|
|
10 years ago | |
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| images/nginx | 10 years ago | |
| README.md | 10 years ago | |
| architecture.png | 10 years ago | |
| wordpress-resources.yaml | 10 years ago | |
| wordpress.jinja | 10 years ago | |
| wordpress.jinja.schema | 10 years ago | |
| wordpress.yaml | 10 years ago | |
README.md
Wordpress Example
Welcome to the Wordpress example. It shows you how to deploy a Wordpress application using Deployment Manager.
Prerequisites
Deployment Manager
First, make sure DM is installed in your Kubernetes cluster by following the instructions in the top level README.md.
Google Cloud Resources
The Wordpress application will make use of several persistent disks, which we will host on Google Cloud. To create these disks we will create a deployment using Google Cloud Deployment Manager:
gcloud deployment-manager deployments create wordpress-resources --config wordpress-resources.yaml
where wordpress-resources.yaml looks as follows:
resources:
- name: nfs-disk
type: compute.v1.disk
properties:
zone: us-central1-b
sizeGb: 200
- name: mysql-disk
type: compute.v1.disk
properties:
zone: us-central1-b
sizeGb: 200
Privileged containers
To use NFS we need to be able to launch privileged containers. Since the release of Kubernetes 1.1 privileged container support is enabled by default. If your Kubernetes cluster doesn't support privileged containers you need to manually change this by setting the flag at kubernetes/saltbase/pillar/privilege.sls to true.
NFS Library
Mounting NFS volumes requires NFS libraries. Since the release of Kubernetes 1.1 the NFS libraries are installed by default. If they are not installed on your Kubernetes cluster you need to install them manually.
Understanding the Wordpress example template
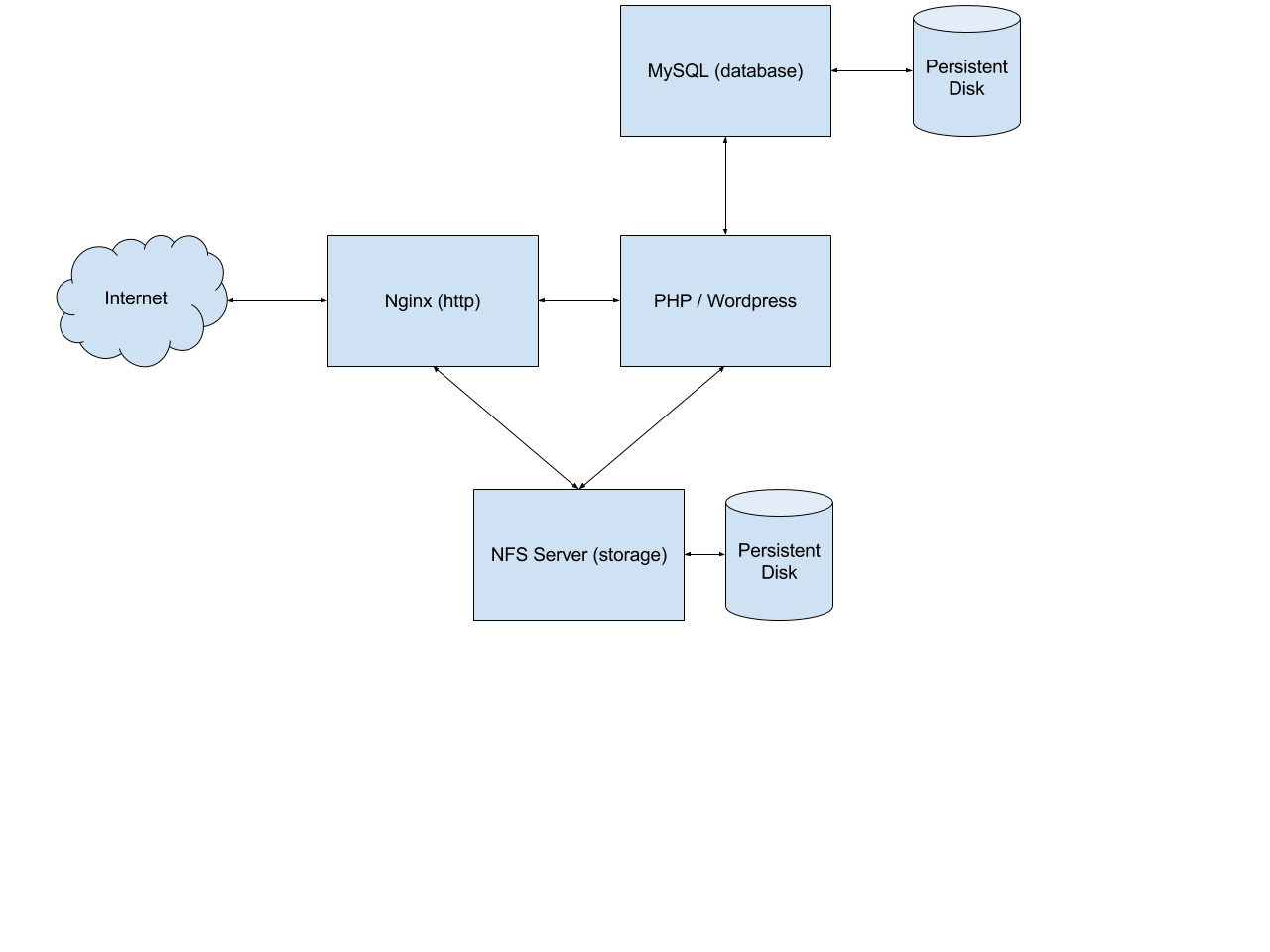
Let's take a closer look at the template used by the Wordpress example. The Wordpress application consists of 4 microservices: an nginx service, a wordpress-php service, a MySQL service, and an NFS service. The architecture looks as follows:
Variables
The template contains the following variables:
{% set PROPERTIES = properties or {} %}
{% set PROJECT = PROPERTIES['project'] or 'dm-k8s-testing' %}
{% set NFS_SERVER = PROPERTIES['nfs-server'] or {} %}
{% set NFS_SERVER_IP = NFS_SERVER['ip'] or '10.0.253.247' %}
{% set NFS_SERVER_PORT = NFS_SERVER['port'] or 2049 %}
{% set NFS_SERVER_DISK = NFS_SERVER['disk'] or 'nfs-disk' %}
{% set NFS_SERVER_DISK_FSTYPE = NFS_SERVER['fstype'] or 'ext4' %}
{% set NGINX = PROPERTIES['nginx'] or {} %}
{% set NGINX_PORT = 80 %}
{% set NGINX_REPLICAS = NGINX['replicas'] or 2 %}
{% set WORDPRESS_PHP = PROPERTIES['wordpress-php'] or {} %}
{% set WORDPRESS_PHP_REPLICAS = WORDPRESS_PHP['replicas'] or 2 %}
{% set WORDPRESS_PHP_PORT = WORDPRESS_PHP['port'] or 9000 %}
{% set MYSQL = PROPERTIES['mysql'] or {} %} {% set MYSQL_PORT = MYSQL['port'] or 3306 %} {% set MYSQL_PASSWORD = MYSQL['password'] or 'mysql-password' %} {% set MYSQL_DISK = MYSQL['disk'] or 'mysql-disk' %} {% set MYSQL_DISK_FSTYPE = MYSQL['fstype'] or 'ext4' %}
Nginx service
The nginx service is a replicated service with 2 replicas:
- name: nginx
type: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/deployment-manager/master/templates/replicatedservice/v2/replicatedservice.py
properties:
service_port: {{ NGINX_PORT }}
container_port: {{ NGINX_PORT }}
replicas: {{ NGINX_REPLICAS }}
external_service: true
image: gcr.io/{{ PROJECT }}/nginx:latest
volumes:
- mount_path: /var/www/html
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: nfs
The nginx image builds upon the standard nginx image and simply copies a custom configuration file.
Wordpress-php service
The wordpress-php service is a replicated service with 2 replicas:
- name: wordpress-php
type: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/deployment-manager/master/templates/replicatedservice/v2/replicatedservice.py
properties:
service_name: wordpress-php
service_port: {{ WORDPRESS_PHP_PORT }}
container_port: {{ WORDPRESS_PHP_PORT }}
replicas: 2
image: wordpress:fpm
env:
- name: WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD
value: {{ MYSQL_PASSWORD }}
- name: WORDPRESS_DB_HOST
value: mysql-service
volumes:
- mount_path: /var/www/html
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: nfs
MySQL service
The MySQL service is a replicated service with a single replica:
- name: mysql
type: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/deployment-manager/master/templates/replicatedservice/v2/replicatedservice.py
properties:
service_port: {{ MYSQL_PORT }}
container_port: {{ MYSQL_PORT }}
replicas: 1
image: mysql:5.6
env:
- name: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD
value: {{ MYSQL_PASSWORD }}
volumes:
- mount_path: /var/lib/mysql
gcePersistentDisk:
pdName: {{ MYSQL_DISK }}
fsType: {{ MYSQL_DISK_FSTYPE }}
NFS service
The NFS service is a replicated service with a single replica that is available as a type:
- name: nfs
type: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/deployment-manager/master/templates/nfs/v1/nfs.jinja
properties:
ip: {{ NFS_SERVER_IP }}
port: {{ NFS_SERVER_PORT }}
disk: {{ NFS_SERVER_DISK }}
fstype: {{NFS_SERVER_DISK_FSTYPE }}
Deploying Wordpress
We can now deploy Wordpress using:
dm deploy examples/wordpress/wordpress.yaml
where wordpress.yaml looks as follows:
imports:
- path: wordpress.jinja
resources:
- name: wordpress
type: wordpress.jinja
properties:
project: <YOUR PROJECT>