# Browser Extension Project Part 1: All about Browsers
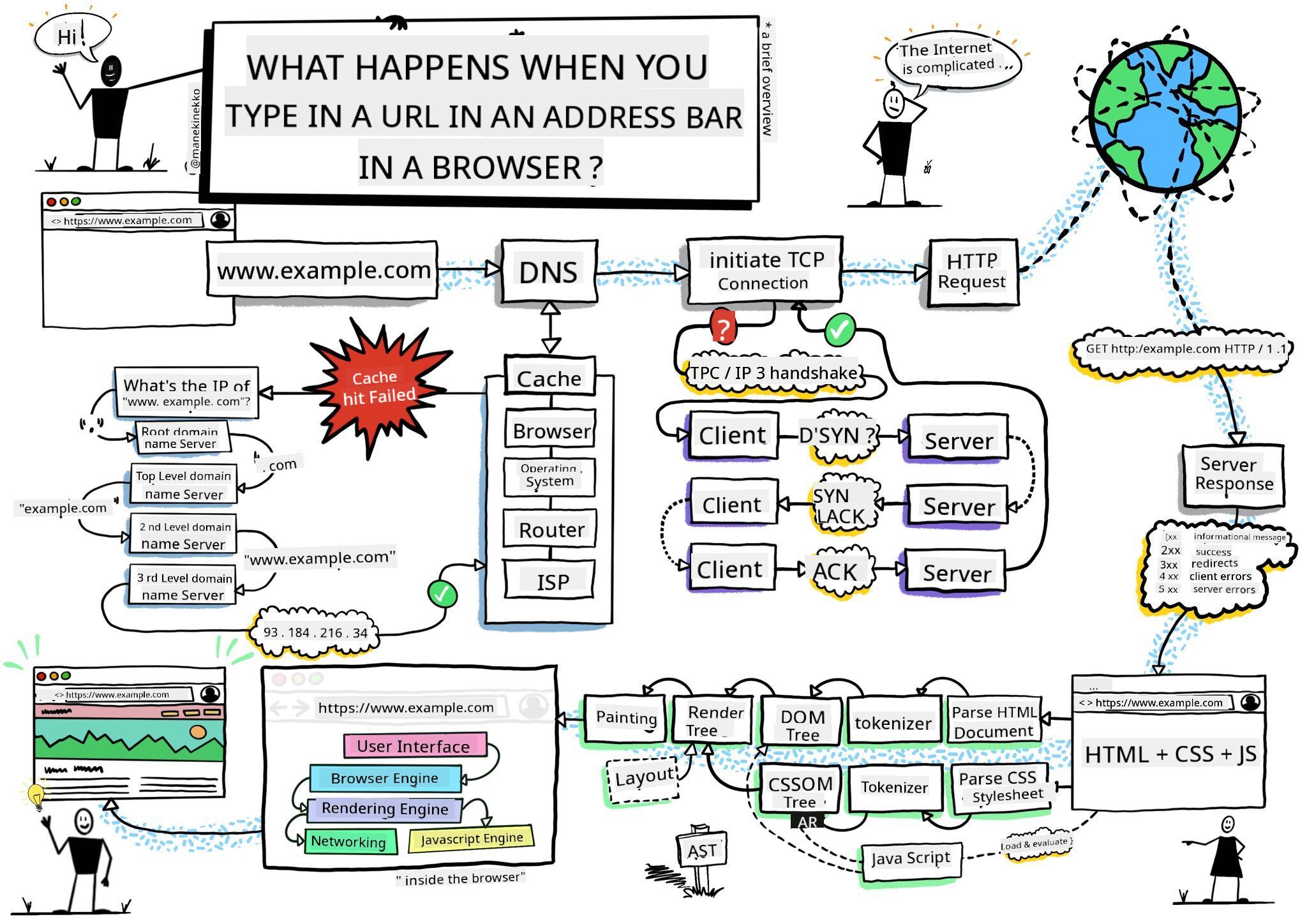
> Sketchnote by [Wassim Chegham](https://dev.to/wassimchegham/ever-wondered-what-happens-when-you-type-in-a-url-in-an-address-bar-in-a-browser-3dob)
## Pre-Lecture Quiz
[Pre-lecture quiz](https://ff-quizzes.netlify.app/web/quiz/23)
### Introduction
Browser extensions enhance the functionality of a browser. Before diving into building one, it's important to understand how browsers operate.
### About the browser
In this series of lessons, you'll learn how to create a browser extension compatible with Chrome, Firefox, and Edge. In this part, you'll explore how browsers function and set up the foundational elements of a browser extension.
So, what exactly is a browser? It's a software application that enables users to access content from a server and display it on web pages.
✅ A bit of history: The first browser, called 'WorldWideWeb,' was created by Sir Timothy Berners-Lee in 1990.
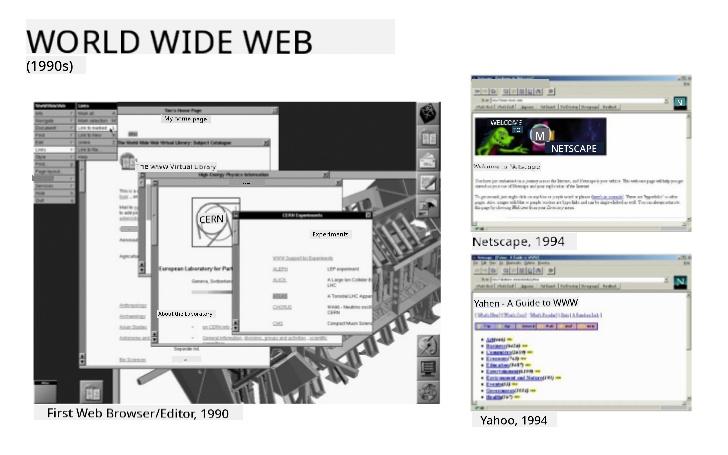
> Some early browsers, via [Karen McGrane](https://www.slideshare.net/KMcGrane/week-4-ixd-history-personal-computing)
When a user connects to the internet using a URL (Uniform Resource Locator), typically through Hypertext Transfer Protocol (`http` or `https`), the browser communicates with a web server to retrieve a web page.
The browser's rendering engine then displays the page on the user's device, which could be a mobile phone, desktop, or laptop.
Browsers also have features like caching content to avoid fetching it repeatedly from the server, recording browsing history, and storing 'cookies'—small pieces of data that track user activity.
It's crucial to remember that browsers are not all the same! Each has its own strengths and weaknesses. A professional web developer must ensure web pages perform well across different browsers, including handling small screens like mobile phones and offline users.
A helpful resource to bookmark is [caniuse.com](https://www.caniuse.com). It provides lists of supported technologies, making it easier to build web pages that cater to your users.
✅ How can you determine which browsers are most popular among your website's users? Check your analytics! You can integrate analytics tools into your web development process to see which browsers are most commonly used.
## Browser extensions
Why create a browser extension? Extensions are convenient tools that provide quick access to repetitive tasks. For instance, you might use a color-picker extension to check colors on web pages or a password manager extension to store and retrieve passwords.
Developing browser extensions is also enjoyable. They focus on specific tasks and perform them efficiently.
✅ What are your favorite browser extensions? What tasks do they help you with?
### Installing extensions
Before building your own extension, familiarize yourself with the process of creating and deploying one. While each browser has slight variations, the process is similar across Chrome, Firefox, and Edge. Here's an example for Edge:
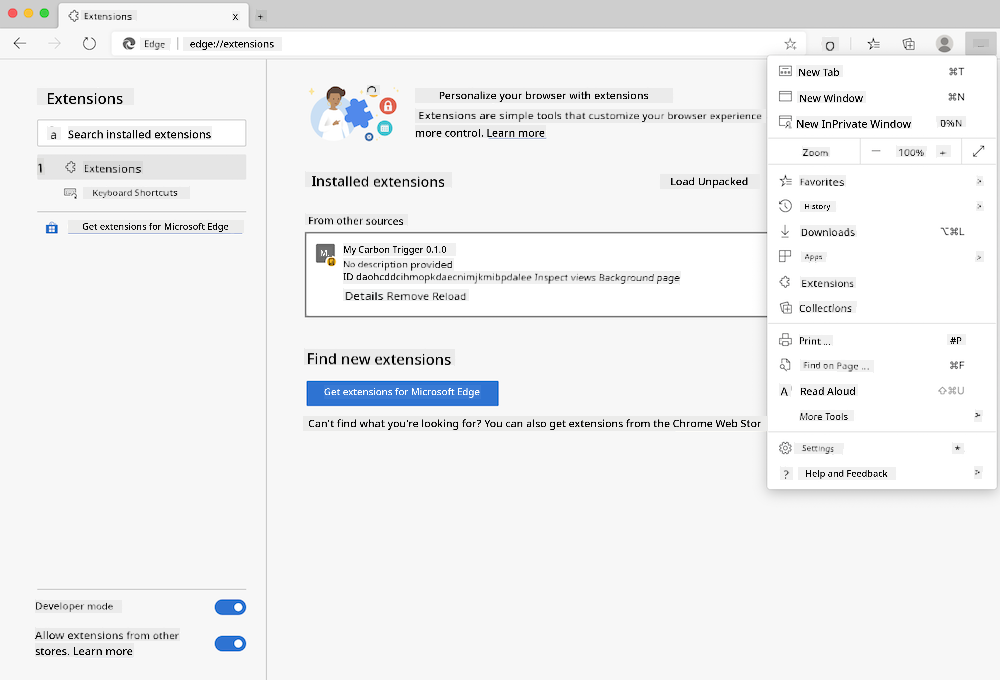
> Note: Make sure to toggle on developer mode and allow extensions from other stores.
The general process involves:
- Building your extension using `npm run build`
- Navigating to the extensions page in the browser via the "Settings and more" button (the `...` icon) in the top-right corner
- For a new installation, selecting `load unpacked` to upload the extension from its build folder (in this case, `/dist`)
- Clicking `reload` if you're updating an already-installed extension
✅ These instructions apply to extensions you create yourself. To install extensions from a browser's extension store, visit the respective [stores](https://microsoftedge.microsoft.com/addons/Microsoft-Edge-Extensions-Home) and install your desired extension.
### Get Started
You'll build a browser extension that displays your region's carbon footprint, including energy usage and its sources. The extension will feature a form to collect an API key for accessing CO2 Signal's API.
**What you'll need:**
- [An API key](https://www.co2signal.com/): Enter your email on this page to receive one.
- The [code for your region](http://api.electricitymap.org/v3/zones) from the [Electricity Map](https://www.electricitymap.org/map) (e.g., for Boston, use 'US-NEISO').
- The [starter code](../../../../5-browser-extension/start): Download the `start` folder to complete the code.
- [NPM](https://www.npmjs.com): Install NPM locally to manage packages listed in your `package.json` file.
✅ Learn more about package management in this [excellent Learn module](https://docs.microsoft.com/learn/modules/create-nodejs-project-dependencies/?WT.mc_id=academic-77807-sagibbon)
Take a moment to review the codebase:
dist
-|manifest.json (defaults set here)
-|index.html (front-end HTML markup here)
-|background.js (background JS here)
-|main.js (built JS)
src
-|index.js (your JS code goes here)
✅ Once you have your API key and region code, save them somewhere for future use.
### Build the HTML for the extension
This extension has two views: one for collecting the API key and region code:
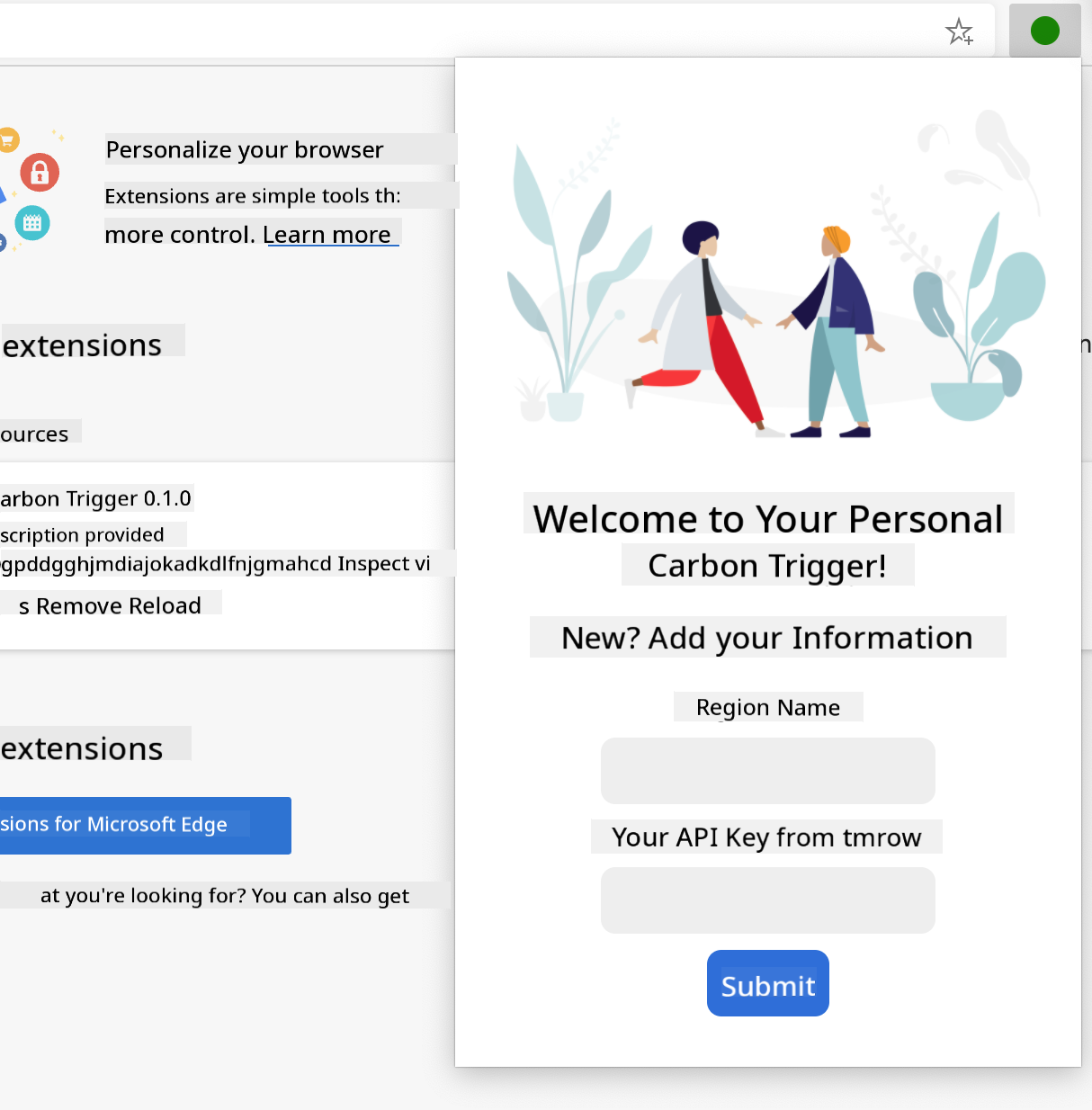
And another for displaying the region's carbon usage:
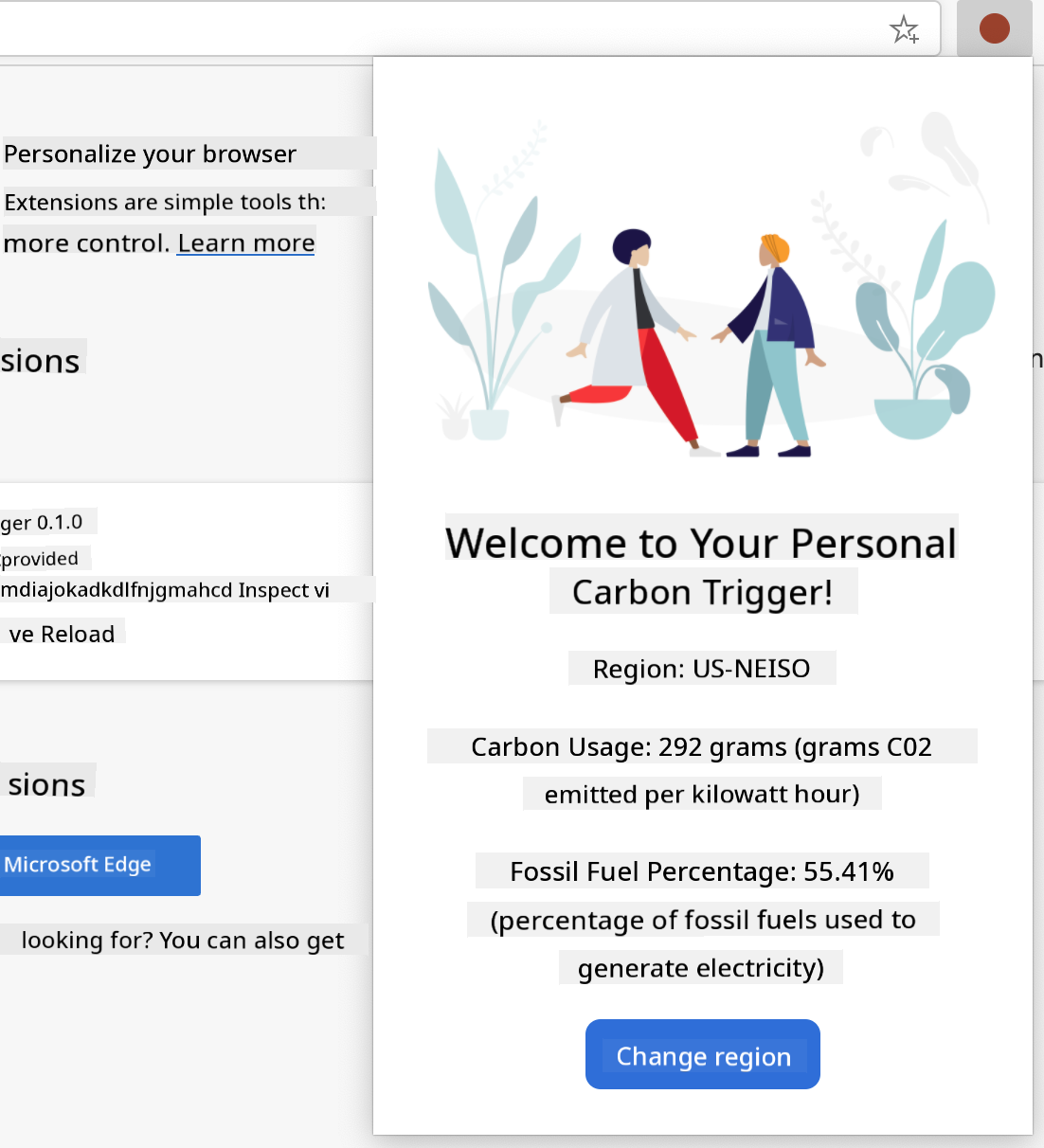
Start by creating the HTML for the form and styling it with CSS.
In the `/dist` folder, build a form and a results area. In the `index.html` file, populate the designated form area:
```HTML
```
This form will save the input information to local storage.
Next, create the results area. Add some divs below the final form tag:
```HTML
loading...
Region:
Carbon Usage:
Fossil Fuel Percentage:
```
Now, try building the extension. Install the package dependencies:
```
npm install
```
This command uses npm (Node Package Manager) to install webpack for the build process. Webpack bundles the code, and you can see the output in `/dist/main.js`.
At this stage, the extension should build successfully. If you deploy it in Edge, you'll see a neatly displayed form.
Congratulations! You've taken the first steps toward building a browser extension. In the next lessons, you'll add more functionality and features.
---
## 🚀 Challenge
Explore a browser extension store and install an extension. Examine its files to uncover interesting details. What do you find?
## Post-Lecture Quiz
[Post-lecture quiz](https://ff-quizzes.netlify.app/web/quiz/24)
## Review & Self Study
In this lesson, you learned about the history of web browsers. Take some time to explore how the inventors of the World Wide Web envisioned its use. Here are some useful resources:
[The History of Web Browsers](https://www.mozilla.org/firefox/browsers/browser-history/)
[History of the Web](https://webfoundation.org/about/vision/history-of-the-web/)
[An interview with Tim Berners-Lee](https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2019/mar/12/tim-berners-lee-on-30-years-of-the-web-if-we-dream-a-little-we-can-get-the-web-we-want)
## Assignment
[Restyle your extension](assignment.md)
---
**Disclaimer**:
This document has been translated using the AI translation service [Co-op Translator](https://github.com/Azure/co-op-translator). While we strive for accuracy, please note that automated translations may contain errors or inaccuracies. The original document in its native language should be regarded as the authoritative source. For critical information, professional human translation is recommended. We are not responsible for any misunderstandings or misinterpretations resulting from the use of this translation.