5.1 KiB
Control a Relay - Virtual IoT Hardware
In this part of the lesson, you will add a relay to your virtual IoT device alongside the soil moisture sensor and control it based on the soil moisture level.
Virtual Hardware
The virtual IoT device will use a simulated Grove relay. This ensures the lab remains consistent with using a Raspberry Pi and a physical Grove relay.
In a physical IoT device, the relay would typically be a normally-open relay (meaning the output circuit is open, or disconnected, when no signal is sent to the relay). Such a relay can handle output circuits up to 250V and 10A.
Add the Relay to CounterFit
To use a virtual relay, you need to add it to the CounterFit app.
Task
Add the relay to the CounterFit app.
-
Open the
soil-moisture-sensorproject from the previous lesson in VS Code if it’s not already open. You will be adding to this project. -
Ensure the CounterFit web app is running.
-
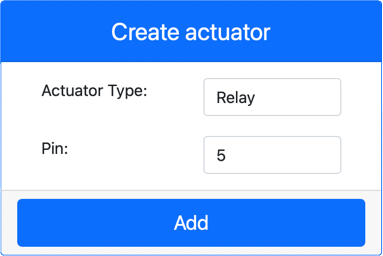
Create a relay:
-
In the Create actuator box in the Actuators pane, open the Actuator type dropdown and select Relay.
-
Set the Pin to 5.
-
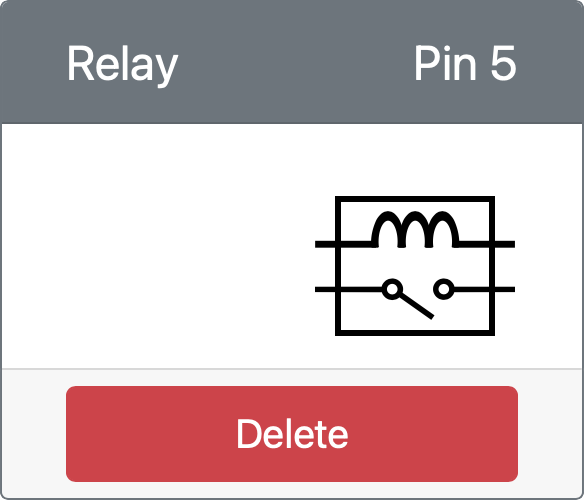
Click the Add button to create the relay on Pin 5.
The relay will be created and will appear in the actuators list.
-
Program the Relay
The soil moisture sensor app can now be programmed to use the virtual relay.
Task
Program the virtual device.
-
Open the
soil-moisture-sensorproject from the previous lesson in VS Code if it’s not already open. You will be adding to this project. -
Add the following code to the
app.pyfile below the existing imports:from counterfit_shims_grove.grove_relay import GroveRelayThis statement imports the
GroveRelayfrom the Grove Python shim libraries to interact with the virtual Grove relay. -
Add the following code below the declaration of the
ADCclass to create aGroveRelayinstance:relay = GroveRelay(5)This creates a relay using pin 5, the same pin you connected the relay to.
-
To test if the relay is working, add the following code to the
while True:loop:relay.on() time.sleep(.5) relay.off()This code turns the relay on, waits 0.5 seconds, and then turns it off.
-
Run the Python app. The relay will turn on and off every 10 seconds, with a half-second delay between turning on and off. You will see the virtual relay in the CounterFit app close and open as the relay is turned on and off.
Control the Relay Based on Soil Moisture
Now that the relay is working, it can be controlled in response to soil moisture readings.
Task
Control the relay.
-
Delete the 3 lines of code you added to test the relay. Replace them with the following code:
if soil_moisture > 450: print("Soil Moisture is too low, turning relay on.") relay.on() else: print("Soil Moisture is ok, turning relay off.") relay.off()This code checks the soil moisture level from the soil moisture sensor. If the level is above 450, it turns on the relay. If it drops below 450, it turns the relay off.
💁 Remember, the capacitive soil moisture sensor works such that the lower the soil moisture level, the more moisture there is in the soil, and vice versa.
-
Run the Python app. You will see the relay turn on or off depending on the soil moisture levels. Adjust the Value or the Random settings for the soil moisture sensor to observe the changes.
Soil Moisture: 638 Soil Moisture is too low, turning relay on. Soil Moisture: 452 Soil Moisture is too low, turning relay on. Soil Moisture: 347 Soil Moisture is ok, turning relay off.
💁 You can find this code in the code-relay/virtual-device folder.
😀 Congratulations! Your virtual soil moisture sensor successfully controls a relay!
Disclaimer:
This document has been translated using the AI translation service Co-op Translator. While we aim for accuracy, please note that automated translations may include errors or inaccuracies. The original document in its native language should be regarded as the authoritative source. For critical information, professional human translation is advised. We are not responsible for any misunderstandings or misinterpretations resulting from the use of this translation.