17 KiB
30 Days Of HTML
| # Day | Topics |
|---|---|
| 01 | Introduction |
| 02 | DOM(Document Object Model) |
| 03 | |
| 04 |
🧡🧡🧡 HAPPY CODING 🧡🧡🧡
Terminologies
Some of the terminologies you may come across in this challenge: client, server, web developer, web designer, UI, UX, web development, browser, code editor, command lines, Git, GitHub, Version Control, semantic, accessibility, responsiveness, compatibility, request, response, HTML, CSS, JavaScript, viewport, blocking element, non-blocking element, tag, opening tag, closing tag, self closing tag, attribute, style, script, property, value, render, comment, HTTP, path, URL, absolute path, relative path, landing page, single page application, hero image, HTML element, content, SEO, feature image, carousel, sidebar, website, web application
Day 1
Introduction
Congratulations on deciding to participate in 30 days of HTML challenge. In this challenge you will learn everything you need to know about HTML, and in general, the foundation of web development. In the end of the challenge, you will get a 30DaysOfHTML challenge completion certificate. In case you need help or if you would like to help others you may join the telegram group.
A 30DaysOfHTML challenge is a complete guide for both beginners and advanced developers. Welcome to 30DaysOfHTM! HTML is the build-block of the web. There is no website without HTML, therefore, to develop a website it requires an HTML.
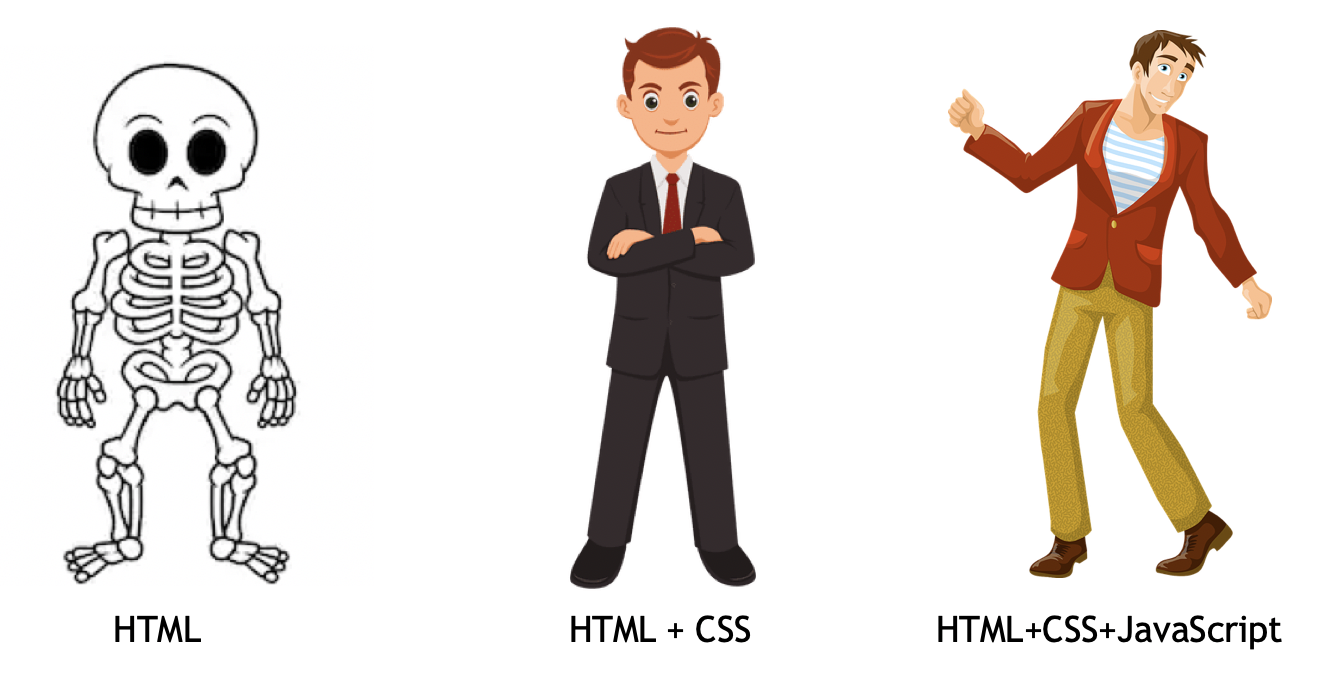
In this step by step HTML challenge, you will learn HTML, the standard markup language for the web. HTML is used to build the skeleton or outline of any website. The skeleton or outline of the website is styled(beautified) by CSS(Cascading Style Sheet). JavaScript (JS) can make a website interactive and dynamic. HTML, CSS and JS are the core technologies to build websites and these are the skills required to be a web developer. This challenge will focus on HTML but we will use little CSS to make some HTML concepts more clear to the readers. A 30DaysOfCSS will be a follow up challenge after 30DaysOfHTML. There are 30 Days of JavaScript, 30 Days of React, and 30 Days of Python by the same author.
Look at the following picture to understand the purpose of HTML, CSS and JavaScript very well.
The image has been taken from medium article, source.
By the end of the challenge:
- You will have a clear understanding of how the web works
- You will be able to develop a modest static website with HTML and little CSS
- You will know what to do next to become a web developer
The main goal of this challenge is to teach the core building block of the web that is HTML. Therefore, let's get started by understanding some the terminologies in this field such as web development, front end development, back end development, and full-stack.
⚠️ This is not a proof read material. You may find typo, grammar and some technical errors here and there. The content will be updated now and then. Therefore, do not be surprised you find a typo or a grammar or other mistakes.
Requirements
The minimum requirement to follow this challenge:
- Motivation
- Computer
- Internet
Web Development
Web development is a process of designing, building, testing, and maintaining a website which ranges from a simple single page static website to a complex full-stack applications. This field has two broad categories.
- Frontend
- Backend
Frontend Web Development
A front end(client-side) is a website that a user can see and interact with. It can be also called a client-side because it is the part that the user(client) can see and interact with. Therefore, anything we see on any website when we surf on the internet is part of the front end and it includes the colors, fonts, buttons, images, videos, audios and any other content on the website. The technologies that uses to build front end parts of a website are called front end technologies. The core technologies to build a front end are:
- HTML
- CSS
- JavaScript
There are hundreds of JavaScript that allows building a dynamic web applications. Currently, the three most popular JavaScript libraries are:
- React
- Vue
- Angular
Do not learn learn JavaScript before, HTML and CSS. Do not learn JavaScript libraries before you learn JavaScript. This the right sequence of learning:HTML > CSS > JavaScript > React or Vue or Angular.
Backend Web Development
Backed(Server-side) development refers to the activities that happens behind the scene. Backend development consists of backend a programming language and a database. The backend interacts with frontend and the database using a backend programming language that could be (Node.js, Python, Ruby, PHP, etc). Look at the following figure to understand the interaction between client. A client send a HTTP request to the backend and the backend return a HTTP response to the client computer(The response could be an HTML page, txt, image, or any other form of data). HTTP(Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is a communication protocol that allow transmitting data between a client and a sever. It is designed for communication between web browsers(client) and web servers.
Full-stack Web Development
Full-stack is another buzzword that no one agrees on the definition. You can understand Full-stack web development as a sum of frontend, backend, testing, and including some other technologies. I believe now you have a big picture of web development.
How the Web Works
By now you should have clear understanding how the web works based on the information you get on the above two sections. If you want to know more you may also read this article.
Web Development Tools
Tools you need as a web developer
- Motivation
- Computer
- Internet: To access information or resources
- Browser: allows to render HTML code to a human readable output(website pages). Examples of browsers(Chrome, Firefox, IE, Safari, Opera, Brave, etc)
- Design Software: allow to create a design or a prototype of the website. Examples of (Figma, Adobe XD, etc)
- Code Editor: allows to write code. For example(Visual Studio Code, Atom, Sublime Text, Bracket, etc)
- Git(Version Control Software): allows to manage different version of our code
Before we start developing a website, it is good to recall the common parts(components) of a website. In the next section, we will cover this.
Parts of a website
A website can have a couple of features or several features. There is no guideline that tells what a website should have but most of the time a website has the following common parts(components). For instance, if you look at the first ever created website, it has just one page and several links. However, since 1993 to today, for the last three decades HTML has been evolving and with only HTML it is possible to develop a decent static website.
Let's see the most common parts(components) of a website:
- Website Logo
- Header/Banner
- Navigation Bar/Menu Bar
- Carousel
- Sections
- Forms
- Buttons
- Links
- Images
- Videos
- Audios
- Social Links
- Footer
If you agree that these are components of a website, then you will create these components to build a website. Actually, once you create a certain feature it can be used in different projects(reusable). Therefore, whenever you create a certain part try to consider maintainability and reusability. You don't have to have all the mentioned above features when you develop a website. There is no strict guidelines what to have on your website.
Exercises
- What is web development?
- What is frontend?
- Mention at least four frontend technologies
- What is backend?
- Mention at least four backend technologies
- What is full-stack
- What is client?
- What is server
- What is HTTP?
- What is HTTP request ?
- What is HTTP response?
- What are the necessary tools for a web development?
- Mention parts of a website
- What is the purpose of HTML
- What is the purpose of CSS?
- What is the purpose of JavaScript
- Is it possible to develop using only HTML?
- Is there any strict guidelines what a website should look like?
- What are Git and GitHub? Did you install Git? Do you have GitHub account?
- Do you need a prototype or mockup or a wireframe before you start building the website?
- First open this website, then right click on the page then click source, after that you will get an HTML source code. Count the number of the different HTML tag that have been used on this site.
Day - 2
Setting Development Environment
Browser
There are many browsers out there but most developers prefer to use Google Chrome or FireFox. I usually use Google chrome for development and I recommend it too. Download Google Chrome if you do not have one.
The browser render your HTML code to a human read website.
Code Editor
As web developer, you should write code using a text or code editor. Therefore, to write HTML code, CSS, JS, React or other you need to have a code edit.
I will use Visual studio code and I will use it in this challenge too. I strongly suggest to use Visual Studio Code because it has lots of productivity extensions that makes super productive. Now, let's download visual studio code.
How to use Visual Studio Code
Introductin to HTML
History of HTML
The initial release of HTML was 1993. The first version of HTML was written by Tim Berners-Lee in 1993. HTML has been evolving for the last three decades and the now the latest version is HTML5.
What is HTML?
The word HTML is an acronym. That is stands for Hypertext Markup Language. It is the standard markup languages to develop websites. HTML is the build block of the web that allows building layouts of page using HTML elements. HTML is not not a programming language instead it is a markup language.
HTML code will be rendered by a browser and it give a human readable output. Look at the figure bellow to understand better how the HTML code convert to a website using a browser.
HTML Element
HTML elements consists of an open tag(<>), attribute(s), content and closing tag(<>). Look at the figure below to understand a syntax of an HTML element.
<h1>Welcome to 30 Days of HTML</h1>
The tag name is h1 and the content is 30 Days of HTML. The h1 will tell the browser to make the text a big font size that why we call HTML a markup language.
<p>
HTML elements are the blocking of a website. There is not website without
HTML. Learn HTML and build a website.
</p>
The p tag marks the text to be paragraph that why we call HTML a markup language.
Attribute
HTML attributes provide additional information about the element. An attribute can added only in the opening tag. It will be difficult to list down all HTML attributes but we can list down the most common ones.
- alt - to add information about added image, use with img element.
- autocompelete - to enable auto complete feature of a form, use with form and input.
- autofocus - enable auto focus of input fields
- autoplay - allows playing an audio/video on the page loads
- charset - enable character encoding of meta tag
- checked - to make a checkbox checked of an input element
- class - to give a common identifier for HTML elements
- cols - to determine the width of a textarea element
- contenteditable - make any element editable
- download - allows a link to download a resource(image, pdf, PPT, etc)
- draggable - to make an element draggable, apply to all elements
- for - to connect/bound a label element with a specific input field, use with a label tag
- href - to specify a URL or a path of a resource, use with a link tag
- id - a unique id for an HTML element, apply to all elements
- lang - specifies the language of the page
- type - specifies the type of the element and it uses with only a certain elements
- src - to specify URL of a media file(img, audio, video, source, embed, script)
- style - to add an inline CSS style to an element
There are also event listener attribute that listen mouse or keyboard. For instance, onclick, onsubmit, onkeydown, onkeyup, onscroll, etc. Remember, do not try to remember by hard. For detail information about, HTML attributes you may check this link
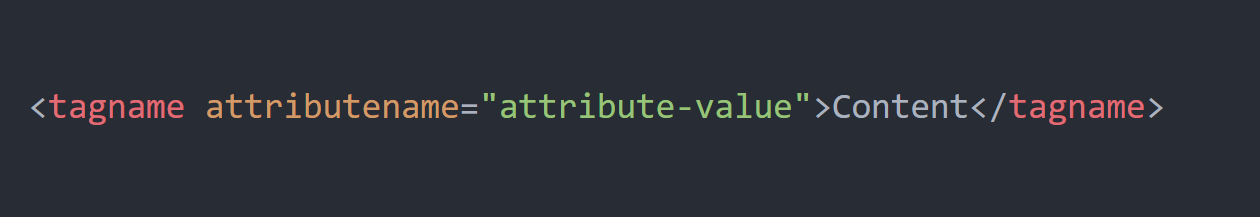 An attribute is optional in an HTML element. See the following h1 tag with an id attribute value of first-title.
An attribute is optional in an HTML element. See the following h1 tag with an id attribute value of first-title.
<h1 id="first-title">Welcome to 30 Days of HTML</h1>
An HTML element with multiple attributes
<h1 id="first-title" class="title">Welcome to 30 Days of HTML</h1>
<p style="color:gray;">
HTML elements are the blocking of a website. There is not website without
HTML. Learn HTML and build a website.
</p>
The above p tag has a style attribute. The style attribute has a color property and a value gray. The style changes the text color to gray. You can try it by adding other property and value in the style. Each value has to be separated by a semicolon.
Some HTML elements do not have closing tag, instead they have self-closing tag.
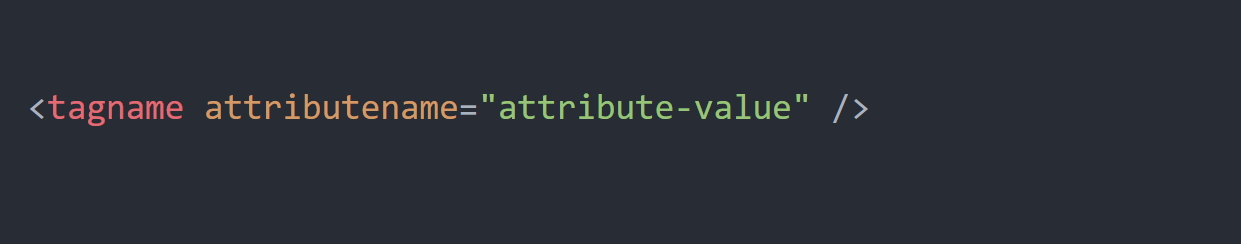 An example of self closing tags:
An example of self closing tags:
<area />
<base />
<br />
<col />
<embed />
<hr />
<img />
<input />
<link />
<meta />
<para />
<source />
<track />
<wbr />
The slash is optional but I strongly recommend to use the slash with self-closing tags. For instance, React.js does not allow you to use without the slash.
HTML Comment
Comment in any programming language help a code to be more readable. Therefore, it is common to leave some text on a code to make it more readable and maintainable. Let us the syntax of an HTML comment, it has opening ()
<!-- The is an HTML comment and it makes the code more readable -->
Exercise
- What is the acronym HTML stands for?
- What is an HTML element?
- What is an attribute
- Write at least five HTML attributes
- Where do you write an attribute to HTML element?
- Write an HTML comment that says, I am enjoying 30 Days of HTML
- What is the purpose of Visual studio code?
- What is the purpose of the browser?
- Does every element need to have attributes?