8.4 KiB
Hardware
The T in IoT stands for Things, referring to devices that interact with the world around us. Each project is based on real-world hardware accessible to students and hobbyists. We offer two options for IoT hardware, depending on your personal preferences, programming language knowledge, learning goals, and availability. Additionally, we provide a 'virtual hardware' option for those who don't have access to physical hardware or want to explore more before making a purchase.
💁 You don't need to buy any IoT hardware to complete the assignments. Everything can be done using virtual IoT hardware.
The physical hardware options are Arduino or Raspberry Pi. Each platform has its own advantages and disadvantages, which are discussed in one of the initial lessons. If you haven't chosen a hardware platform yet, you can review lesson two of the first project to decide which platform interests you most.
The specific hardware was selected to simplify the lessons and assignments. While other hardware might work, we cannot guarantee that all assignments will be compatible with your device without additional components. For instance, many Arduino devices lack WiFi, which is essential for cloud connectivity. The Wio Terminal was chosen because it has built-in WiFi.
You will also need a few non-technical items, such as soil or a potted plant, and some fruits or vegetables.
Buy the kits
Seeed Studios has kindly made all the hardware available as easy-to-purchase kits:
Arduino - Wio Terminal
IoT for beginners with Seeed and Microsoft - Wio Terminal Starter Kit
Raspberry Pi
IoT for beginners with Seeed and Microsoft - Raspberry Pi 4 Starter Kit
Arduino
All the device code for Arduino is written in C++. To complete all the assignments, you will need the following:
Arduino hardware
- Wio Terminal
- Optional - USB-C cable or USB-A to USB-C adapter. The Wio Terminal has a USB-C port and comes with a USB-C to USB-A cable. If your PC or Mac only has USB-C ports, you will need a USB-C cable or a USB-A to USB-C adapter.
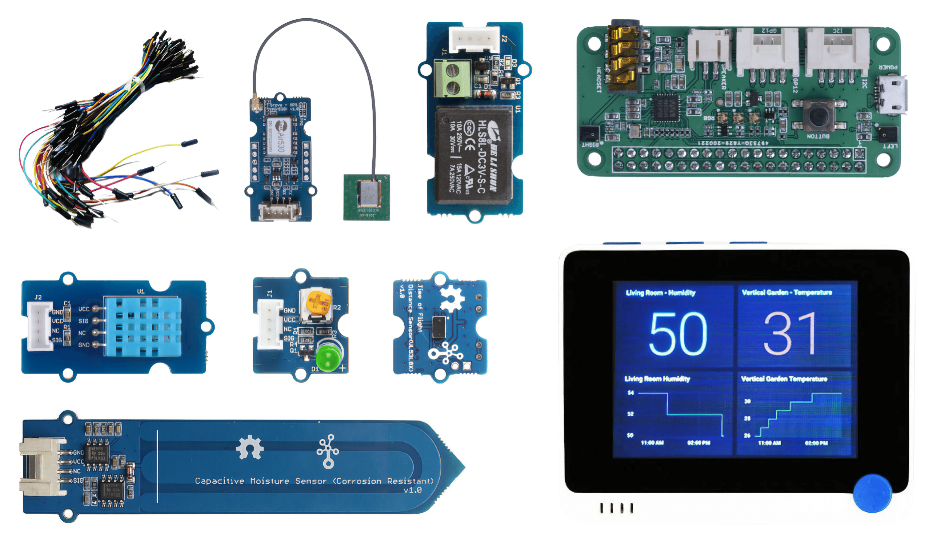
Arduino-specific sensors and actuators
These components are specific to the Wio Terminal Arduino device and are not relevant for the Raspberry Pi.
- ArduCam Mini 2MP Plus - OV2640
- ReSpeaker 2-Mics Pi HAT
- Breadboard Jumper Wires
- Headphones or another speaker with a 3.5mm jack, or a JST speaker such as:
- microSD Card (16GB or less) and a connector to use the SD card with your computer if it doesn’t have a built-in slot. NOTE - The Wio Terminal only supports SD cards up to 16GB.
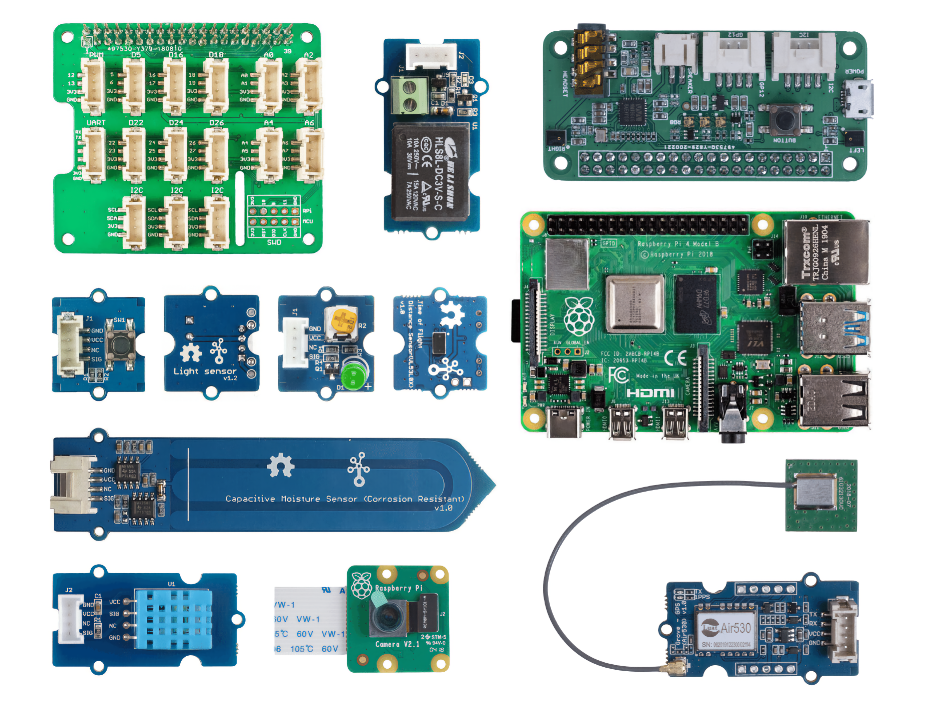
Raspberry Pi
All the device code for Raspberry Pi is written in Python. To complete all the assignments, you will need the following:
Raspberry Pi hardware
- Raspberry Pi
💁 Versions from the Pi 2B and above should work with the assignments in these lessons. If you plan to run VS Code directly on the Pi, a Pi 4 with 2GB or more of RAM is recommended. If you plan to access the Pi remotely, any Pi 2B or newer will work.
- microSD Card (Raspberry Pi kits often include one) and a connector to use the SD card with your computer if it doesn’t have a built-in slot.
- USB power supply (Raspberry Pi 4 kits often include one). If you are using a Raspberry Pi 4, you’ll need a USB-C power supply; earlier models require a micro-USB power supply.
Raspberry Pi-specific sensors and actuators
These components are specific to the Raspberry Pi and are not relevant for the Arduino device.
-
Microphone and speaker:
Use one of the following (or equivalent):
- Any USB microphone with any USB speaker, or a speaker with a 3.5mm jack cable, or HDMI audio output if your Raspberry Pi is connected to a monitor or TV with speakers
- Any USB headset with a built-in microphone
- ReSpeaker 2-Mics Pi HAT with:
- Headphones or another speaker with a 3.5mm jack, or a JST speaker such as:
- Mono Enclosed Speaker - 2W 6 Ohm
- USB Speakerphone
Sensors and actuators
Most of the sensors and actuators required are used in both the Arduino and Raspberry Pi learning paths:
- Grove LED x 2
- Grove humidity and temperature sensor
- Grove capacitive soil moisture sensor
- Grove relay
- Grove GPS (Air530)
- Grove Time of Flight Distance Sensor
Optional hardware
The lessons on automated watering use a relay. Optionally, you can connect this relay to a water pump powered by USB using the following hardware:
- 6V water pump
- USB terminal
- Silicone pipes
- Red and black wires
- Small flat-head screwdriver
Virtual hardware
The virtual hardware option provides simulators for the sensors and actuators, implemented in Python. Depending on your hardware availability, you can run this on your regular development device (e.g., Mac, PC) or on a Raspberry Pi, simulating only the hardware you don’t have. For example, if you have the Raspberry Pi camera but not the Grove sensors, you can run the virtual device code on your Pi and simulate the Grove sensors while using the physical camera.
The virtual hardware uses the CounterFit project.
To complete these lessons, you’ll need a webcam, microphone, and audio output such as speakers or headphones. These can be built-in or external and must be configured to work with your operating system and accessible from all applications.
Disclaimer:
This document has been translated using the AI translation service Co-op Translator. While we strive for accuracy, please note that automated translations may contain errors or inaccuracies. The original document in its native language should be regarded as the authoritative source. For critical information, professional human translation is recommended. We are not responsible for any misunderstandings or misinterpretations resulting from the use of this translation.