|
|
3 weeks ago | |
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| README.md | 3 weeks ago | |
| assignment.md | 3 weeks ago | |
README.md
Train a stock detector
Sketchnote by Nitya Narasimhan. Click the image for a larger version.
This video provides an overview of Object Detection using the Azure Custom Vision service, which will be explored in this lesson.
🎥 Click the image above to watch the video
Pre-lecture quiz
Introduction
In the previous project, you used AI to train an image classifier—a model that can determine whether an image contains something, such as ripe or unripe fruit. Another type of AI model that works with images is object detection. These models don’t classify an image by tags; instead, they are trained to recognize objects and locate them within images. This means they can not only detect the presence of an object but also identify its position in the image, enabling you to count objects.
In this lesson, you will learn about object detection, including its applications in retail. You will also learn how to train an object detector in the cloud.
In this lesson, we’ll cover:
- Object detection
- Use object detection in retail
- Train an object detector
- Test your object detector
- Retrain your object detector
Object detection
Object detection involves identifying objects in images using AI. Unlike the image classifier you trained in the last project, object detection doesn’t focus on predicting the best tag for an entire image. Instead, it identifies one or more objects within an image.
Object detection vs image classification
Image classification is about categorizing an image as a whole—determining the probabilities that the entire image matches each tag. The model returns probabilities for every tag it was trained on.
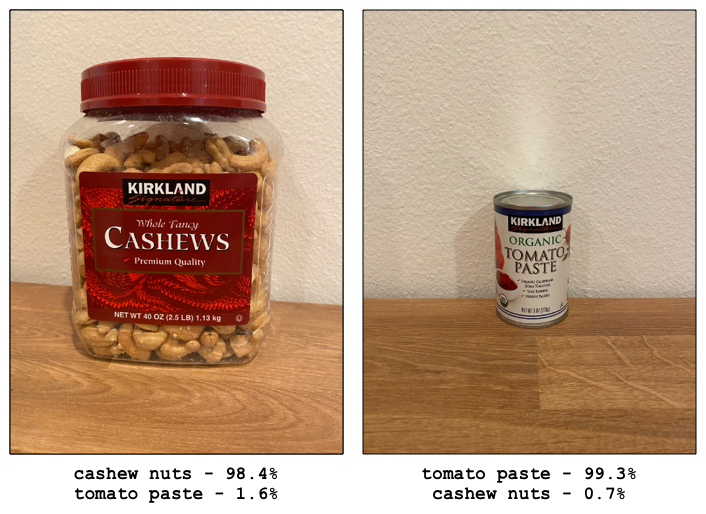
In the example above, two images are classified using a model trained to identify tubs of cashew nuts or cans of tomato paste. The first image is a tub of cashew nuts, and the classifier provides the following results:
| Tag | Probability |
|---|---|
cashew nuts |
98.4% |
tomato paste |
1.6% |
The second image is a can of tomato paste, and the results are:
| Tag | Probability |
|---|---|
cashew nuts |
0.7% |
tomato paste |
99.3% |
You could use these probabilities with a threshold percentage to predict what’s in the image. But what if an image contained multiple cans of tomato paste or both cashew nuts and tomato paste? The results might not provide the information you need. This is where object detection becomes useful.
Object detection involves training a model to recognize objects. Instead of providing images containing the object and labeling the entire image with a tag, you highlight the specific section of the image containing the object and tag that. You can tag a single object or multiple objects in an image. This way, the model learns what the object itself looks like, not just what images containing the object look like.
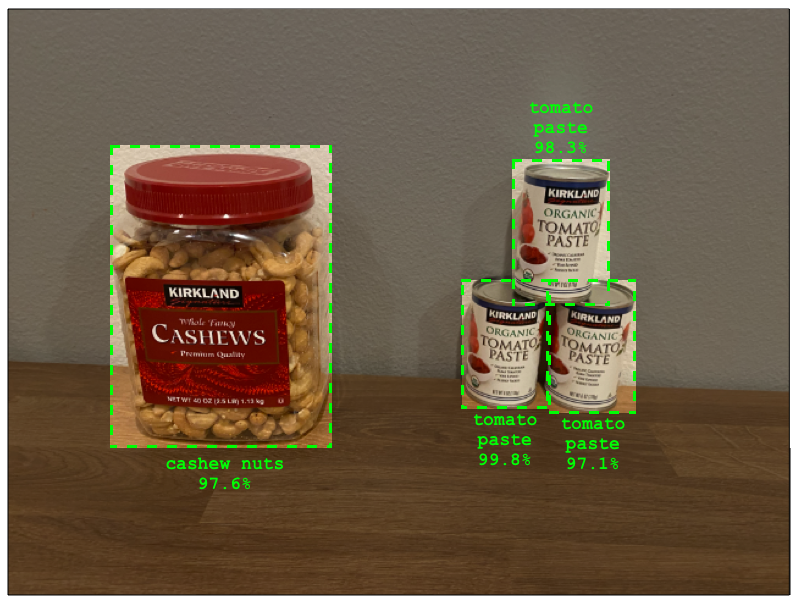
When you use the model to make predictions, instead of receiving a list of tags and probabilities, you get a list of detected objects, their bounding boxes, and the probability that each object matches its assigned tag.
🎓 Bounding boxes are the rectangles drawn around an object.
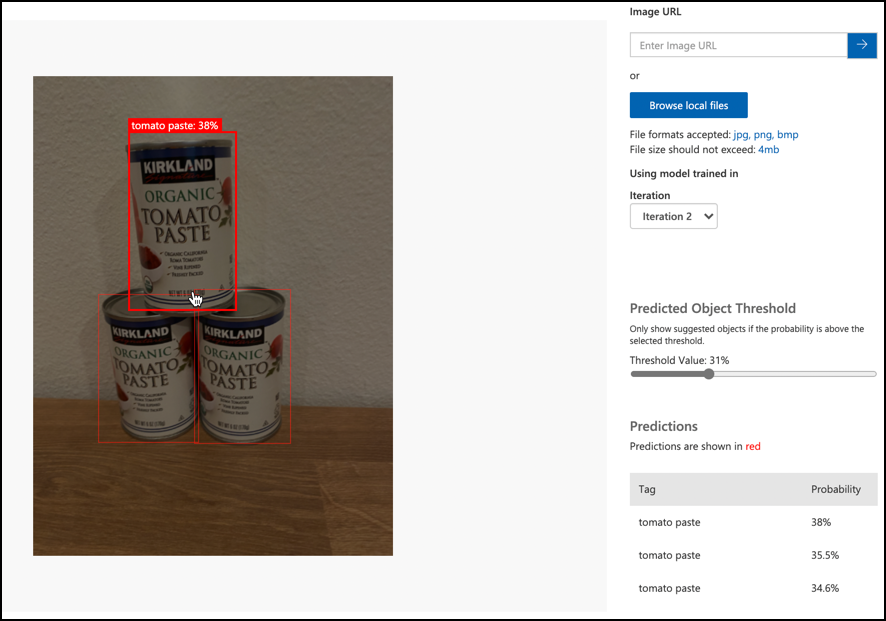
The image above contains both a tub of cashew nuts and three cans of tomato paste. The object detector identifies the cashew nuts, returning the bounding box around the cashew nuts along with the probability (97.6%) that the bounding box contains the object. The detector also identifies three cans of tomato paste, providing separate bounding boxes for each detected can, along with the probability for each.
✅ Think of some scenarios where you might want to use image-based AI models. Which ones would require classification, and which would require object detection?
How object detection works
Object detection uses complex ML models. These models divide the image into multiple cells and check whether the center of a bounding box matches the center of an image that resembles one of the training images. You can think of this as running an image classifier over different parts of the image to find matches.
💁 This is a simplified explanation. There are many techniques for object detection, and you can learn more about them on the Object detection page on Wikipedia.
There are several models capable of object detection. One well-known model is YOLO (You Only Look Once), which is extremely fast and can detect 20 different classes of objects, such as people, dogs, bottles, and cars.
✅ Learn more about the YOLO model at pjreddie.com/darknet/yolo/
Object detection models can be retrained using transfer learning to detect custom objects.
Use object detection in retail
Object detection has many applications in retail, including:
- Stock checking and counting - Identifying when stock is low on shelves. If stock levels are too low, notifications can be sent to staff or robots to restock shelves.
- Mask detection - In stores with mask policies during public health events, object detection can identify people wearing masks and those without.
- Automated billing - Detecting items picked off shelves in automated stores and billing customers accordingly.
- Hazard detection - Identifying broken items on the floor or spilled liquids and alerting cleaning crews.
✅ Research additional use cases for object detection in retail.
Train an object detector
You can train an object detector using Custom Vision, similar to how you trained an image classifier.
Task - create an object detector
-
Create a Resource Group for this project called
stock-detector. -
Create a free Custom Vision training resource and a free Custom Vision prediction resource in the
stock-detectorresource group. Name themstock-detector-trainingandstock-detector-prediction.💁 You can only have one free training and prediction resource, so ensure you’ve cleaned up your project from earlier lessons.
⚠️ Refer to the instructions for creating training and prediction resources from project 4, lesson 1 if needed.
-
Open the Custom Vision portal at CustomVision.ai and sign in with the Microsoft account linked to your Azure account.
-
Follow the Create a new Project section of the Build an object detector quickstart on the Microsoft docs to create a new Custom Vision project. The UI may change, so these docs are the most up-to-date reference.
Name your project
stock-detector.When creating your project, use the
stock-detector-trainingresource you created earlier. Select the Object Detection project type and the Products on Shelves domain.✅ The Products on Shelves domain is specifically designed for detecting stock on store shelves. Learn more about the different domains in the Select a domain documentation on Microsoft Docs.
✅ Take some time to explore the Custom Vision UI for your object detector.
Task - train your object detector
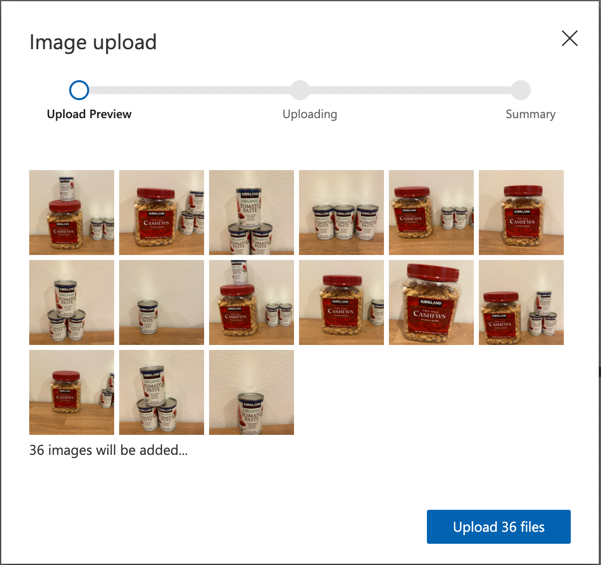
To train your model, you’ll need a set of images containing the objects you want to detect.
-
Collect images of the object you want to detect. You’ll need at least 15 images of each object from various angles and lighting conditions, but more is better. Since this object detector uses the Products on Shelves domain, try to arrange the objects as if they were on a store shelf. You’ll also need a few images to test the model. If you’re detecting multiple objects, include testing images with all the objects.
💁 Images with multiple objects count toward the 15-image minimum for all objects in the image.
Your images should be in PNG or JPEG format and smaller than 6MB. If you use an iPhone, for example, the images may be high-resolution HEIC files, so you’ll need to convert and possibly resize them. The more images you have, the better, and you should aim for a balanced number of images for each object.
You can find example images of cashew nuts and tomato paste in the images folder.
-
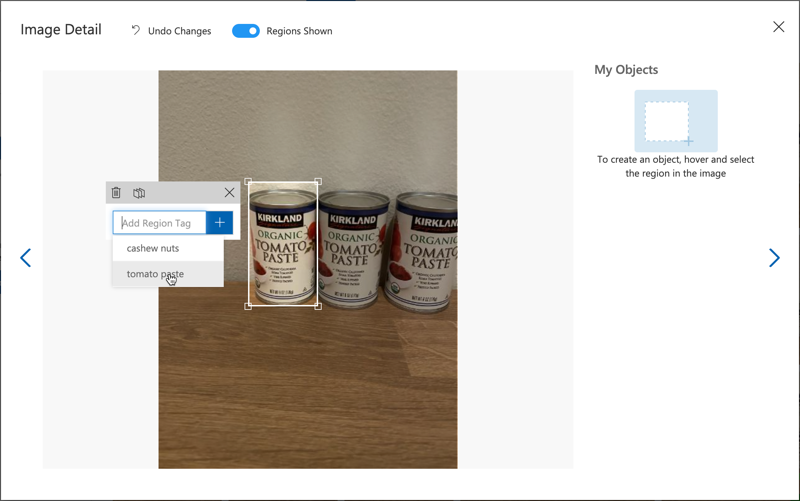
Follow the Upload and tag images section of the Build an object detector quickstart on the Microsoft docs to upload your training images. Create relevant tags for the objects you want to detect.
When drawing bounding boxes around objects, keep them tight around the object. Tagging all the images can take time, but the tool will suggest bounding boxes, speeding up the process.
💁 If you have more than 15 images per object, you can train after tagging 15 images and use the Suggested tags feature. This uses the trained model to detect objects in untagged images. You can confirm or reject the suggested bounding boxes, saving time.
-
Follow the Train the detector section of the Build an object detector quickstart on the Microsoft docs to train the object detector on your tagged images.
Choose Quick Training as the training type.
The object detector will begin training. This process takes a few minutes.
Test your object detector
Once your object detector is trained, you can test it by providing new images to detect objects.
Task - test your object detector
-
Use the Quick Test button to upload testing images and verify that the objects are detected. Use the testing images you prepared earlier, not the ones used for training.
-
Test all the available testing images and observe the probabilities.
Retrain your object detector
When testing your object detector, it may not perform as expected, just like image classifiers in the previous project. You can improve your object detector by retraining it with images where it made mistakes.
Every time you make a prediction using the quick test option, the image and results are saved. You can use these images to retrain your model.
-
Go to the Predictions tab to find the images you used for testing.
-
Confirm any correct detections, delete incorrect ones, and add any missing objects.
-
Retrain and re-test the model.
🚀 Challenge
What would happen if you used the object detector with similar-looking items, such as cans of tomato paste and chopped tomatoes from the same brand?
If you have similar-looking items, test this by adding images of them to your object detector.
Post-lecture quiz
Review & Self Study
- When you trained your object detector, you would have seen values for Precision, Recall, and mAP that evaluate the performance of the model you created. Learn more about these metrics by reading the Evaluate the detector section of the Build an object detector quickstart on the Microsoft docs.
- Explore additional information about object detection on the Object detection page on Wikipedia.
Assignment
Disclaimer:
This document has been translated using the AI translation service Co-op Translator. While we aim for accuracy, please note that automated translations may include errors or inaccuracies. The original document in its native language should be regarded as the authoritative source. For critical information, professional human translation is advised. We are not responsible for any misunderstandings or misinterpretations resulting from the use of this translation.