|
|
1 week ago | |
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| README.md | 1 week ago | |
| assignment.md | 1 week ago | |
README.md
JavaScript Basics: Arrays and Loops
Sketchnote by Tomomi Imura
Pre-Lecture Quiz
This lesson introduces the fundamentals of JavaScript, the programming language that adds interactivity to websites. In this lesson, you'll explore arrays and loops, which are essential for working with and manipulating data.
🎥 Click the images above to watch videos about arrays and loops.
You can also take this lesson on Microsoft Learn!
Arrays
Handling data is a common task in programming, and it becomes much easier when the data is organized in a structured format, like arrays. Arrays store data in a list-like structure. One key advantage of arrays is that they can hold different types of data within the same array.
✅ Arrays are everywhere! Can you think of a real-world example of an array, like a solar panel array?
The syntax for creating an array involves square brackets.
let myArray = [];
This is an empty array, but arrays can also be initialized with data already inside them. Multiple values in an array are separated by commas.
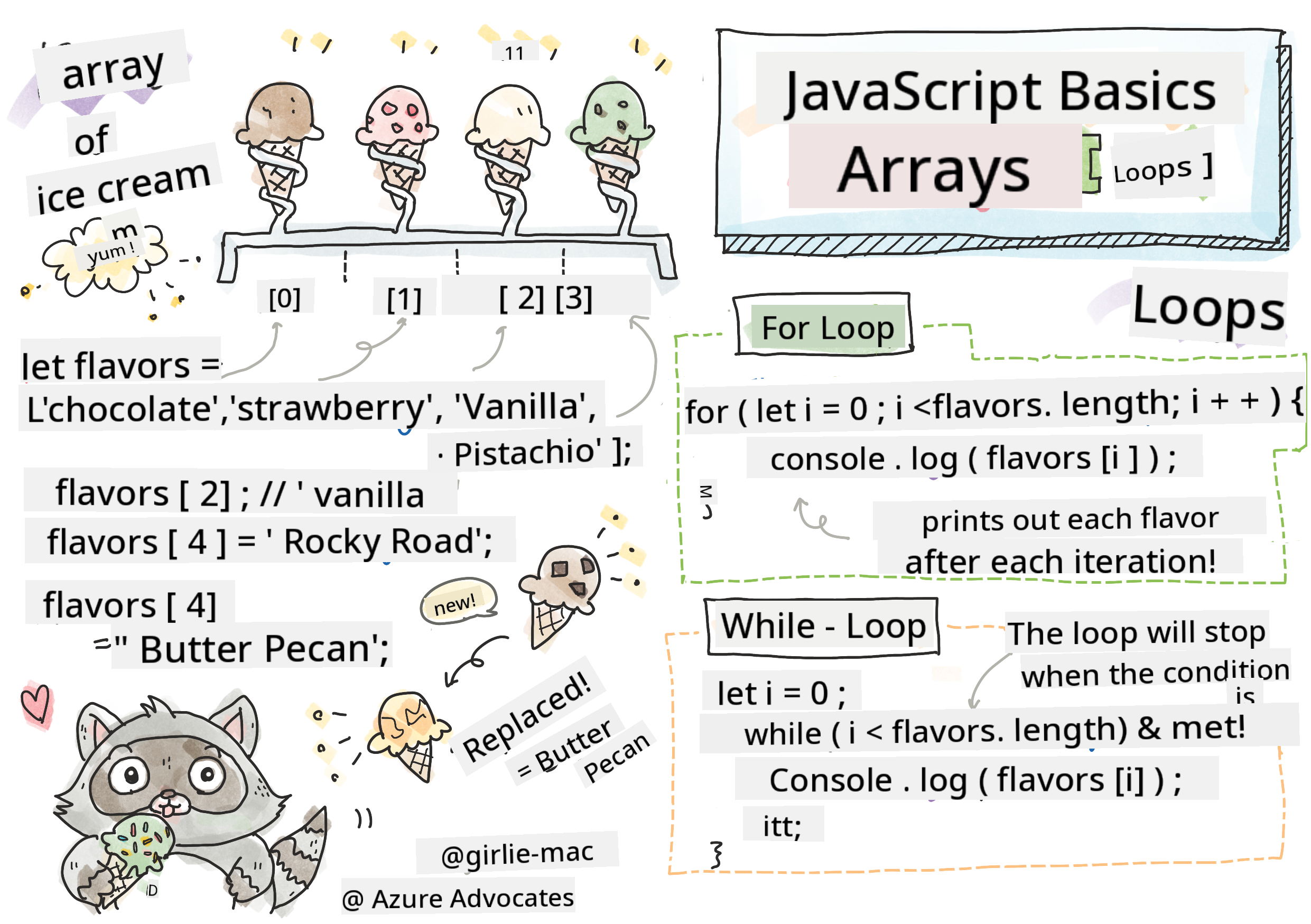
let iceCreamFlavors = ["Chocolate", "Strawberry", "Vanilla", "Pistachio", "Rocky Road"];
Each value in an array is assigned a unique identifier called the index, which is a whole number based on its position in the array. In the example above, the string "Chocolate" has an index of 0, while "Rocky Road" has an index of 4. You can use the index with square brackets to access, modify, or add values to the array.
✅ Did you know that arrays start at index 0? In some programming languages, indexes begin at 1. There's an interesting history behind this, which you can read about on Wikipedia.
let iceCreamFlavors = ["Chocolate", "Strawberry", "Vanilla", "Pistachio", "Rocky Road"];
iceCreamFlavors[2]; //"Vanilla"
You can use the index to update a value like this:
iceCreamFlavors[4] = "Butter Pecan"; //Changed "Rocky Road" to "Butter Pecan"
And you can add a new value at a specific index like this:
iceCreamFlavors[5] = "Cookie Dough"; //Added "Cookie Dough"
✅ A more common way to add values to an array is by using array methods like array.push().
To find out how many items are in an array, use the length property.
let iceCreamFlavors = ["Chocolate", "Strawberry", "Vanilla", "Pistachio", "Rocky Road"];
iceCreamFlavors.length; //5
✅ Try it out! Open your browser's console and create an array of your own. Experiment with adding, modifying, and accessing its values.
Loops
Loops allow you to perform repetitive or iterative tasks, saving time and reducing the amount of code you need to write. Each iteration can involve different variables, values, or conditions. JavaScript offers several types of loops, each with slight differences, but all serve the same purpose: iterating over data.
For Loop
A for loop requires three components to work:
counter: A variable, usually initialized with a number, that tracks the number of iterations.condition: An expression that uses comparison operators to stop the loop when it evaluates tofalse.iteration-expression: Executes at the end of each iteration, typically used to update the counter.
// Counting up to 10
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
console.log(i);
}
✅ Run this code in your browser's console. What happens if you tweak the counter, condition, or iteration expression? Can you make the loop run in reverse, like a countdown?
While Loop
Unlike the for loop, a while loop only requires a condition to stop the loop when it evaluates to false. Conditions in loops often depend on other values, like counters, which must be managed during the loop. Initial values for counters must be set outside the loop, and any expressions needed to meet the condition, including updating the counter, must be handled inside the loop.
//Counting up to 10
let i = 0;
while (i < 10) {
console.log(i);
i++;
}
✅ Why would you choose a for loop over a while loop? This question has intrigued 17K viewers on StackOverflow, and you might find their opinions interesting.
Loops and Arrays
Loops are frequently used with arrays because the array's length often serves as the condition to stop the loop, and the index can act as the counter.
let iceCreamFlavors = ["Chocolate", "Strawberry", "Vanilla", "Pistachio", "Rocky Road"];
for (let i = 0; i < iceCreamFlavors.length; i++) {
console.log(iceCreamFlavors[i]);
} //Ends when all flavors are printed
✅ Try looping over an array of your own creation in your browser's console.
🚀 Challenge
There are other ways to loop through arrays besides for and while loops. Explore forEach, for-of, and map. Rewrite your array loop using one of these methods.
Post-Lecture Quiz
Review & Self Study
JavaScript arrays come with many built-in methods that are incredibly useful for manipulating data. Learn more about these methods and try using some of them (like push, pop, slice, and splice) on an array you create.
Assignment
Disclaimer:
This document has been translated using the AI translation service Co-op Translator. While we strive for accuracy, please note that automated translations may contain errors or inaccuracies. The original document in its native language should be regarded as the authoritative source. For critical information, professional human translation is recommended. We are not responsible for any misunderstandings or misinterpretations resulting from the use of this translation.