|
|
4 years ago | |
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| README.de.md | 4 years ago | |
| README.es.md | 4 years ago | |
| README.id.md | 4 years ago | |
| README.ja.md | 4 years ago | |
| README.ko.md | 4 years ago | |
| assignment.de.md | 4 years ago | |
| assignment.es.md | 4 years ago | |
| assignment.id.md | 4 years ago | |
| assignment.ja.md | 4 years ago | |
README.ko.md
JavaScript 기초: 결정하기
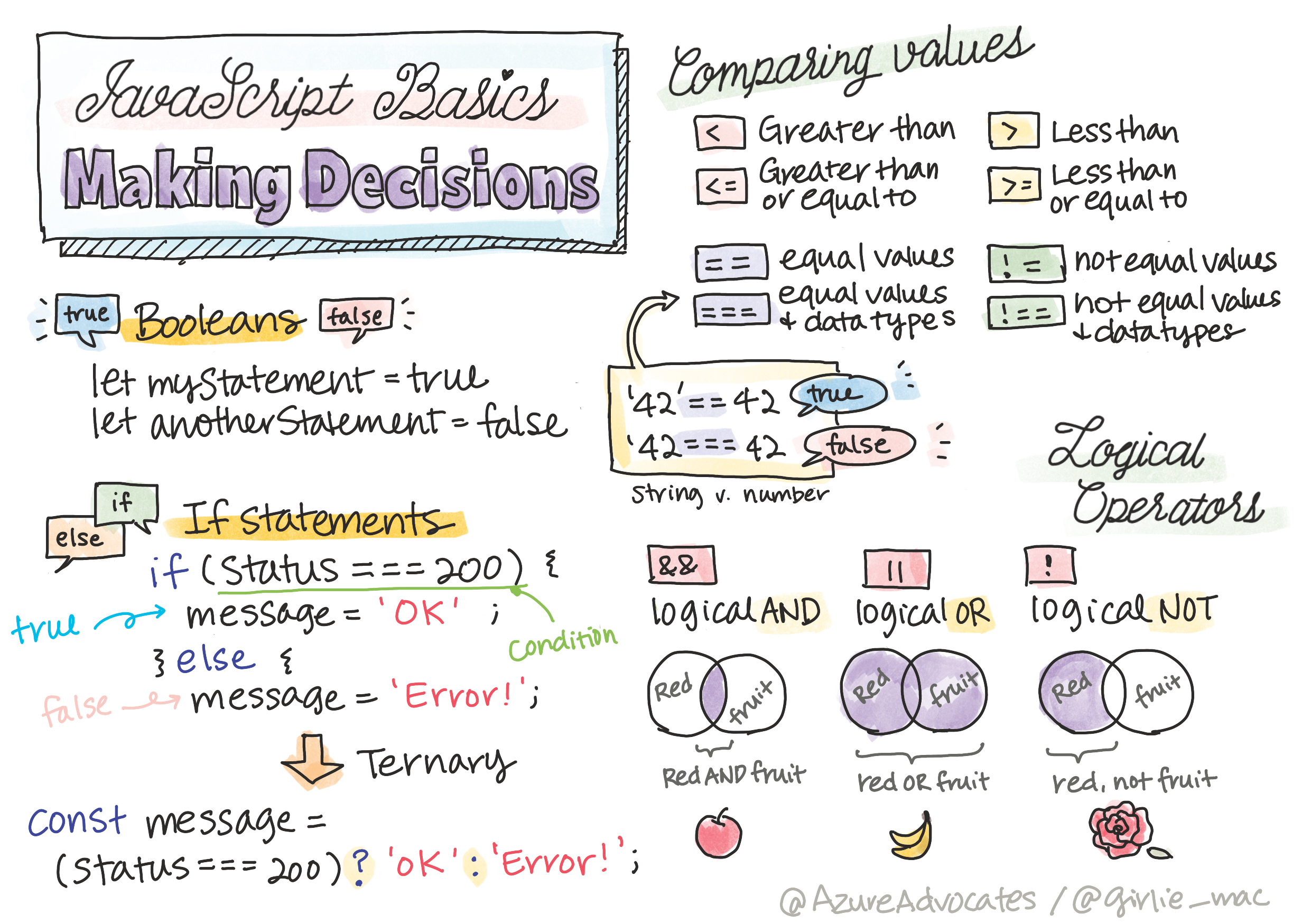
Sketchnote by Tomomi Imura
강의 전 퀴즈
결정을 내리고 코드가 실행되는 순서를 제어하면 코드를 재사용하며 강력하게 만들 수 있습니다. 이 강의에서는 JavaScript에서 데이터 흐름을 제어하기 위한 구문과 논리 자료형 데이터 타입을 함께 사용하는 중요성을 다룹니다.
논리 자료형에 대한 간략한 요약
논리 자료형은 true 또는 false 두 가지 값만 가능합니다. 논리 자료형은 조건이 충족하는 순간 실행하는 코드 라인을 결정하는 데 도움 줄 수 있습니다.
이렇게 참 또는 거짓으로 논리 자료형을 지정합니다:
let myTrueBool = true
let myFalseBool = false
✅ Booleans(=논리 자료형)은 영국의 수학자, 철학자이자 논리 학자인 George Boole (1815-1864)의 이름에서 유래되었습니다.
비교 연산자와 논리 연산자
연산자는 논리 자료형 값을 비교하여 조건을 평가하는 데 사용합니다. 자주 사용되는 연산자 목록입니다.
| Symbol | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
< |
Greater than: Compares two values and returns the true Boolean data type if the value on the right side is larger than the left |
5 < 6 // true |
<= |
Greater than or equal to: Compares two values and returns the true Boolean data type if the value on the right side is larger than or equal to the left |
5 <= 6 // true |
> |
Less than: Compares two values and returns the true Boolean data type if the value on the left side is larger than the right |
5 > 6 // false |
>= |
Less than or equal to: Compares two values and returns the true Boolean data type if the value on the left side is larger than or equal to the right |
5 >= 6 // false |
=== |
Strict equality: Compares two values and returns the true Boolean data type if values on the right and left are equal AND are the same data type. |
5 === 6 // false |
!== |
Inequality: Compares two values and returns the opposite Boolean value of what a strict equality operator would return | 5 !== 6 // true |
✅ 브라우저 콘솔에서 비교문을 작성하여 복습해보십시오. 반환된 데이터가 놀랍나요?
If 문
조건이 참이면 if 문은 블록 사이에서 코드를 실행합니다.
if (condition){
//Condition was true. Code in this block will run.
}
논리 연산자는 조건을 만들 때 종종 사용됩니다.
let currentMoney;
let laptopPrice;
if (currentMoney >= laptopPrice){
//Condition was true. Code in this block will run.
console.log("Getting a new laptop!");
}
IF..Else 문
else 문은 조건이 거짓일 때만 블록 사이에서 코드를 실행합니다. if 문와 함께 사용하는 것은 선택 사항입니다.
let currentMoney;
let laptopPrice;
if (currentMoney >= laptopPrice){
//Condition was true. Code in this block will run.
console.log("Getting a new laptop!");
}
else{
//Condition was true. Code in this block will run.
console.log("Can't afford a new laptop, yet!");
}
✅ 위 코드들을 브라우저 콘솔에서 실행하여 이해했는지 테스트하십시오. currentMoney 및 laptopPrice 변수 값이 변경하여 반환된 console.log ()가 변경됩니다.
논리 연산자와 논리 자료형
결정에는 두개 이상의 비교문이 필요할 수 있으며, 논리 연산자과 합쳐서 논리 자료형 값을 생성할 수 있습니다.
| Symbol | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
&& |
Logical AND: Compares two Boolean expressions. Returns true only if both sides are true | (5 > 6) && (5 < 6 ) //One side is false, other is true. Returns false |
| ` | ` | |
! |
Logical NOT: Returns the opposite value of a Boolean expression | !(5 > 6) // 5 is not greater than 6, but "!" will return true |
논리 연산자의 조건 및 결정
논리 연산자는 if..else 문에서 조건을 만들 때 사용됩니다.
let currentMoney;
let laptopPrice;
let laptopDiscountPrice = laptopPrice - (laptopPrice * .20) //Laptop price at 20 percent off
if (currentMoney >= laptopPrice || currentMoney >= laptopDiscountPrice){
//Condition was true. Code in this block will run.
console.log("Getting a new laptop!");
}
else {
//Condition was true. Code in this block will run.
console.log("Can't afford a new laptop, yet!");
}
부정 연산자
if...else 문으로 사용하여 조건부 로직을 만드는 방법을 살펴 보았습니다. if에 들어가는 모든 것은 참/거짓으로 평가되어야 합니다. ! 연산자를 사용하여 표현식을 부정 할 수 있습니다. 이렇게 보입니다:
if (!condition) {
// runs if condition is false
} else {
// runs if condition is true
}
삼항식
if...else가 결정 로직을 표현하는 유일한 방법은 아닙니다. 삼항 연산자라는 것을 사용할 수 있습니다. 구문은 다음과 같습니다:
let variable = condition ? <return this if true> : <return this if false>`
다음은 확실한 예시입니다:
let firstNumber = 20;
let secondNumber = 10
let biggestNumber = firstNumber > secondNumber ? firstNumber: secondNumber;
✅ 잠시 시간을 내서 코드를 몇 번 읽으시기 바랍니다. 연산자가 어떻게 작동하는지 이해하나요?
위의 내용은
firstNumber가secondNumber보다 큰 경우biggestNumber에firstNumber를 할당하고- 그렇지 않으면
secondNumber를 할당한다는 내용입니다.
삼항 표현식은 아래 코드를 간단히 작성했습니다.
let biggestNumber;
if (firstNumber > secondNumber) {
biggestNumber = firstNumber;
} else {
biggestNumber = secondNumber;
}
🚀 도전
논리 연산자로 프로그램을 먼저 만든 뒤, 삼항 표현식을 사용하여 다시 작성하십시오. 어떤 구문을 선호합니까?
강의 후 퀴즈
리뷰 & 자기주도 학습
MDN에서 사용할 수 있는 많은 연산자에 대해 자세히 알아보십시오.
Josh Comeau'의 wonderful operator lookup을 통할 수 있습니다!