14 KiB
Data Science in the Cloud: The "Azure ML SDK" way
Table of contents:
- Data Science in the Cloud: The "Azure ML SDK" way
Pre-Lecture Quiz
Pre-lecture quiz
1. Introduction
1.1 What is Azure ML SDK?
Data scientists and AI developers use the Azure Machine Learning SDK to build and run machine learning workflows with the Azure Machine Learning service. You can interact with the service in any Python environment, including Jupyter Notebooks, Visual Studio Code, or your favorite Python IDE.
Key areas of the SDK include:
- Explore, prepare and manage the lifecycle of your datasets used in machine learning experiments.
- Manage cloud resources for monitoring, logging, and organizing your machine learning experiments.
- Train models either locally or by using cloud resources, including GPU-accelerated model training.
- Use automated machine learning, which accepts configuration parameters and training data. It automatically iterates through algorithms and hyperparameter settings to find the best model for running predictions.
- Deploy web services to convert your trained models into RESTful services that can be consumed in any application.
Learn more about the Azure Machine Learning SDK
In the previous lesson, we saw how to train, deploy and consume a model in a Low code/No code fashion. We used the Heart Failure dataset to generate and Heart failure prediction model. In this lesson, we are going to do the exact same thing but using the Azure Machine Learning SDK.
1.2 Heart failure prediction project and dataset introduction
Check here the Heart failure prediction project and dataset introduction.
2. Training a model with the Azure ML SDK
2.1 Create an Azure ML workspace
For simplicity, we are going to work on a jupyter notebook. This implies that you already have a Workspace and a compute instance. If you already have a Workspace, you can directly jump to the section 2.3 Notebook creation.
If not, please follow the instructions in the section 2.1 Create an Azure ML workspace in the previous lesson to create a workspace.
2.2 Create a compute instance
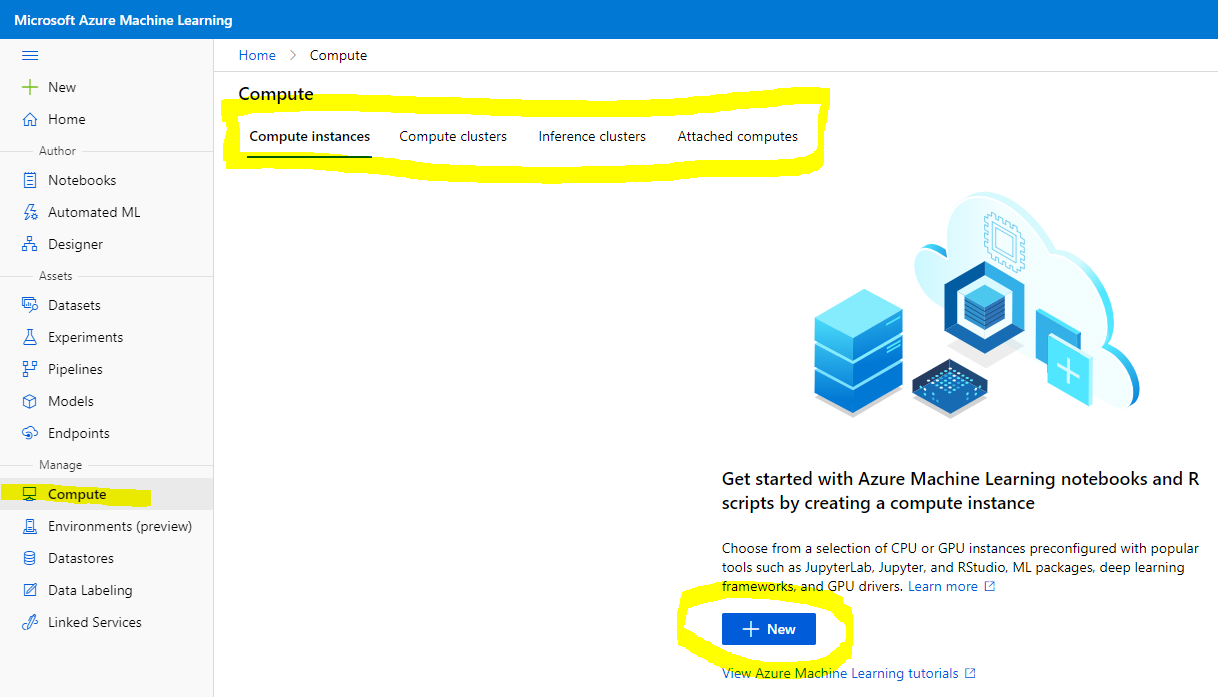
In the Azure ML workspace that we created earlier, go to the compute menue and you will see the different compute resources available
Let's create a compute instance to provision a jupyter notebook.
- Click on the + New button.
- Give a name to your compute instance.
- Choose your options: CPU or GPU, VM size and core number.
- Click in the Create button.
Congratulations, you have just created a compute instance! We will use this compute instance to create a Notebook the Creating Notebooks section.
2.3 Loading the Dataset
Refer the previous lesson in the section 2.3 Loading the Dataset if you have not uploaded the dataset yet.
2.4 Creating Notebooks
Notebook are a really important part of the data science process. They can be used to Conduct Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA), call out to a computer cluster to train a model, call out to an inference cluster to deploy an endpoint.
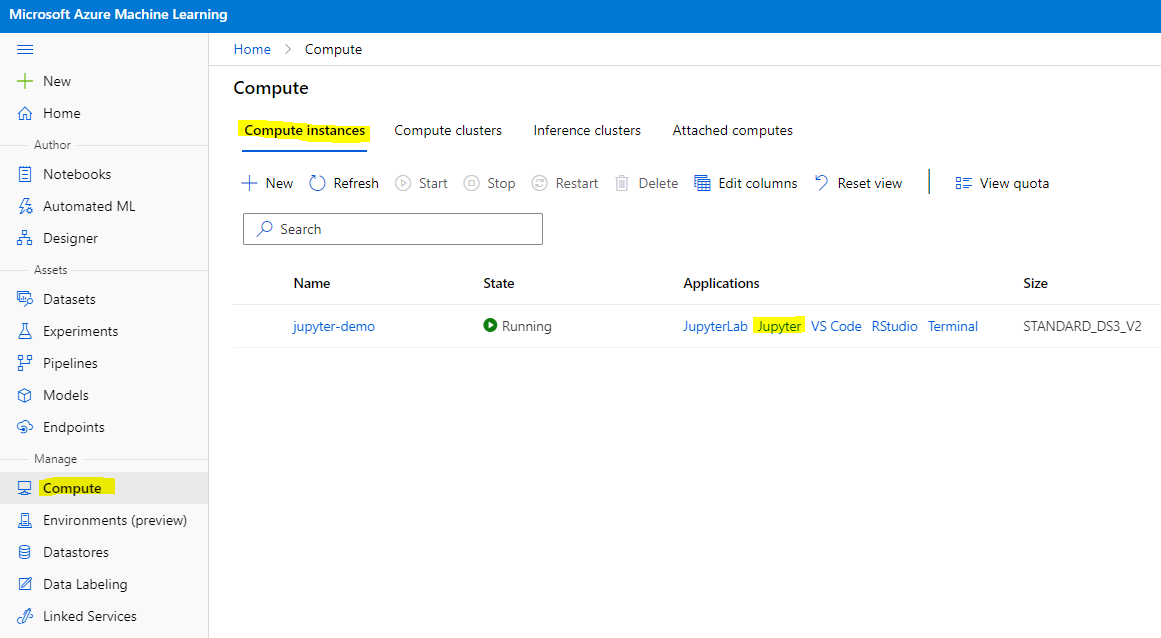
To create a Notebook, we need a compute node that is serving out the jupyter notebook instance. Go back to the Azure ML workspace and click on Compute instances. In the list of compute instances you should see the compute instance we created earlier.
- In the Applications section, click on the Jupyter option.
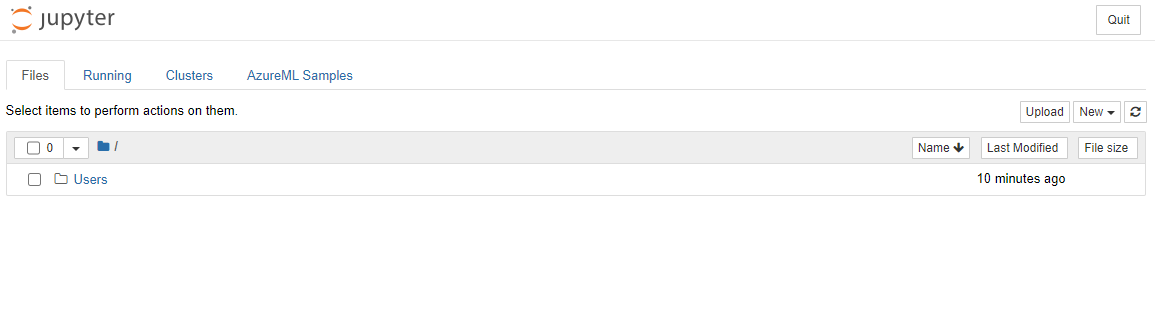
- Tick the "Yes, I understand" box and click on the Continue button.
- This should open a new browser tab with your jupyter notebook instance as follow. Click on the "New" button to create a notebook.
Now that we have a Notebook, we can start training the model with Azure ML SDK.
2.5 Training a model
First of all, if you ever have a doubt, refer to the Azure ML SDK documentation. In contains all the necessary information to understand the modules we are going to see in this lesson.
2.5.1 Setup Workspace, experiment, compute cluster and dataset
You need to load the workspace from the configuration file using the following code:
from azureml.core import Workspace
ws = Workspace.from_config()
This returns an object of type Workspace that represents the workspace. The you need to create an experiment using the following code:
from azureml.core import Experiment
experiment_name = 'aml-experiment'
experiment = Experiment(ws, experiment_name)
To get or create an experiment from a workspace, you request the experiment using the experiment name. Experiment name must be 3-36 characters, start with a letter or a number, and can only contain letters, numbers, underscores, and dashes. If the experiment is not found in the workspace, a new experiment is created.
Now you need to create a compute cluster for the training using the following code. Note that this step can take a few minutes.
from azureml.core.compute import ComputeTarget, AmlCompute
aml_name = "heart-f-cluster"
try:
aml_compute = AmlCompute(ws, aml_name)
print('Found existing AML compute context.')
except:
print('Creating new AML compute context.')
aml_config = AmlCompute.provisioning_configuration(vm_size = "Standard_D2_v2", min_nodes=1, max_nodes=3)
aml_compute = AmlCompute.create(ws, name = aml_name, provisioning_configuration = aml_config)
aml_compute.wait_for_completion(show_output = True)
cts = ws.compute_targets
compute_target = cts[aml_name]
You can get the dataset from the workspace using the dataset name in the following way:
dataset = ws.datasets['heart-failure-records']
df = dataset.to_pandas_dataframe()
df.describe()
2.5.2 AutoML Configuration and training
To set the AutoML configuration, use the AutoMLConfig class.
As described in the doc, there are a lot of parameters with which you can play with. For this project, we will use the following parameters:
experiment_timeout_minutes: The maximum amount of time (in minutes) that the experiment is allowed to run before it is automatically stopped and results are automatically made availablemax_concurrent_iterations: The maximum number of concurrent training iterations allowed for the experiment.primary_metric: The primary metric used to determine the experiment's status.compute_target: The Azure Machine Learning compute target to run the Automated Machine Learning experiment on.task: The type of task to run. Values can be 'classification', 'regression', or 'forecasting' depending on the type of automated ML problem to solve.training_data: The training data to be used within the experiment. It should contain both training features and a label column (optionally a sample weights column).label_column_name: The name of the label column.path: The full path to the Azure Machine Learning project folder.enable_early_stopping: Whether to enable early termination if the score is not improving in the short term.featurization: Indicator for whether featurization step should be done automatically or not, or whether customized featurization should be used.debug_log: The log file to write debug information to.
from azureml.train.automl import AutoMLConfig
project_folder = './aml-project'
automl_settings = {
"experiment_timeout_minutes": 20,
"max_concurrent_iterations": 3,
"primary_metric" : 'AUC_weighted'
}
automl_config = AutoMLConfig(compute_target=compute_target,
task = "classification",
training_data=dataset,
label_column_name="DEATH_EVENT",
path = project_folder,
enable_early_stopping= True,
featurization= 'auto',
debug_log = "automl_errors.log",
**automl_settings
)
Now that you have your configuration set, you can train the model using the following code. This step can take up to an hour depending on your cluster size.
remote_run = experiment.submit(automl_config)
You can run the RunDetails widget to show the different experiments.
from azureml.widgets import RunDetails
RunDetails(remote_run).show()
3. Model deployment and endpoint consumption with the Azure ML SDK
3.1 Saving the best model
The remote_run an object of type AutoMLRun. This object contains the method get_output() which returns the best run and the corresponding fitted model.
best_run, fitted_model = remote_run.get_output()
You can see the parameters used for the best model by just printing the fitted_model and see the properties of the best model by using the get_properties() method.
best_run.get_properties()
Now register the model with the register_model method.
model_name = best_run.properties['model_name']
script_file_name = 'inference/score.py'
best_run.download_file('outputs/scoring_file_v_1_0_0.py', 'inference/score.py')
description = "aml heart failure project sdk"
model = best_run.register_model(model_name = model_name,
model_path = './outputs/',
description = description,
tags = None)
3.2 Model Deployment
Once the best model is saved, we can deploy it with the InferenceConfig class. InferenceConfig represents the configuration settings for a custom environment used for deployment. The AciWebservice class represents a machine learning model deployed as a web service endpoint on Azure Container Instances. A deployed service is created from a model, script, and associated files. The resulting web service is a load-balanced, HTTP endpoint with a REST API. You can send data to this API and receive the prediction returned by the model.
The model is deployed using the deploy method.
from azureml.core.model import InferenceConfig, Model
from azureml.core.webservice import AciWebservice, Webservice
inference_config = InferenceConfig(entry_script=script_file_name, environment=best_run.get_environment())
aciconfig = AciWebservice.deploy_configuration(cpu_cores = 1,
memory_gb = 1,
tags = {'type': "automl-heart-failure-prediction"},
description = 'Sample service for AutoML Heart Failure Prediction')
aci_service_name = 'automl-hf-sdk'
aci_service = Model.deploy(ws, aci_service_name, [model], inference_config, aciconfig)
aci_service.wait_for_deployment(True)
print(aci_service.state)
This step should take a few minutes.
3.3 Endpoint consumption
You consume your endpoint by creating a sample input:
data = {
"data":
[
{
'age': "60",
'anaemia': "false",
'creatinine_phosphokinase': "500",
'diabetes': "false",
'ejection_fraction': "38",
'high_blood_pressure': "false",
'platelets': "260000",
'serum_creatinine': "1.40",
'serum_sodium': "137",
'sex': "false",
'smoking': "false",
'time': "130",
},
],
}
test_sample = str.encode(json.dumps(data))
And then you can send this input to your model for prediction :
response = aci_service.run(input_data=test_sample)
response
This should output '{"result": [false]}'. This means that the patient input we sent to the endpoint generated the prediction false which means this person is not likely to have a heart attack.
Congratulations! You just consumed the model deployed and trained on Azure ML!
🚀 Challenge
Post-Lecture Quiz
Post-lecture quiz