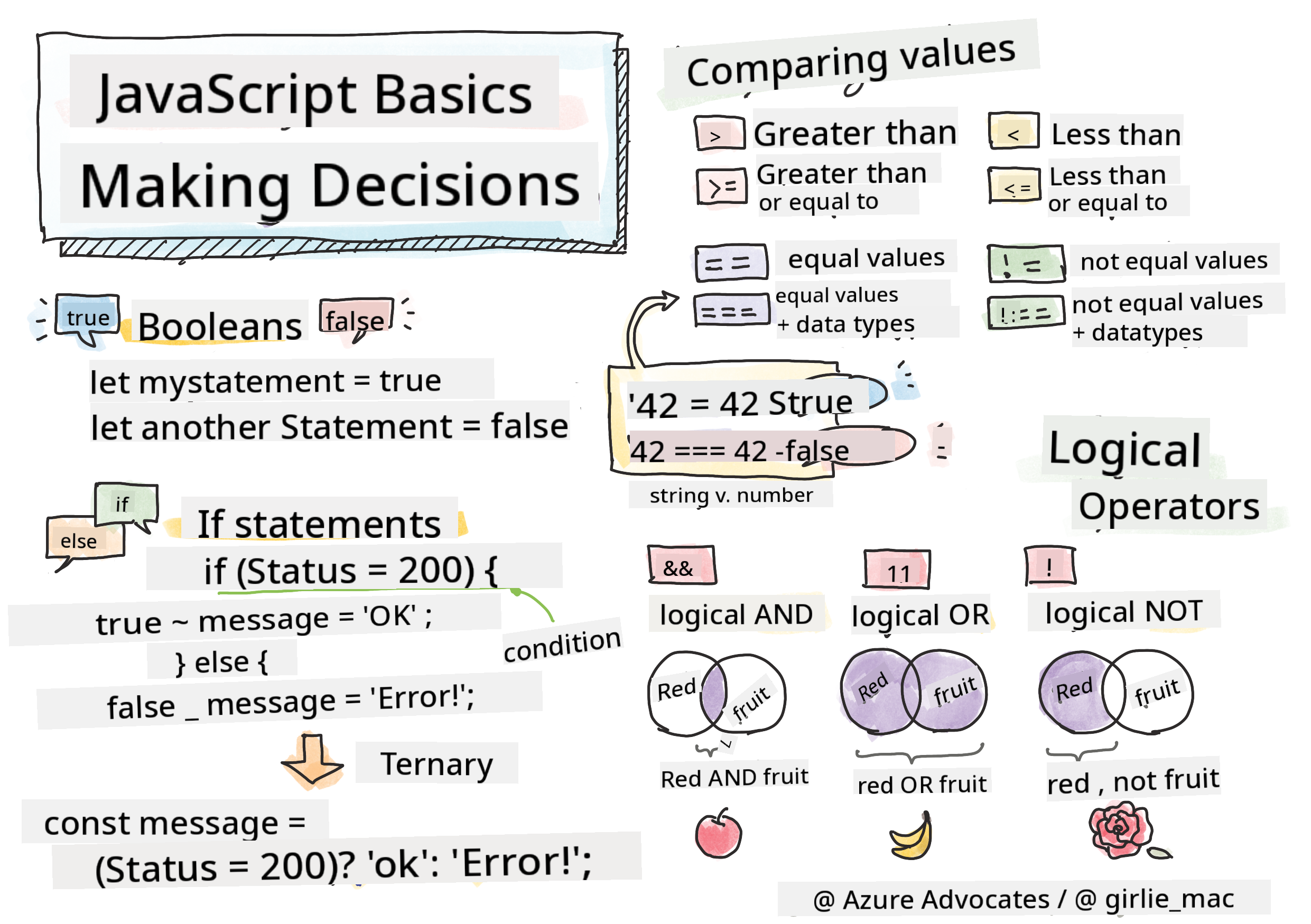
Sketchnote by Tomomi Imura
Pre-Lecture Quiz
Making decisions and controlling the flow of your code makes it reusable and reliable. This section explains the syntax for managing data flow in JavaScript and its importance when working with Boolean data types.
🎥 Click the image above for a video about making decisions.
You can take this lesson on Microsoft Learn!
A Brief Recap on Booleans
Booleans can only have two values: true or false. They are used to decide which lines of code should execute based on specific conditions.
You can set a Boolean value like this:
let myTrueBool = true
let myFalseBool = false
✅ Booleans are named after George Boole, an English mathematician, philosopher, and logician (1815–1864).
Comparison Operators and Booleans
Operators are used to evaluate conditions by comparing values, resulting in a Boolean value. Below is a list of commonly used operators:
| Symbol | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
< |
Less than: Compares two values and returns true if the value on the left is smaller than the value on the right |
5 < 6 // true |
<= |
Less than or equal to: Compares two values and returns true if the value on the left is smaller than or equal to the value on the right |
5 <= 6 // true |
> |
Greater than: Compares two values and returns true if the value on the left is larger than the value on the right |
5 > 6 // false |
>= |
Greater than or equal to: Compares two values and returns true if the value on the left is larger than or equal to the value on the right |
5 >= 6 // false |
=== |
Strict equality: Compares two values and returns true if both values are equal and of the same data type |
5 === 6 // false |
!== |
Inequality: Compares two values and returns the opposite Boolean value of what a strict equality operator would return | 5 !== 6 // true |
✅ Test your understanding by writing some comparisons in your browser's console. Were any results unexpected?
If Statement
The if statement executes the code within its block if the condition evaluates to true.
if (condition) {
//Condition is true. Code in this block will run.
}
Logical operators are often used to create the condition.
let currentMoney;
let laptopPrice;
if (currentMoney >= laptopPrice) {
//Condition is true. Code in this block will run.
console.log("Getting a new laptop!");
}
If..Else Statement
The else statement executes the code within its block when the condition is false. It is optional when using an if statement.
let currentMoney;
let laptopPrice;
if (currentMoney >= laptopPrice) {
//Condition is true. Code in this block will run.
console.log("Getting a new laptop!");
} else {
//Condition is false. Code in this block will run.
console.log("Can't afford a new laptop, yet!");
}
✅ Test your understanding of this code and the following code by running it in a browser console. Modify the values of the currentMoney and laptopPrice variables to see how the console.log() output changes.
Switch Statement
The switch statement allows you to perform different actions based on different conditions. Use it to select one of many code blocks to execute.
switch (expression) {
case x:
// code block
break;
case y:
// code block
break;
default:
// code block
}
// program using switch statement
let a = 2;
switch (a) {
case 1:
a = "one";
break;
case 2:
a = "two";
break;
default:
a = "not found";
break;
}
console.log(`The value is ${a}`);
✅ Test your understanding of this code and the following code by running it in a browser console. Modify the value of the variable a to see how the console.log() output changes.
Logical Operators and Booleans
Sometimes decisions require multiple comparisons, which can be combined using logical operators to produce a Boolean value.
| Symbol | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
&& |
Logical AND: Compares two Boolean expressions. Returns true only if both sides are true |
(5 > 6) && (5 < 6) // One side is false, the other is true. Returns false |
|| |
Logical OR: Compares two Boolean expressions. Returns true if at least one side is true |
(5 > 6) || (5 < 6) // One side is false, the other is true. Returns true |
! |
Logical NOT: Returns the opposite value of a Boolean expression | !(5 > 6) // 5 is not greater than 6, but "!" will return true |
Conditions and Decisions with Logical Operators
Logical operators can be used to create conditions in if..else statements.
let currentMoney;
let laptopPrice;
let laptopDiscountPrice = laptopPrice - laptopPrice * 0.2; //Laptop price at 20 percent off
if (currentMoney >= laptopPrice || currentMoney >= laptopDiscountPrice) {
//Condition is true. Code in this block will run.
console.log("Getting a new laptop!");
} else {
//Condition is true. Code in this block will run.
console.log("Can't afford a new laptop, yet!");
}
Negation Operator
You've seen how if...else statements can be used to create conditional logic. Anything inside an if must evaluate to true or false. The ! operator allows you to negate an expression, like this:
if (!condition) {
// runs if condition is false
} else {
// runs if condition is true
}
Ternary Expressions
if...else isn't the only way to express decision-making logic. You can also use a ternary operator, which has the following syntax:
let variable = condition ? <return this if true> : <return this if false>
Here's a more practical example:
let firstNumber = 20;
let secondNumber = 10;
let biggestNumber = firstNumber > secondNumber ? firstNumber : secondNumber;
✅ Take a moment to read this code carefully. Do you understand how these operators work?
The example above states:
- If
firstNumberis greater thansecondNumber,
assignfirstNumbertobiggestNumber. - Otherwise, assign
secondNumber.
The ternary expression is simply a compact way of writing the following code:
let biggestNumber;
if (firstNumber > secondNumber) {
biggestNumber = firstNumber;
} else {
biggestNumber = secondNumber;
}
🚀 Challenge
Write a program using logical operators, then rewrite it using a ternary expression. Which syntax do you prefer?
Post-Lecture Quiz
Review & Self Study
Learn more about the various operators available to you on MDN.
Check out Josh Comeau's excellent operator lookup!
Assignment
Disclaimer:
This document has been translated using the AI translation service Co-op Translator. While we aim for accuracy, please note that automated translations may include errors or inaccuracies. The original document in its native language should be regarded as the authoritative source. For critical information, professional human translation is advised. We are not responsible for any misunderstandings or misinterpretations resulting from the use of this translation.