4.1 KiB
Build a nightlight - Raspberry Pi
In this part of the lesson, you will add a light sensor to your Raspberry Pi.
Hardware
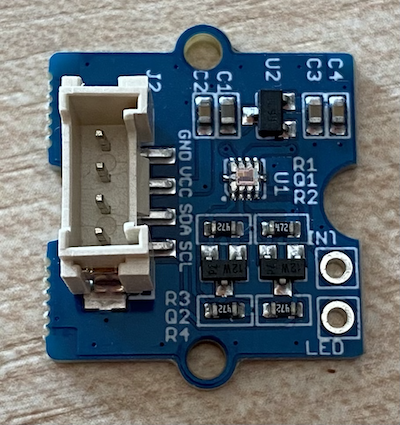
The sensor for this lesson is a sunlight sensor that uses photodiodes to convert visible and infrared light to an electrical signal. This is an analog sensor that sends an integer value from 0 to 1,023 indicating a relative amount of light, but this can be used to calculate exact values in lux by taking data from the separate infrared and visible light sensors.
The sunlight sensor is an eternal Grove sensor and needs to be connected to the Grove Base hat on the Raspberry Pi.
Connect the sunlight sensor
The Grove sunlight sensor that is used to detect the light levels needs to be connected to the Raspberry Pi.
Task - connect the sunlight sensor
Connect the sunlight sensor
-
Insert one end of a Grove cable into the socket on the sunlight sensor module. It will only go in one way round.
-
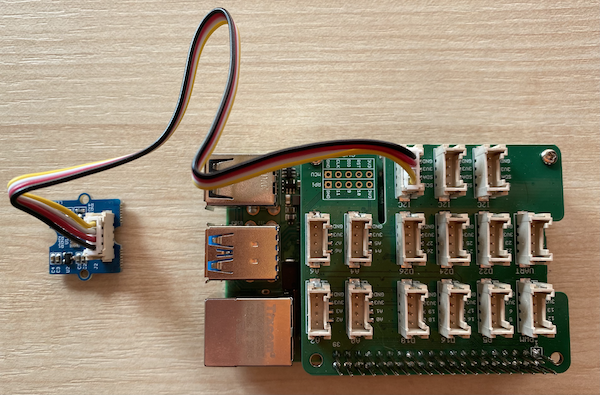
With the Raspberry Pi powered off, connect the other end of the Grove cable to one of the three the I2C sockets marked I2C on the Grove Base hat attached to the Pi. This socket is the second from the right, on the row of sockets next to the GPIO pins.
💁 I2C is a way sensors and actuators can communicate with an IoT device. It will be covered in more detail in a later lesson.
Program the sunlight sensor
The device can now be programmed using the Grove sunlight sensor.
Task - program the sunlight sensor
Program the device.
-
Power up the Pi and wait for it to boot
-
Open the nightlight project in VS Code that you created in the previous part of this assignment, either running directly on the Pi or connected using the Remote SSH extension.
-
Run the following command to install a pip package for working with the sunlight sensor:
pip3 install seeed-python-si114xNot all the libraries for the Grove Sensors are installed with the Grove install script you used in an earlier lesson. Some need additional packages.
-
Open the
app.pyfile and remove all code from it -
Add the following code to the
app.pyfile to import some required libraries:import time import seeed_si114xThe
import timestatement imports thetimemodule that will be used later in this assignment.The
import seeed_si114xstatement imports theseeed_si114xmodule that has code to interact with the Grove sunlight sensor. -
Add the following code after the code above to create an instance of the class that manages the light sensor:
light_sensor = seeed_si114x.grove_si114x()The line
light_sensor = seeed_si114x.grove_si114x()creates an instance of thegrove_si114xsunlight sensor class. -
Add an infinite loop after the code above to poll the light sensor value and print it to the console:
while True: light = light_sensor.ReadVisible print('Light level:', light)This will read the current sunlight level on a scale of 0-1,023 using the
ReadVisibleproperty of thegrove_si114xclass. This value is then printed to the console. -
Add a small sleep of one second at the end of the
loopas the light levels don't need to be checked continuously. A sleep reduces the power consumption of the device.time.sleep(1) -
From the VS Code Terminal, run the following to run your Python app:
python3 app.pyYou should see sunlight values being output to the console. Cover and uncover the sunlight sensor to see the values change:
pi@raspberrypi:~/nightlight $ python3 app.py Light level: 259 Light level: 265 Light level: 265 Light level: 584 Light level: 550 Light level: 497
💁 You can find this code in the code-sensor/pi folder.
😀 Adding a sensor to your nightlight program was a success!