25 KiB
前言
在上一篇APIServer-P3-APIServer的认证机制中,讲述了请求进入后的认证过程,在通过认证之后,请求将进入鉴权环节,本篇就此展开。
审查请求属性
Kubernetes 仅审查以下 API 请求属性:
- 用户 - 身份验证期间提供的
user字符串。 - 组 - 经过身份验证的用户所属的组名列表。
- 额外信息 - 由身份验证层提供的任意字符串键到字符串值的映射。
- API - 指示请求是否针对 API 资源。
- 请求路径 - 各种非资源端点的路径,如
/api或/healthz。 - API 请求动词 - API 动词
get、list、create、update、patch、watch、proxy、redirect、delete和deletecollection用于资源请求。 要确定资源 API 端点的请求动词,请参阅 确定请求动词。 - HTTP 请求动词 - HTTP 动词
get、post、put和delete用于非资源请求。 - Resource - 正在访问的资源的 ID 或名称(仅限资源请求)- 对于使用
get、update、patch和delete动词的资源请求,你必须提供资源名称。 - 子资源 - 正在访问的子资源(仅限资源请求)。
- 名字空间 - 正在访问的对象的名称空间(仅适用于名字空间资源请求)。
- API 组 - 正在访问的 API 组 (仅限资源请求)。空字符串表示核心 API 组
鉴权的描述
鉴权策略分类
目前支持6种鉴权策略,每种鉴权策略对应一个鉴权器,使用的鉴权策略需要在APIServer启动时以参数--authorization-mode的形式指定,多种策略同时指定时使用','号连接:
策略分类有:
--authorization-mode=ABAC基于属性的访问控制(ABAC)模式允许你 使用本地文件配置策略。--authorization-mode=RBAC基于角色的访问控制(RBAC)模式允许你使用 Kubernetes API 创建和存储策略。--authorization-mode=WebhookWebHook 是一种 HTTP 回调模式,允许你使用远程 REST 端点管理鉴权。--authorization-mode=Node节点鉴权是一种特殊用途的鉴权模式,专门对 kubelet 发出的 API 请求执行鉴权。--authorization-mode=AlwaysDeny该标志阻止所有请求。仅将此标志用于测试。--authorization-mode=AlwaysAllow此标志允许所有请求。仅在你不需要 API 请求 的鉴权时才使用此标志。
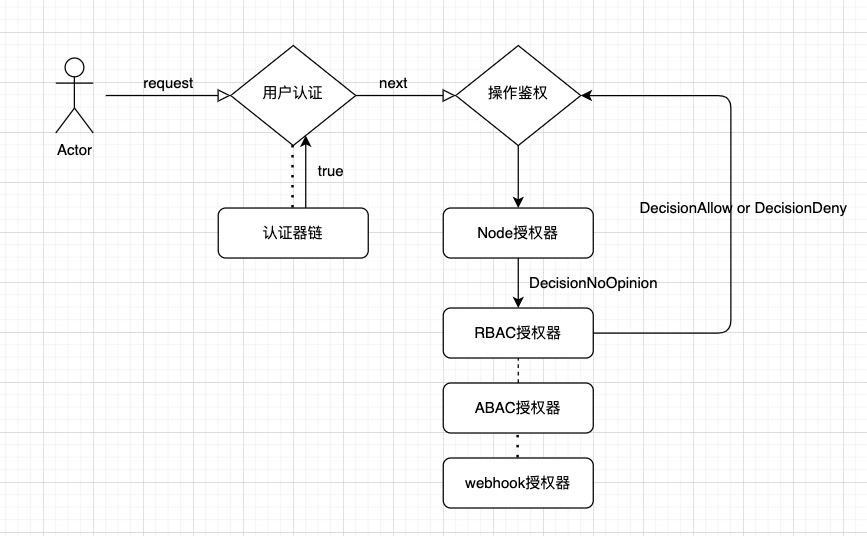
与上一篇的认证模块不同的是,当配置多个鉴权模块时,鉴权模块按顺序检查,靠前的模块具有更高的优先级来允许或拒绝请求。
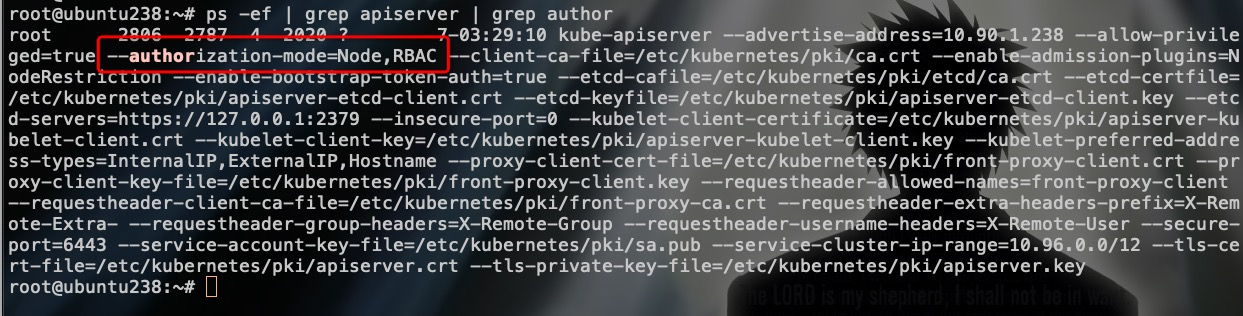
来看看现有的kubeadm部署集群启用的鉴权策略:
可以看到,默认启用了Node授权和RBAC授权模块。
鉴权结果
对于每一个请求的鉴权结果,有专门为其设计的健全结果描述结构体,如下:
vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/authorization/authorizer/interfaces.go:148
type Decision int
const (
// 拒绝
DecisionDeny Decision = iota
// 允许,则鉴权流程视为成功,请求顺利进入
DecisionAllow
// 无操作,进入下一个鉴权模块,相当于pass
DecisionNoOpinion
)
鉴权接口方法
vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/authorization/authorizer/interfaces.go:69
// Authorizer makes an authorization decision based on information gained by making
// zero or more calls to methods of the Attributes interface. It returns nil when an action is
// authorized, otherwise it returns an error.
type Authorizer interface {
Authorize(a Attributes) (authorized Decision, reason string, err error)
}
所有的鉴权模块(鉴权器)都要实现这个Authorize方法,返回鉴权结果。
规则解析器
规则解析器可以根据认证之后所得到的用户信息,获取该用户对应的资源对象的操作权限。
// RuleResolver provides a mechanism for resolving the list of rules that apply to a given user within a namespace.
type RuleResolver interface {
// RulesFor get the list of cluster wide rules, the list of rules in the specific namespace, incomplete status and errors.
RulesFor(user user.Info, namespace string) ([]ResourceRuleInfo, []NonResourceRuleInfo, bool, error)
}
以这里的返回值类型ResourceRuleInfo为例,默认的DefaultResourceRuleInfo结构体是这样的:
vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/authorization/authorizer/rule.go:31
// DefaultResourceRuleInfo holds information that describes a rule for the resource
type DefaultResourceRuleInfo struct {
Verbs []string
APIGroups []string
Resources []string
ResourceNames []string
}
例如对pod资源的任意操作权限的描述可以描述为:
DefaultResourceRuleInfo{
Verbs []string{"*"}
APIGroups []string{"*"}
Resources []string{"pod"}
}
这个DefaultResourceRuleInfo对象描述的规则是,允许对所有api group 的pod资源进行的所有类型的操作,包括{"get", "list", "update", "patch","create", "delete", "watch", "deletecollection"}操作。
鉴权流程图
鉴权器
AlwaysAllow和AlwaysDeny这两种鉴权器很少使用,就不看了,直接略过.
ABAC鉴权器
简介
基于属性的访问控制(Attribute-based access control - ABAC)定义了访问控制范例,其中通过使用将属性组合在一起的策略来向用户授予访问权限。
启用ABAC鉴权器需要额外增加一个--authorization-policy-file=SOME_FILENAME参数,指定一个json格式的文件预设鉴权策略,是一种静态的权限配置方式。json格式样例如下:
// 授予pod资源的任意操作权限给用户podManager
{
"apiVersion":"abac.authorization.kubernetes.io/v1beta1",
"kind":"Policy",
"spec":{
"user":"podManager",
"namespace":"*",
"resource":"pods",
"readonly":true
}
}
代码实现
pkg/auth/authorizer/abac/abac.go:224
// Authorizer implements authorizer.Authorize
func (pl policyList) Authorize(a authorizer.Attributes) (authorizer.Decision, string, error) {
for _, p := range pl {
if matches(*p, a) {
return authorizer.DecisionAllow, "", nil
}
}
return authorizer.DecisionNoOpinion, "No policy matched.", nil
}
--> pkg/auth/authorizer/abac/abac.go:117
func matches(p abac.Policy, a authorizer.Attributes) bool {
if subjectMatches(p, a.GetUser()) {
// 操作类型与规则匹配
if verbMatches(p, a) {
// Resource and non-resource requests are mutually exclusive, at most one will match a policy
// 资源类型与规则匹配(包含namespace/APIGroup/Resource)
if resourceMatches(p, a) {
return true
}
// 针对非资源对象的操作匹配(请求路径匹配)
if nonResourceMatches(p, a) {
return true
}
}
}
return false
}
RBAC鉴权器
简介
基于角色(Role)的访问控制(RBAC)是一种基于组织中用户的角色来调节控制对 计算机或网络资源的访问的方法。
RBAC 鉴权机制使用 rbac.authorization.k8s.io API 组 来驱动鉴权决定,允许你通过 Kubernetes API 动态配置策略。
通过创建Role 或 ClusterRole来描述具体的资源授权策略,再通过创建RoleBinding/ClusterRoleBinding将策略绑定到用户/群组/服务上。
RBAC模式的详细描述和使用样例请参考我之前的文章:
代码实现
plugin/pkg/auth/authorizer/rbac/rbac.go:74
func (r *RBACAuthorizer) Authorize(requestAttributes authorizer.Attributes) (authorizer.Decision, string, error) {
ruleCheckingVisitor := &authorizingVisitor{requestAttributes: requestAttributes}
// 规则解析器解析请求的属性,返回鉴权结果,判断匹配用的是ruleCheckingVisitor.visit方法
r.authorizationRuleResolver.VisitRulesFor(requestAttributes.GetUser(), requestAttributes.GetNamespace(), ruleCheckingVisitor.visit)
if ruleCheckingVisitor.allowed {
return authorizer.DecisionAllow, ruleCheckingVisitor.reason, nil
}
...
reason := ""
if len(ruleCheckingVisitor.errors) > 0 {
reason = fmt.Sprintf("RBAC: %v", utilerrors.NewAggregate(ruleCheckingVisitor.errors))
}
return authorizer.DecisionNoOpinion, reason, nil
}
对比规则和请求属性,返回true or false的visit方法:
plugin/pkg/auth/authorizer/rbac/rbac.go:62
func (v *authorizingVisitor) visit(source fmt.Stringer, rule *rbacv1.PolicyRule, err error) bool {
if rule != nil && RuleAllows(v.requestAttributes, rule) {
// 请求与规则匹配,则鉴权成功
v.allowed = true
v.reason = fmt.Sprintf("RBAC: allowed by %s", source.String())
// 返回false是为了提前break鉴权过程
return false
}
if err != nil {
v.errors = append(v.errors, err)
}
return true
}
获取规则并调用visit方法的是VisitRulesFor接口方法,找一下VisitRulesFor方法:
pkg/registry/rbac/validation/rule.go:178
func (r *DefaultRuleResolver) VisitRulesFor(user user.Info, namespace string, visitor func(source fmt.Stringer, rule *rbacv1.PolicyRule, err error) bool) {
// 先拿到所有的ClusterRoleBinding对象,ClusterRoleBinding资源是cluster级别的,不区分命名空间
if clusterRoleBindings, err := r.clusterRoleBindingLister.ListClusterRoleBindings(); err != nil {
if !visitor(nil, nil, err) {
return
}
} else {
sourceDescriber := &clusterRoleBindingDescriber{}
for _, clusterRoleBinding := range clusterRoleBindings {
// clusterRoleBinding.Subjects指定的绑定的用户对象,对比请求的所属用户,不匹配则continue
subjectIndex, applies := appliesTo(user, clusterRoleBinding.Subjects, "")
if !applies {
continue
}
rules, err := r.GetRoleReferenceRules(clusterRoleBinding.RoleRef, "")
if err != nil {
if !visitor(nil, nil, err) {
return
}
continue
}
sourceDescriber.binding = clusterRoleBinding
sourceDescriber.subject = &clusterRoleBinding.Subjects[subjectIndex]
for i := range rules {
// visit方法返回false是代表鉴权成功了,提前break鉴权过程
if !visitor(sourceDescriber, &rules[i], nil) {
return
}
}
}
}
// 如果指定了namespace,再取命名空间级别的roleBinding资源对象,重复一次上面的过程
if len(namespace) > 0 {
if roleBindings, err := r.roleBindingLister.ListRoleBindings(namespace); err != nil {
if !visitor(nil, nil, err) {
return
}
} else {
sourceDescriber := &roleBindingDescriber{}
for _, roleBinding := range roleBindings {
subjectIndex, applies := appliesTo(user, roleBinding.Subjects, namespace)
if !applies {
continue
}
rules, err := r.GetRoleReferenceRules(roleBinding.RoleRef, namespace)
if err != nil {
if !visitor(nil, nil, err) {
return
}
continue
}
sourceDescriber.binding = roleBinding
sourceDescriber.subject = &roleBinding.Subjects[subjectIndex]
for i := range rules {
if !visitor(sourceDescriber, &rules[i], nil) {
return
}
}
}
}
}
}
过程总结
参考代码片中的注释,rbac鉴权过程如下:
- 1.取到所有的clusterRoleBinding/roleBindings资源对象,遍历它们对比请求用户
- 2.对比roleBindings/clusterRoleBinding指向的用户(主体)与请求用户,相同则选中,不相同continue
- 3.对比规则与请求属性,符合则提前结束鉴权
Node鉴权器
上面有提过,node鉴权器是专为kubelet组件设计的,按照kubeadm集群的默认配置,它是排序在第一位的鉴权器,为什么把它放在后面再讲呢,因为node鉴权器本质上也是利用了rbac鉴权器,是通过为system:node这个内置用户授权来实现的,来看一下。
默认Node规则生成
plugin/pkg/auth/authorizer/rbac/bootstrappolicy/policy.go:97
func NodeRules() []rbacv1.PolicyRule {
nodePolicyRules := []rbacv1.PolicyRule{
// Needed to check API access. These creates are non-mutating
rbacv1helpers.NewRule("create").Groups(authenticationGroup).Resources("tokenreviews").RuleOrDie(),
rbacv1helpers.NewRule("create").Groups(authorizationGroup).Resources("subjectaccessreviews", "localsubjectaccessreviews").RuleOrDie(),
// Needed to build serviceLister, to populate env vars for services
rbacv1helpers.NewRule(Read...).Groups(legacyGroup).Resources("services").RuleOrDie(),
// Nodes can register Node API objects and report status.
// Use the NodeRestriction admission plugin to limit a node to creating/updating its own API object.
rbacv1helpers.NewRule("create", "get", "list", "watch").Groups(legacyGroup).Resources("nodes").RuleOrDie(),
rbacv1helpers.NewRule("update", "patch").Groups(legacyGroup).Resources("nodes/status").RuleOrDie(),
rbacv1helpers.NewRule("update", "patch").Groups(legacyGroup).Resources("nodes").RuleOrDie(),
// TODO: restrict to the bound node as creator in the NodeRestrictions admission plugin
rbacv1helpers.NewRule("create", "update", "patch").Groups(legacyGroup).Resources("events").RuleOrDie(),
// TODO: restrict to pods scheduled on the bound node once field selectors are supported by list/watch authorization
rbacv1helpers.NewRule(Read...).Groups(legacyGroup).Resources("pods").RuleOrDie(),
// Needed for the node to create/delete mirror pods.
// Use the NodeRestriction admission plugin to limit a node to creating/deleting mirror pods bound to itself.
rbacv1helpers.NewRule("create", "delete").Groups(legacyGroup).Resources("pods").RuleOrDie(),
// Needed for the node to report status of pods it is running.
// Use the NodeRestriction admission plugin to limit a node to updating status of pods bound to itself.
rbacv1helpers.NewRule("update", "patch").Groups(legacyGroup).Resources("pods/status").RuleOrDie(),
// Needed for the node to create pod evictions.
// Use the NodeRestriction admission plugin to limit a node to creating evictions for pods bound to itself.
rbacv1helpers.NewRule("create").Groups(legacyGroup).Resources("pods/eviction").RuleOrDie(),
// Needed for imagepullsecrets, rbd/ceph and secret volumes, and secrets in envs
// Needed for configmap volume and envs
// Use the Node authorization mode to limit a node to get secrets/configmaps referenced by pods bound to itself.
rbacv1helpers.NewRule("get", "list", "watch").Groups(legacyGroup).Resources("secrets", "configmaps").RuleOrDie(),
// Needed for persistent volumes
// Use the Node authorization mode to limit a node to get pv/pvc objects referenced by pods bound to itself.
rbacv1helpers.NewRule("get").Groups(legacyGroup).Resources("persistentvolumeclaims", "persistentvolumes").RuleOrDie(),
// TODO: add to the Node authorizer and restrict to endpoints referenced by pods or PVs bound to the node
// Needed for glusterfs volumes
rbacv1helpers.NewRule("get").Groups(legacyGroup).Resources("endpoints").RuleOrDie(),
// Used to create a certificatesigningrequest for a node-specific client certificate, and watch
// for it to be signed. This allows the kubelet to rotate it's own certificate.
rbacv1helpers.NewRule("create", "get", "list", "watch").Groups(certificatesGroup).Resources("certificatesigningrequests").RuleOrDie(),
}
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.ExpandPersistentVolumes) {
// Use the Node authorization mode to limit a node to update status of pvc objects referenced by pods bound to itself.
// Use the NodeRestriction admission plugin to limit a node to just update the status stanza.
pvcStatusPolicyRule := rbacv1helpers.NewRule("get", "update", "patch").Groups(legacyGroup).Resources("persistentvolumeclaims/status").RuleOrDie()
nodePolicyRules = append(nodePolicyRules, pvcStatusPolicyRule)
}
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.TokenRequest) {
// Use the Node authorization to limit a node to create tokens for service accounts running on that node
// Use the NodeRestriction admission plugin to limit a node to create tokens bound to pods on that node
tokenRequestRule := rbacv1helpers.NewRule("create").Groups(legacyGroup).Resources("serviceaccounts/token").RuleOrDie()
nodePolicyRules = append(nodePolicyRules, tokenRequestRule)
}
// CSI
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.CSIPersistentVolume) {
volAttachRule := rbacv1helpers.NewRule("get").Groups(storageGroup).Resources("volumeattachments").RuleOrDie()
nodePolicyRules = append(nodePolicyRules, volAttachRule)
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.CSIDriverRegistry) {
csiDriverRule := rbacv1helpers.NewRule("get", "watch", "list").Groups("storage.k8s.io").Resources("csidrivers").RuleOrDie()
nodePolicyRules = append(nodePolicyRules, csiDriverRule)
}
}
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.KubeletPluginsWatcher) &&
utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.CSINodeInfo) {
csiNodeInfoRule := rbacv1helpers.NewRule("get", "create", "update", "patch", "delete").Groups("storage.k8s.io").Resources("csinodes").RuleOrDie()
nodePolicyRules = append(nodePolicyRules, csiNodeInfoRule)
}
// Node leases
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.NodeLease) {
nodePolicyRules = append(nodePolicyRules, rbacv1helpers.NewRule("get", "create", "update", "patch", "delete").Groups("coordination.k8s.io").Resources("leases").RuleOrDie())
}
// RuntimeClass
if utilfeature.DefaultFeatureGate.Enabled(features.RuntimeClass) {
nodePolicyRules = append(nodePolicyRules, rbacv1helpers.NewRule("get", "list", "watch").Groups("node.k8s.io").Resources("runtimeclasses").RuleOrDie())
}
return nodePolicyRules
}
这里初始化了kubelet工作所需要的资源的权限,如(node/pod/cm/secret/pvc等)
Authorize代码实现
plugin/pkg/auth/authorizer/node/node_authorizer.go:80
func (r *NodeAuthorizer) Authorize(attrs authorizer.Attributes) (authorizer.Decision, string, error) {
// 判断是不是node发起的请求(所属的group是不是system:node)
nodeName, isNode := r.identifier.NodeIdentity(attrs.GetUser())
if !isNode {
// reject requests from non-nodes
return authorizer.DecisionNoOpinion, "", nil
}
if len(nodeName) == 0 {
// reject requests from unidentifiable nodes
klog.V(2).Infof("NODE DENY: unknown node for user %q", attrs.GetUser().GetName())
return authorizer.DecisionNoOpinion, fmt.Sprintf("unknown node for user %q", attrs.GetUser().GetName()), nil
}
// subdivide access to specific resources
if attrs.IsResourceRequest() {
// 根据请求属性(路径)获取资源类型,不同类型资源不同的方式处理
requestResource := schema.GroupResource{Group: attrs.GetAPIGroup(), Resource: attrs.GetResource()}
switch requestResource {
case secretResource:
return r.authorizeReadNamespacedObject(nodeName, secretVertexType, attrs)
case configMapResource:
return r.authorizeReadNamespacedObject(nodeName, configMapVertexType, attrs)
case pvcResource:
if r.features.Enabled(features.ExpandPersistentVolumes) {
if attrs.GetSubresource() == "status" {
return r.authorizeStatusUpdate(nodeName, pvcVertexType, attrs)
}
}
return r.authorizeGet(nodeName, pvcVertexType, attrs)
case pvResource:
return r.authorizeGet(nodeName, pvVertexType, attrs)
case vaResource:
if r.features.Enabled(features.CSIPersistentVolume) {
return r.authorizeGet(nodeName, vaVertexType, attrs)
}
return authorizer.DecisionNoOpinion, fmt.Sprintf("disabled by feature gate %s", features.CSIPersistentVolume), nil
case svcAcctResource:
if r.features.Enabled(features.TokenRequest) {
return r.authorizeCreateToken(nodeName, serviceAccountVertexType, attrs)
}
return authorizer.DecisionNoOpinion, fmt.Sprintf("disabled by feature gate %s", features.TokenRequest), nil
case leaseResource:
if r.features.Enabled(features.NodeLease) {
return r.authorizeLease(nodeName, attrs)
}
return authorizer.DecisionNoOpinion, fmt.Sprintf("disabled by feature gate %s", features.NodeLease), nil
case csiNodeResource:
if r.features.Enabled(features.KubeletPluginsWatcher) && r.features.Enabled(features.CSINodeInfo) {
return r.authorizeCSINode(nodeName, attrs)
}
return authorizer.DecisionNoOpinion, fmt.Sprintf("disabled by feature gates %s and %s", features.KubeletPluginsWatcher, features.CSINodeInfo), nil
}
}
// Access to other resources is not subdivided, so just evaluate against the statically defined node rules
if rbac.RulesAllow(attrs, r.nodeRules...) {
return authorizer.DecisionAllow, "", nil
}
return authorizer.DecisionNoOpinion, "", nil
}
WebHook鉴权器
简介
与上一篇中的WebHook认证器类似,WebHook鉴权器也是依赖于集群外部的鉴权服务器,将鉴权请求POST发送给外部的鉴权服务器。
Webhook 模式需要一个 HTTP 配置文件,通过 --authorization-webhook-config-file=SOME_FILENAME 的参数声明。
配置文件的格式使用 kubeconfig。在文件中,"users" 代表着 API 服务器的 webhook,而 "cluster" 代表着远程服务。
使用 HTTPS 客户端认证的配置例子:
# Kubernetes API 版本
apiVersion: v1
# API 对象种类
kind: Config
# clusters 代表远程服务。
clusters:
- name: name-of-remote-authz-service
cluster:
# 对远程服务进行身份认证的 CA。
certificate-authority: /path/to/ca.pem
# 远程服务的查询 URL。必须使用 'https'。
server: https://authz.example.com/authorize
# users 代表 API 服务器的 webhook 配置
users:
- name: name-of-api-server
user:
client-certificate: /path/to/cert.pem # webhook plugin 使用 cert
client-key: /path/to/key.pem # cert 所对应的 key
# kubeconfig 文件必须有 context。需要提供一个给 API 服务器。
current-context: webhook
contexts:
- context:
cluster: name-of-remote-authz-service
user: name-of-api-server
name: webhook
摘自官方文档Webhook 模式
代码实现
vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/plugin/pkg/authorizer/webhook/webhook.go:152
func (w *WebhookAuthorizer) Authorize(attr authorizer.Attributes) (decision authorizer.Decision, reason string, err error) {
r := &authorization.SubjectAccessReview{}
if user := attr.GetUser(); user != nil {
r.Spec = authorization.SubjectAccessReviewSpec{
User: user.GetName(),
UID: user.GetUID(),
Groups: user.GetGroups(),
Extra: convertToSARExtra(user.GetExtra()),
}
}
if attr.IsResourceRequest() {
r.Spec.ResourceAttributes = &authorization.ResourceAttributes{
Namespace: attr.GetNamespace(),
Verb: attr.GetVerb(),
Group: attr.GetAPIGroup(),
Version: attr.GetAPIVersion(),
Resource: attr.GetResource(),
Subresource: attr.GetSubresource(),
Name: attr.GetName(),
}
} else {
r.Spec.NonResourceAttributes = &authorization.NonResourceAttributes{
Path: attr.GetPath(),
Verb: attr.GetVerb(),
}
}
// 将请求的主体/资源/操作等字段放在一个json里
key, err := json.Marshal(r.Spec)
if err != nil {
return w.decisionOnError, "", err
}
// 从本地的缓存里取,有则不发起远端post请求了
if entry, ok := w.responseCache.Get(string(key)); ok {
r.Status = entry.(authorization.SubjectAccessReviewStatus)
} else {
var (
result *authorization.SubjectAccessReview
err error
)
webhook.WithExponentialBackoff(w.initialBackoff, func() error {
// 缓存里没有,则发起post请求给远端鉴权服务器
result, err = w.subjectAccessReview.Create(r)
return err
})
if err != nil {
// An error here indicates bad configuration or an outage. Log for debugging.
klog.Errorf("Failed to make webhook authorizer request: %v", err)
return w.decisionOnError, "", err
}
r.Status = result.Status
// 长度不超过10000则缓存结果
if shouldCache(attr) {
if r.Status.Allowed {
w.responseCache.Add(string(key), r.Status, w.authorizedTTL)
} else {
w.responseCache.Add(string(key), r.Status, w.unauthorizedTTL)
}
}
}
switch {
// 根据远端鉴权服务器的响应状态,返回鉴权结果
case r.Status.Denied && r.Status.Allowed:
return authorizer.DecisionDeny, r.Status.Reason, fmt.Errorf("webhook subject access review returned both allow and deny response")
case r.Status.Denied:
return authorizer.DecisionDeny, r.Status.Reason, nil
case r.Status.Allowed:
return authorizer.DecisionAllow, r.Status.Reason, nil
default:
return authorizer.DecisionNoOpinion, r.Status.Reason, nil
}
}
总结
鉴权的流程与认证的流程大体类似,但也有所不同,例如认证器链的执行顺序是无序的,而鉴权器链的执行顺序是有序的(按参数指定的顺序)。另外鉴权器的数量没有认证器那么多,因此相对容易理解一些。