diff --git a/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P2-启动流程.md b/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P2-启动流程.md
index 453f95a..7a3f014 100644
--- a/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P2-启动流程.md
+++ b/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P2-启动流程.md
@@ -484,7 +484,7 @@ func (config Config) New() (authenticator.Request, *spec.SecurityDefinitions, er
这个New()方法依次生成每一种认证方式的Authenticator,New()方法的流程图如下:
-
+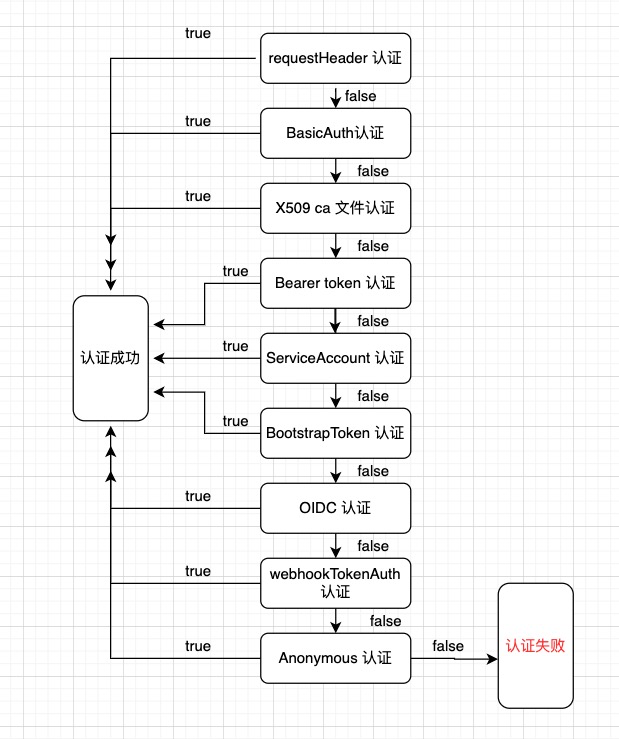
`union.New(authenticators...)`方法集合所有的认证器
diff --git a/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P3-APIServer的认证机制.md b/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P3-APIServer的认证机制.md
index 265dc86..0912eca 100644
--- a/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P3-APIServer的认证机制.md
+++ b/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P3-APIServer的认证机制.md
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ Kubernetes 使用身份认证插件利用客户端证书、持有者令牌(Bea
首先为了加深印象,再贴一下上一章列出的认证流程图:
-
+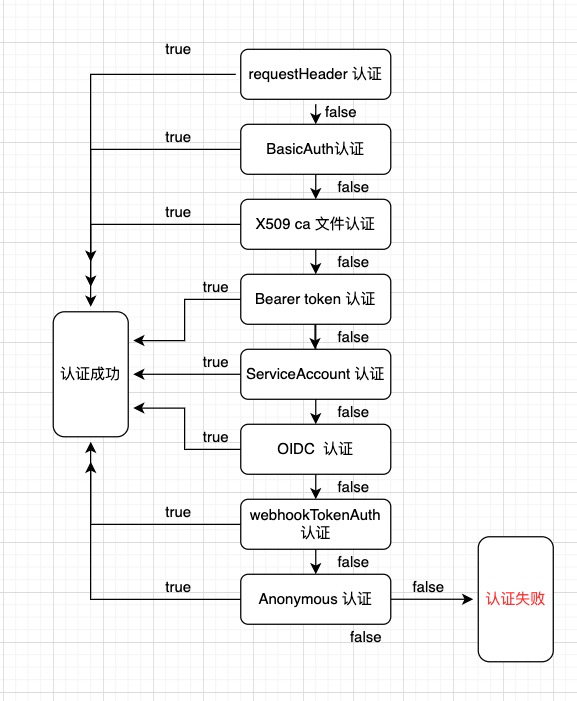
> 注:认证器的执行顺序为随机的,图中流向不代表固定顺序
@@ -94,7 +94,7 @@ func WithAuthentication(handler http.Handler, auth authenticator.Request, failed
`vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/authentication/authenticator/interfaces.go:35`
-
+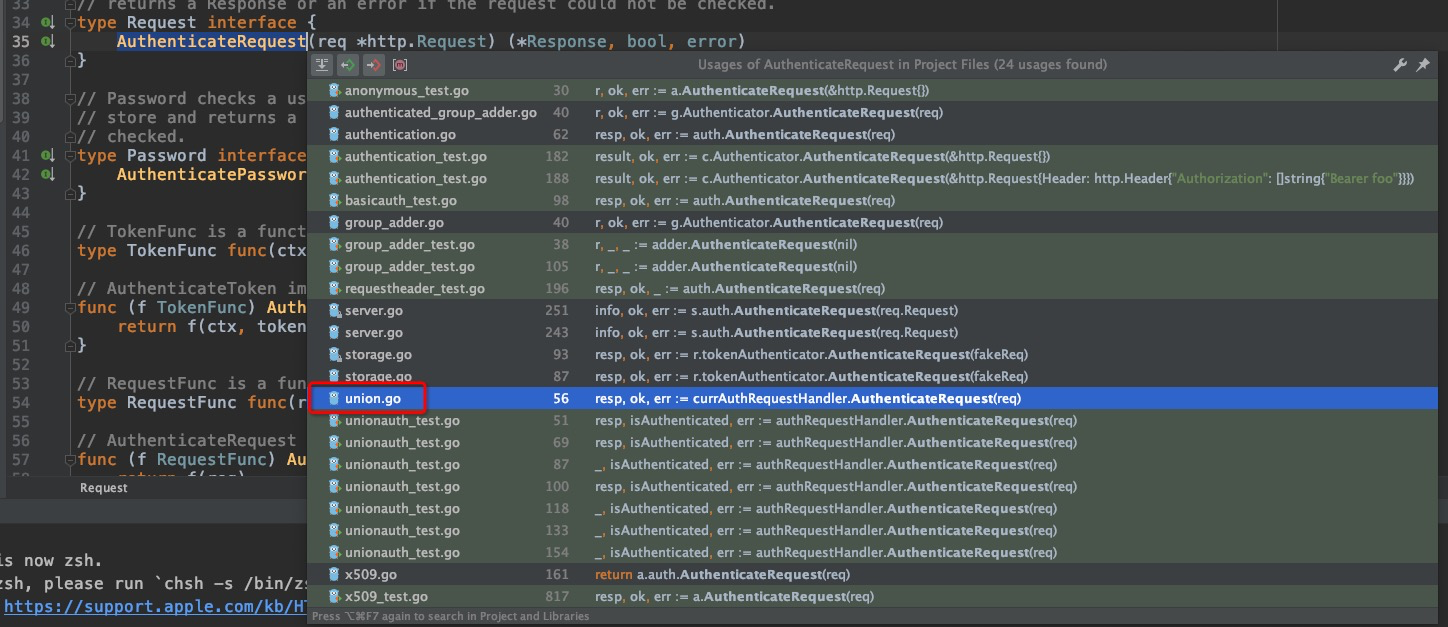
引用中的union.go中,聚合了所有的Authenticator链,进去看看
@@ -126,7 +126,7 @@ func (authHandler *unionAuthRequestHandler) AuthenticateRequest(req *http.Reques
apiserver的各种request相关定义代码大多集中在这个目录里:
- +
+ 那么依次逐个来看看每一种Authenticator对应的AuthenticateRequest方法。
@@ -192,7 +192,7 @@ extra:
使用kubeadm默认部署的集群,就启用了requestheader的配置:
-
+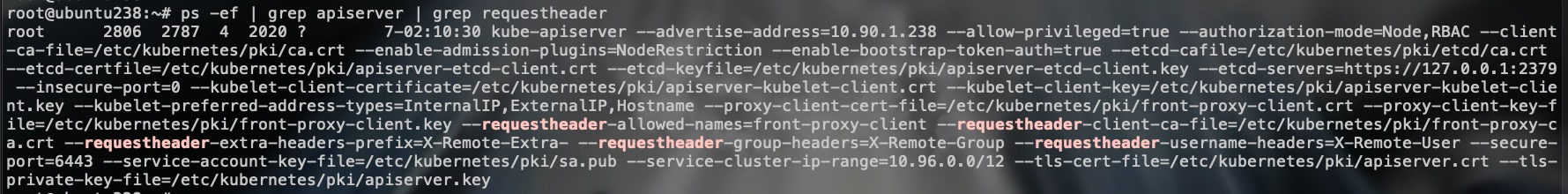
来看看AuthenticateRequest方法的代码:
@@ -500,7 +500,7 @@ SA是一种面向集群内部应用需要调用APIServer的场景所设计的认
在集群上找一个例子,以kube-proxy举例:
-
+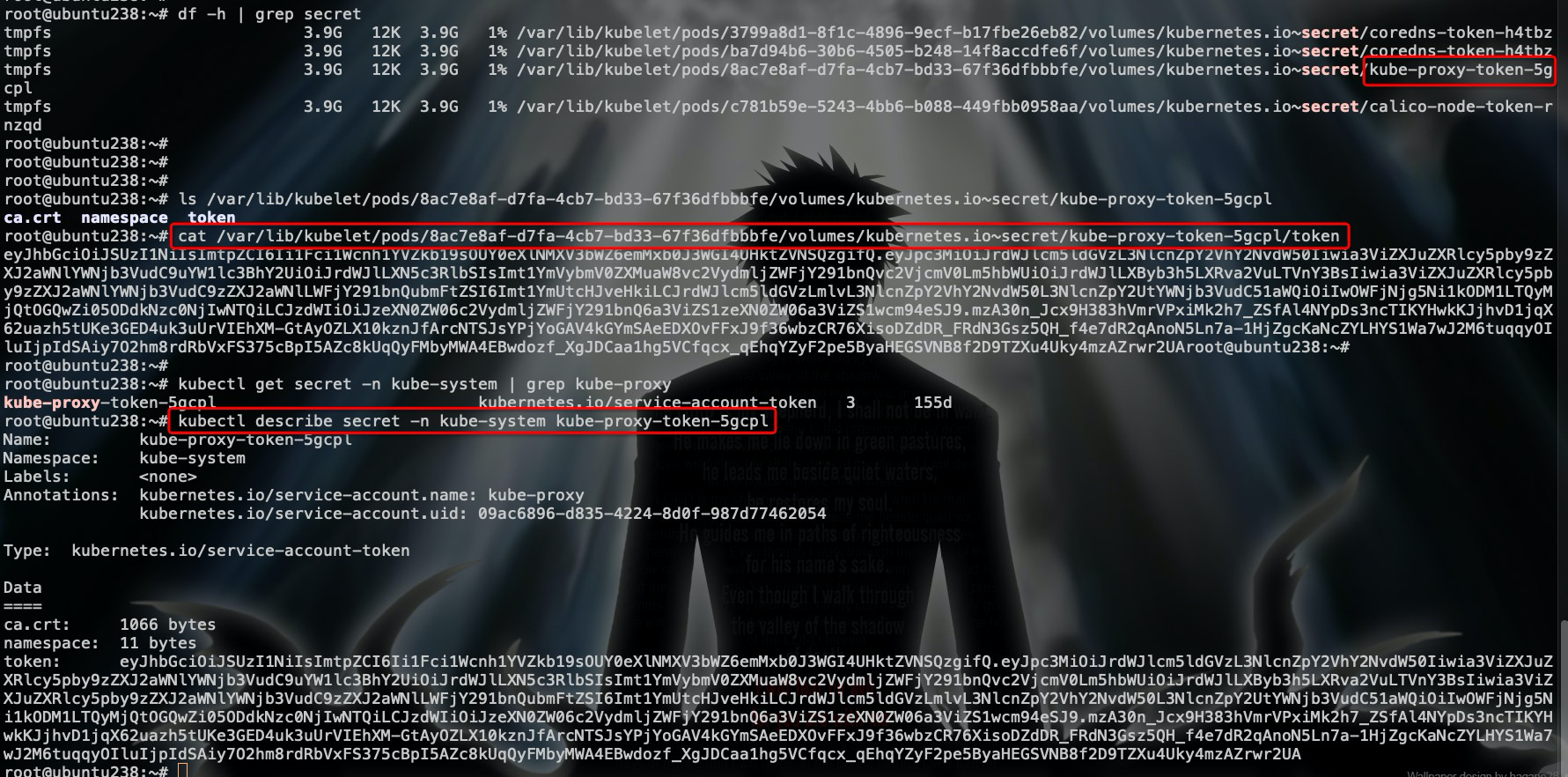
看看代码层面:
diff --git a/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P4-APIServer的鉴权机制.md b/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P4-APIServer的鉴权机制.md
index 7b11785..9e6b3f4 100644
--- a/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P4-APIServer的鉴权机制.md
+++ b/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P4-APIServer的鉴权机制.md
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ Kubernetes 仅审查以下 API 请求属性:
来看看现有的kubeadm部署集群启用的鉴权策略:
-
+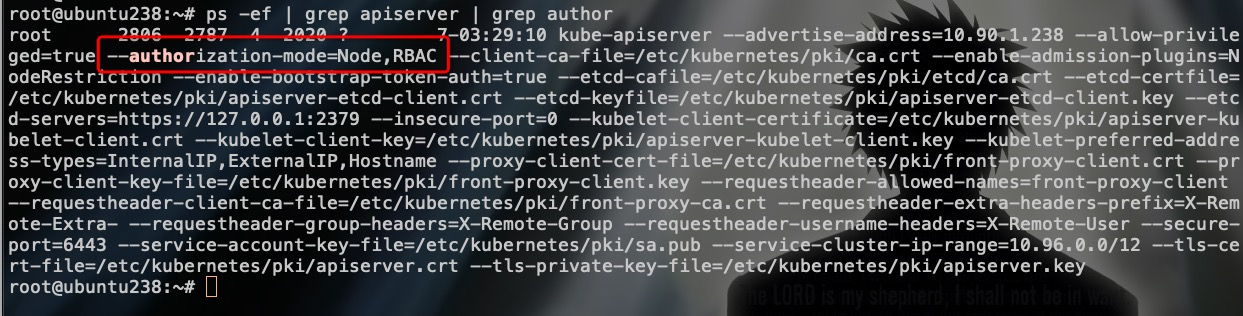
可以看到,默认启用了Node授权和RBAC授权模块。
@@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ DefaultResourceRuleInfo{
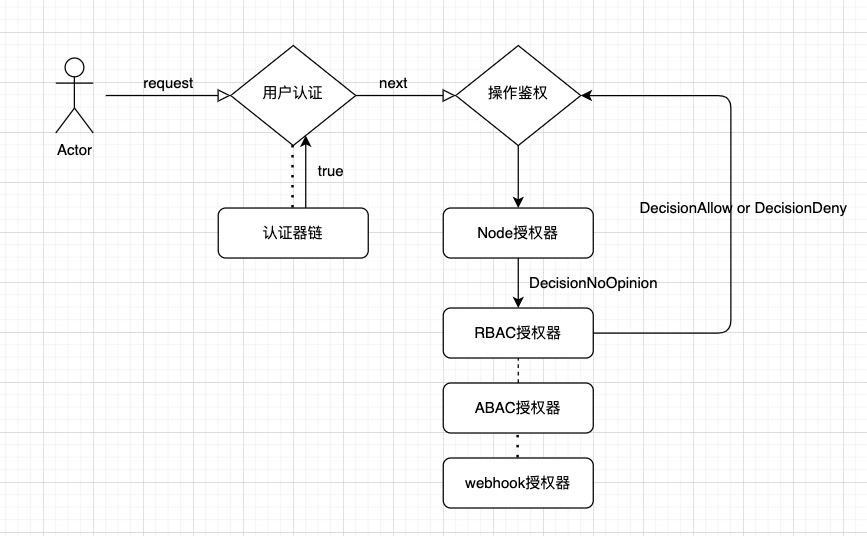
### 鉴权流程图
-
+
@@ -218,7 +218,7 @@ RBAC 鉴权机制使用 `rbac.authorization.k8s.io` [API 组](https://kubernetes
RBAC模式的详细描述和使用样例请参考我之前的文章:
-[k8s(十四)、RBAC权限控制](https://blog.upweto.top/2018/12/06/k8s(%E5%8D%81%E5%9B%9B)%E3%80%81RBAC%E6%9D%83%E9%99%90%E6%8E%A7%E5%88%B6.html)
+[k8s(十四)、RBAC权限控制](https://blog.wqyin.cn/2018/12/06/k8s(%E5%8D%81%E5%9B%9B)%E3%80%81RBAC%E6%9D%83%E9%99%90%E6%8E%A7%E5%88%B6.html)
diff --git a/apiServer/README.md b/apiServer/README.md
index b138769..e96b456 100644
--- a/apiServer/README.md
+++ b/apiServer/README.md
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ APIServer提供了 k8s各类资源对象的CURD/watch、认证授权、准入控
如图所示,这是创建一个资源(Pod)实例过程中,控制层面所经过的调用过程:
-
+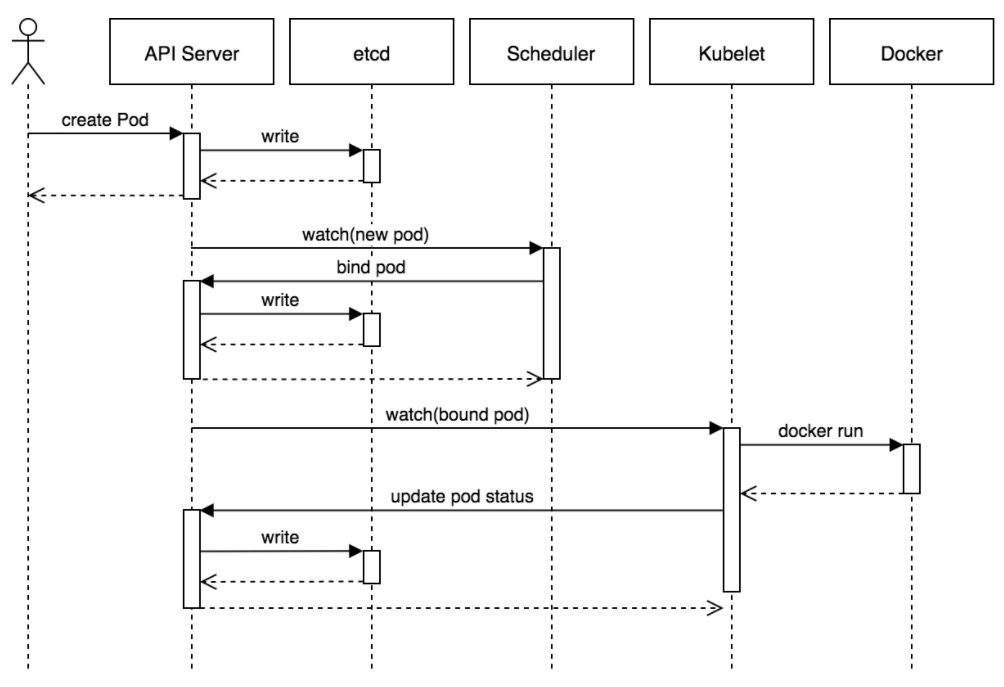
在这个过程中,控制层面的每个组件、每一步骤,都需要与APIServer交互。
diff --git a/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.md b/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.md
index 20733ca..6e87fa4 100644
--- a/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.md
+++ b/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.md
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ watch依然比较麻烦,毕竟list获取的数据以及后续watch到的数据
#### 工作流程图
-
+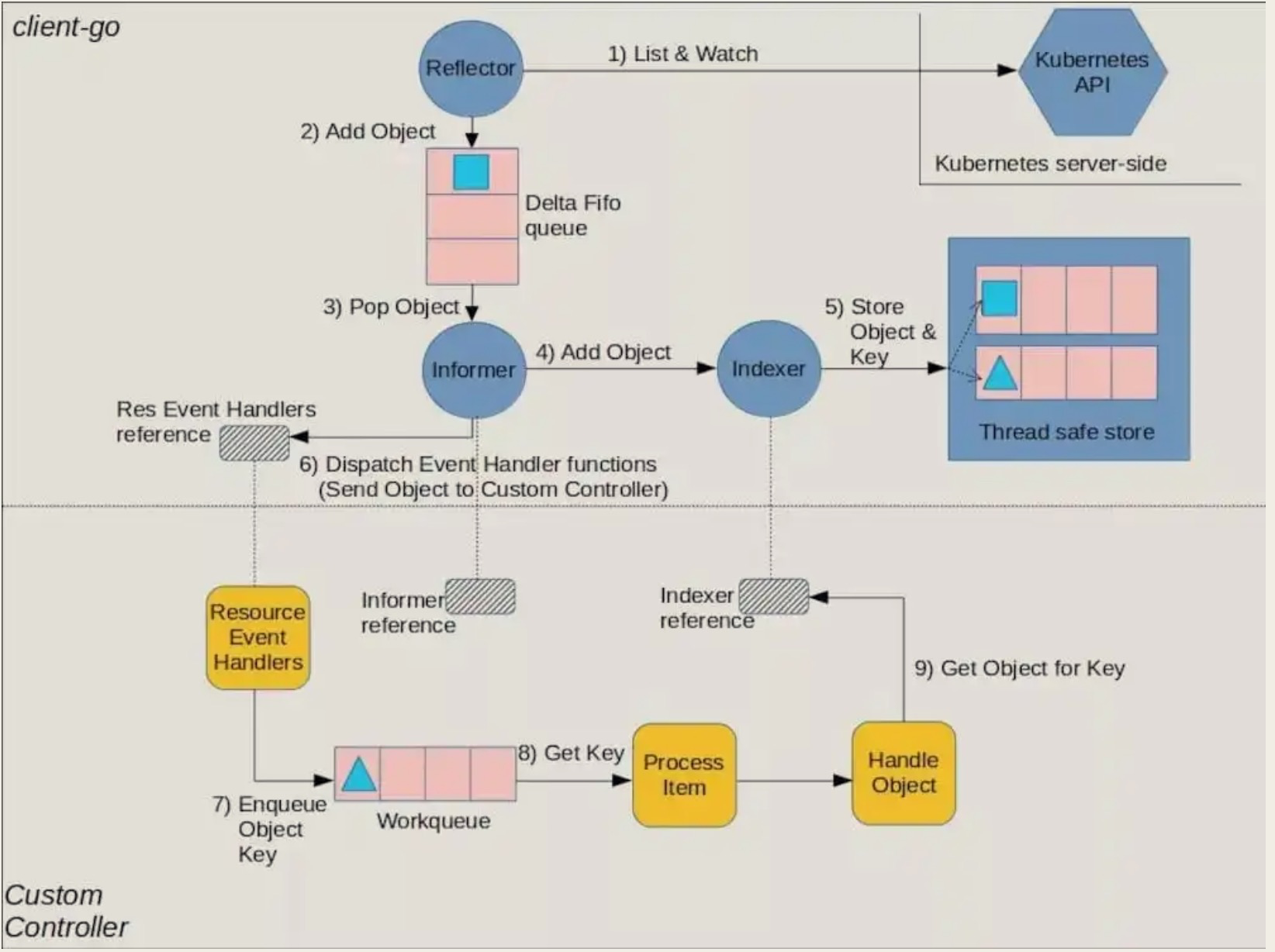
#### 流程图组件解释
diff --git a/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P3-Controller分类与Deployment Controller.md b/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P3-Controller分类与Deployment Controller.md
index 32934c6..c1c52e7 100644
--- a/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P3-Controller分类与Deployment Controller.md
+++ b/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P3-Controller分类与Deployment Controller.md
@@ -6,11 +6,11 @@
Controller部分的第一篇文章中,我们从cobra启动命令入口开始,进入到了多实例leader选举部分的代码,对leader选举流程做了详细地分析:
-[Controller-P1-多实例leader选举](https://blog.upweto.top/gitbooks/kubeSourceCodeNote/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P1-多实例leader选举.html)
+[Controller-P1-多实例leader选举](https://blog.wqyin.cn/gitbooks/kubeSourceCodeNote/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P1-多实例leader选举.html)
接着在第二篇中,文字和图解简单描述了controller是如何结合client-go模块中的informer工作的,为本篇及后面的几篇作铺垫:
-[Controller-P2-Controller与informer](https://blog.upweto.top/gitbooks/kubeSourceCodeNote/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.html)
+[Controller-P2-Controller与informer](https://blog.wqyin.cn/gitbooks/kubeSourceCodeNote/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.html)
那么本篇,就接着第一篇往下,继续看代码。
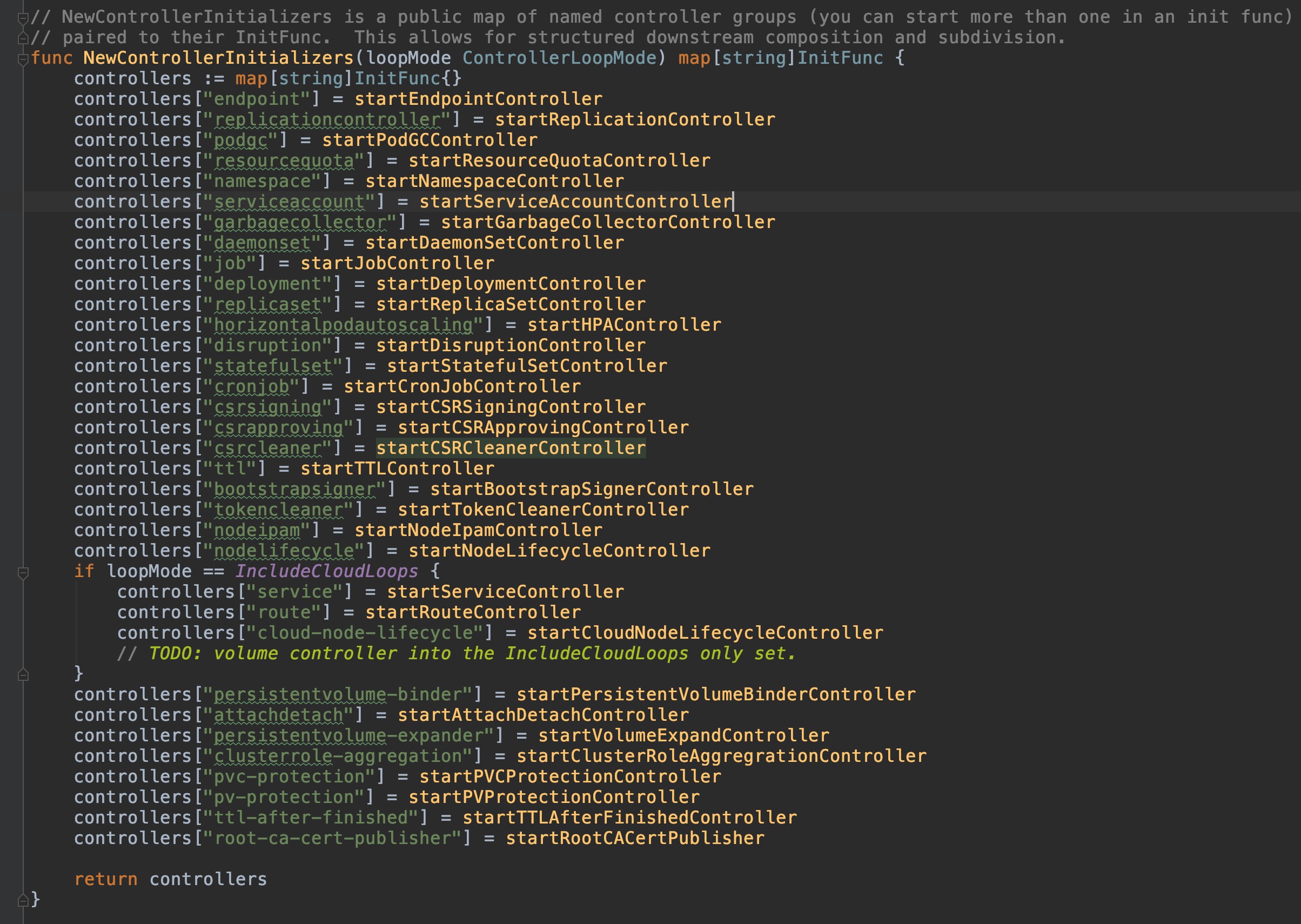
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ if err := StartControllers(controllerContext, saTokenControllerInitFunc, NewCont
==> `cmd/kube-controller-manager/app/controllermanager.go:343`
-
那么依次逐个来看看每一种Authenticator对应的AuthenticateRequest方法。
@@ -192,7 +192,7 @@ extra:
使用kubeadm默认部署的集群,就启用了requestheader的配置:
-
+
来看看AuthenticateRequest方法的代码:
@@ -500,7 +500,7 @@ SA是一种面向集群内部应用需要调用APIServer的场景所设计的认
在集群上找一个例子,以kube-proxy举例:
-
+
看看代码层面:
diff --git a/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P4-APIServer的鉴权机制.md b/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P4-APIServer的鉴权机制.md
index 7b11785..9e6b3f4 100644
--- a/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P4-APIServer的鉴权机制.md
+++ b/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P4-APIServer的鉴权机制.md
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ Kubernetes 仅审查以下 API 请求属性:
来看看现有的kubeadm部署集群启用的鉴权策略:
-
+
可以看到,默认启用了Node授权和RBAC授权模块。
@@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ DefaultResourceRuleInfo{
### 鉴权流程图
-
+
@@ -218,7 +218,7 @@ RBAC 鉴权机制使用 `rbac.authorization.k8s.io` [API 组](https://kubernetes
RBAC模式的详细描述和使用样例请参考我之前的文章:
-[k8s(十四)、RBAC权限控制](https://blog.upweto.top/2018/12/06/k8s(%E5%8D%81%E5%9B%9B)%E3%80%81RBAC%E6%9D%83%E9%99%90%E6%8E%A7%E5%88%B6.html)
+[k8s(十四)、RBAC权限控制](https://blog.wqyin.cn/2018/12/06/k8s(%E5%8D%81%E5%9B%9B)%E3%80%81RBAC%E6%9D%83%E9%99%90%E6%8E%A7%E5%88%B6.html)
diff --git a/apiServer/README.md b/apiServer/README.md
index b138769..e96b456 100644
--- a/apiServer/README.md
+++ b/apiServer/README.md
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ APIServer提供了 k8s各类资源对象的CURD/watch、认证授权、准入控
如图所示,这是创建一个资源(Pod)实例过程中,控制层面所经过的调用过程:
-
+
在这个过程中,控制层面的每个组件、每一步骤,都需要与APIServer交互。
diff --git a/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.md b/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.md
index 20733ca..6e87fa4 100644
--- a/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.md
+++ b/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.md
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ watch依然比较麻烦,毕竟list获取的数据以及后续watch到的数据
#### 工作流程图
-
+
#### 流程图组件解释
diff --git a/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P3-Controller分类与Deployment Controller.md b/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P3-Controller分类与Deployment Controller.md
index 32934c6..c1c52e7 100644
--- a/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P3-Controller分类与Deployment Controller.md
+++ b/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P3-Controller分类与Deployment Controller.md
@@ -6,11 +6,11 @@
Controller部分的第一篇文章中,我们从cobra启动命令入口开始,进入到了多实例leader选举部分的代码,对leader选举流程做了详细地分析:
-[Controller-P1-多实例leader选举](https://blog.upweto.top/gitbooks/kubeSourceCodeNote/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P1-多实例leader选举.html)
+[Controller-P1-多实例leader选举](https://blog.wqyin.cn/gitbooks/kubeSourceCodeNote/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P1-多实例leader选举.html)
接着在第二篇中,文字和图解简单描述了controller是如何结合client-go模块中的informer工作的,为本篇及后面的几篇作铺垫:
-[Controller-P2-Controller与informer](https://blog.upweto.top/gitbooks/kubeSourceCodeNote/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.html)
+[Controller-P2-Controller与informer](https://blog.wqyin.cn/gitbooks/kubeSourceCodeNote/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.html)
那么本篇,就接着第一篇往下,继续看代码。
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ if err := StartControllers(controllerContext, saTokenControllerInitFunc, NewCont
==> `cmd/kube-controller-manager/app/controllermanager.go:343`
- +
+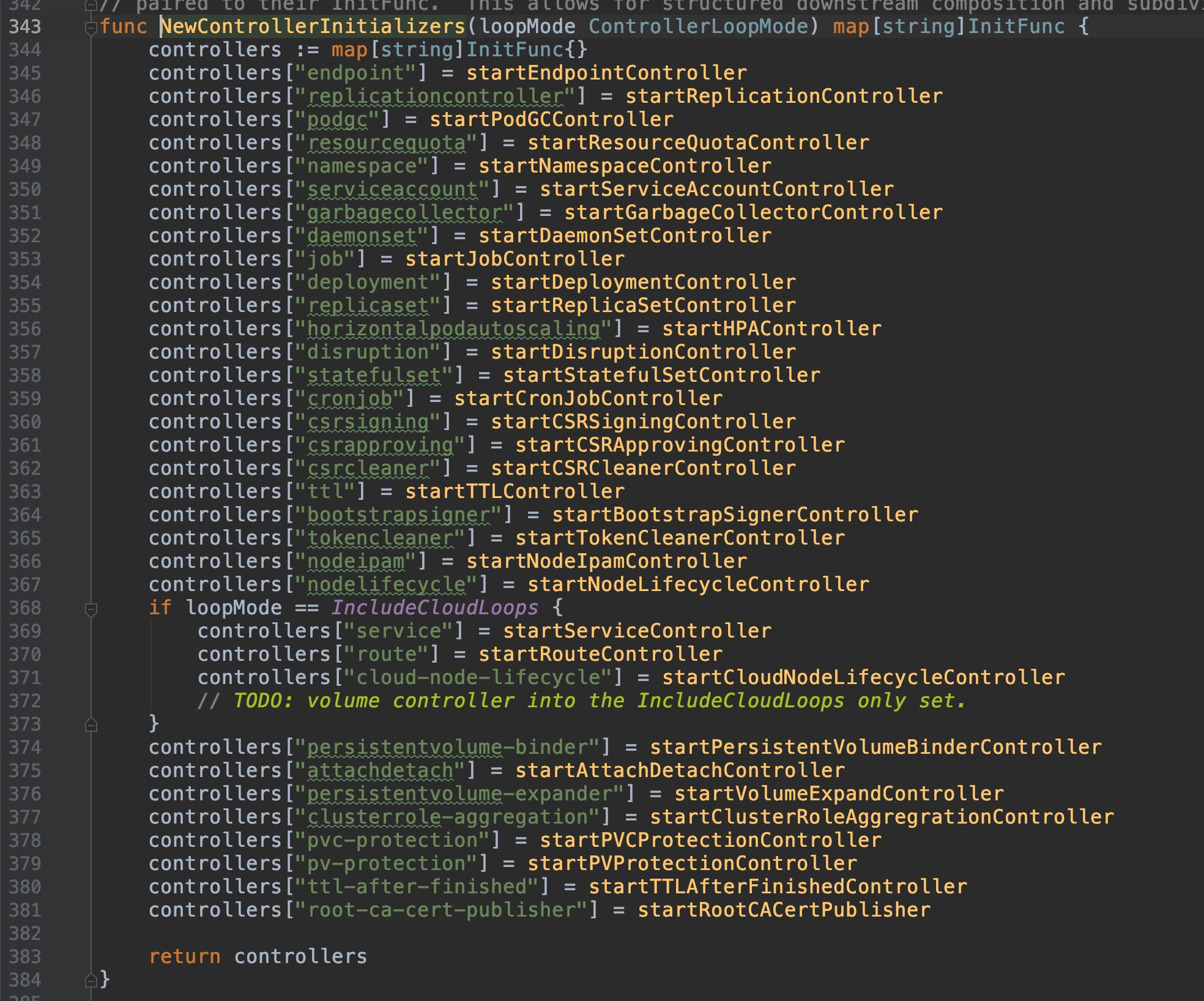 可以看到,controller会对不同的资源,分别初始化相应的controller,包含我们常见的deployment、statefulset、endpoint、pvc等等资源,controller种类有多达30余个。因此,在controller整个章节中,不会对它们逐一分析,只会抽取几个常见有代表性地进行深入,本篇就来看看deployment controller吧。
@@ -745,7 +745,7 @@ func (dc *DeploymentController) syncRolloutStatus(allRSs []*apps.ReplicaSet, new
DeploymentCondition在这里面反复出现,便于理解,参照一个正常状态的deployment condition样例:
-
可以看到,controller会对不同的资源,分别初始化相应的controller,包含我们常见的deployment、statefulset、endpoint、pvc等等资源,controller种类有多达30余个。因此,在controller整个章节中,不会对它们逐一分析,只会抽取几个常见有代表性地进行深入,本篇就来看看deployment controller吧。
@@ -745,7 +745,7 @@ func (dc *DeploymentController) syncRolloutStatus(allRSs []*apps.ReplicaSet, new
DeploymentCondition在这里面反复出现,便于理解,参照一个正常状态的deployment condition样例:
- +
+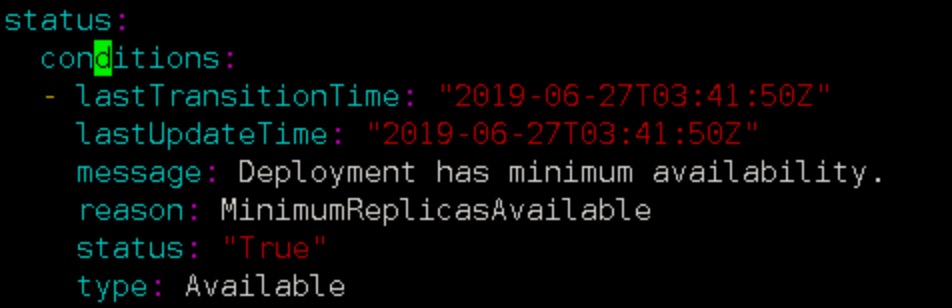 #### 总结
diff --git a/controller/README.md b/controller/README.md
index 83653e1..eeffe87 100644
--- a/controller/README.md
+++ b/controller/README.md
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ for {
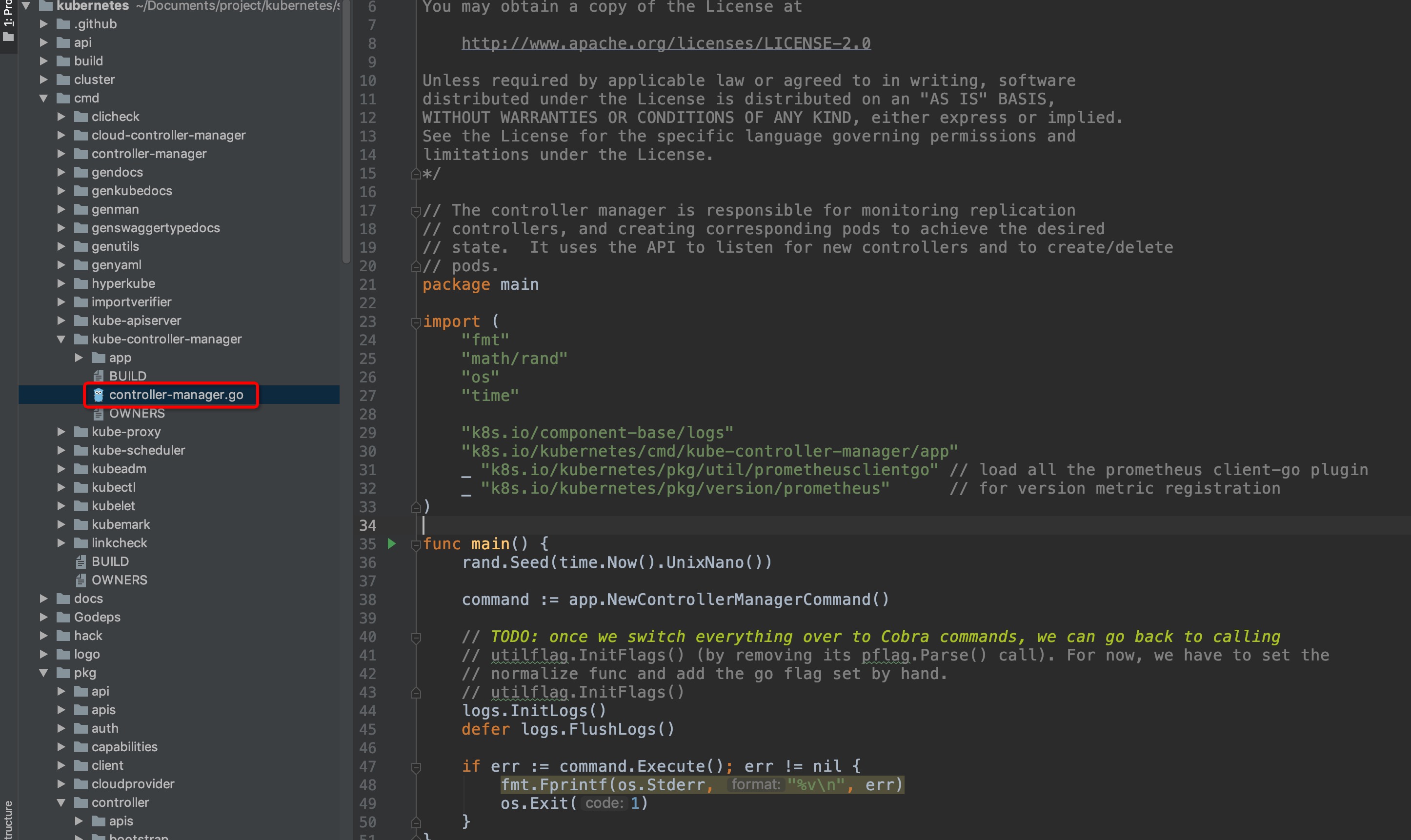
kube-controller是一个控制组件,根据我们的使用经验,有多种经常使用的资源,都不是实际地直接进行任务计算的资源类型,而在申明之后由k8s自动发现并保证以达成申明语义状态的逻辑资源,例如deployment、statefulSet、pvc、endpoint等,这些资源都分别由对应的controller子组件,那么这样的controller子组件有多少呢?如下图:
-
+
可见controller的组件数量是非常之多的,因此在本部分中计划只抽选其中的deploymentController和statefulSetController这两种常见的对pod管理类型资源对应的controller来进行源码分析。
@@ -59,11 +59,11 @@ kube-controller是一个控制组件,根据我们的使用经验,有多种
`kubernetes/src/k8s.io/kubernetes/cmd/kube-controller-manager/controller-manager.go`
-
+
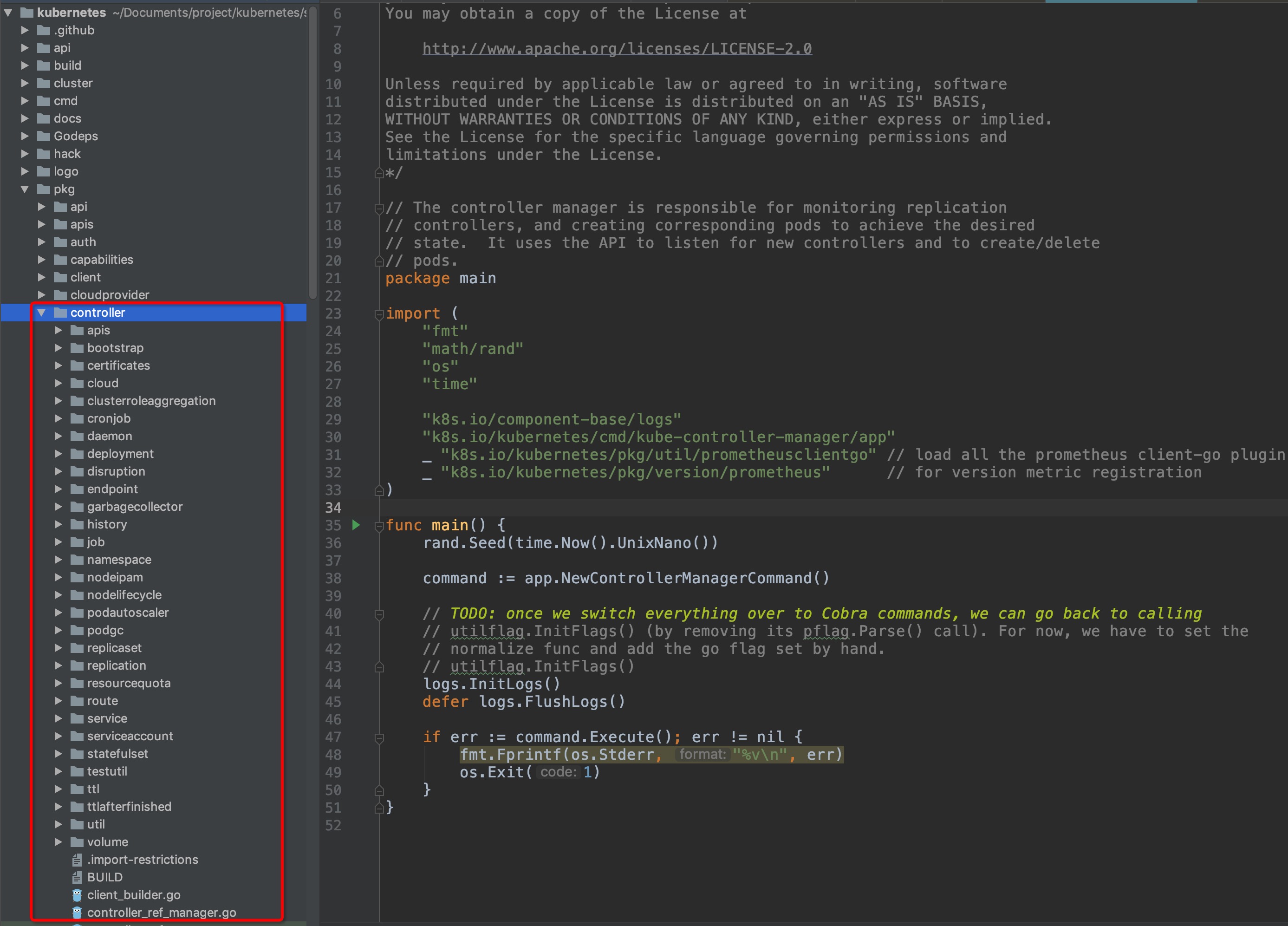
**功能模块**
`kubernetes/src/k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/controller`
-
+
diff --git a/kubelet/Kubernetes源码学习-Kubelet-P1-启动流程篇.md b/kubelet/Kubernetes源码学习-Kubelet-P1-启动流程篇.md
index adf0a47..766d974 100644
--- a/kubelet/Kubernetes源码学习-Kubelet-P1-启动流程篇.md
+++ b/kubelet/Kubernetes源码学习-Kubelet-P1-启动流程篇.md
@@ -768,7 +768,9 @@ func startKubelet(k kubelet.Bootstrap, podCfg *config.PodConfig, kubeCfg *kubele
}
```
-wait.Until()循环执行函数前面的文章中已经分析过多次了,不再赘述,来分析一下k.Run(podCfg.Updates())传的实参是什么:
+wait.Until()循环执行函数前面的文章中已经分析过多次了,不再过多赘述,这里传参是period是0,说明是无间隔死循环调用k.Run()方法,体现在实际环境中kubelet运行时的表现就是:无论运行中遇到什么报错,kubelet都会持续工作。
+
+来分析一下k.Run(podCfg.Updates())传的实参是什么:
--> `pkg/kubelet/config/config.go:105`
diff --git a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P1-调度器入口篇.md b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P1-调度器入口篇.md
index 6a6b3c9..d114afb 100644
--- a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P1-调度器入口篇.md
+++ b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P1-调度器入口篇.md
@@ -56,8 +56,8 @@ matebook-x-pro:local ywq$ go run main.go
# 因需要多次测试,这里所有的测试步骤就把build的步骤跳过,直接使用go run main.go进行测试
```
**我们打开IDE来查看一下testapp的代码结构:**
-
-
+
+
```
# 现在还未创建子命令,那么来创建几个试试:
@@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ add called
```
**来看看新增的子命令是怎么运行的呢?**
-
+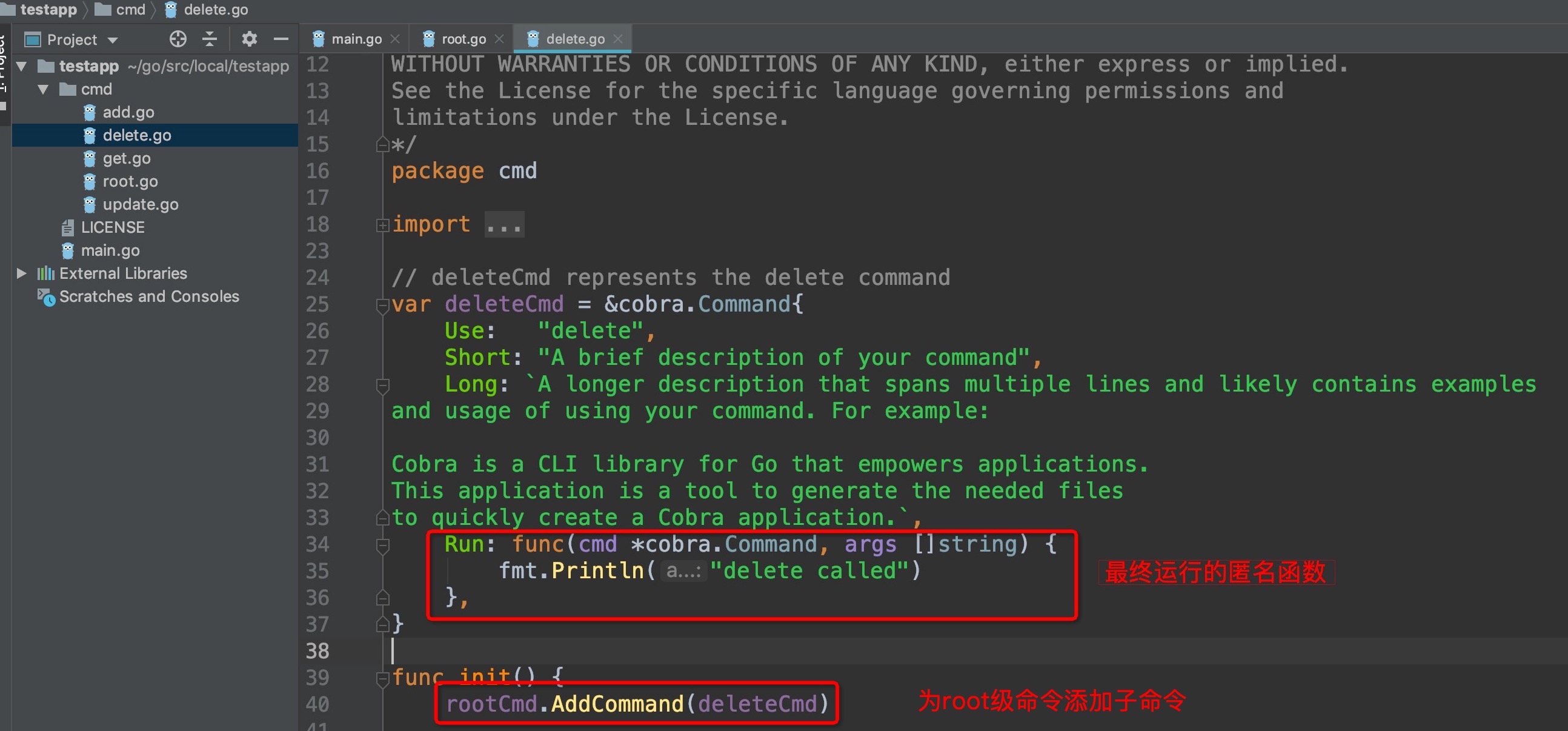
截图圈中部分可以看出,子命令是在init()函数里为root级添加了一个子命令,先不去管底层实现,接着往下.
**测试cobra的强大简洁的flag处理**
@@ -101,7 +101,7 @@ deleteCmd.PersistentFlags().StringVar(&obj,"object", "", "A function to delete a
```
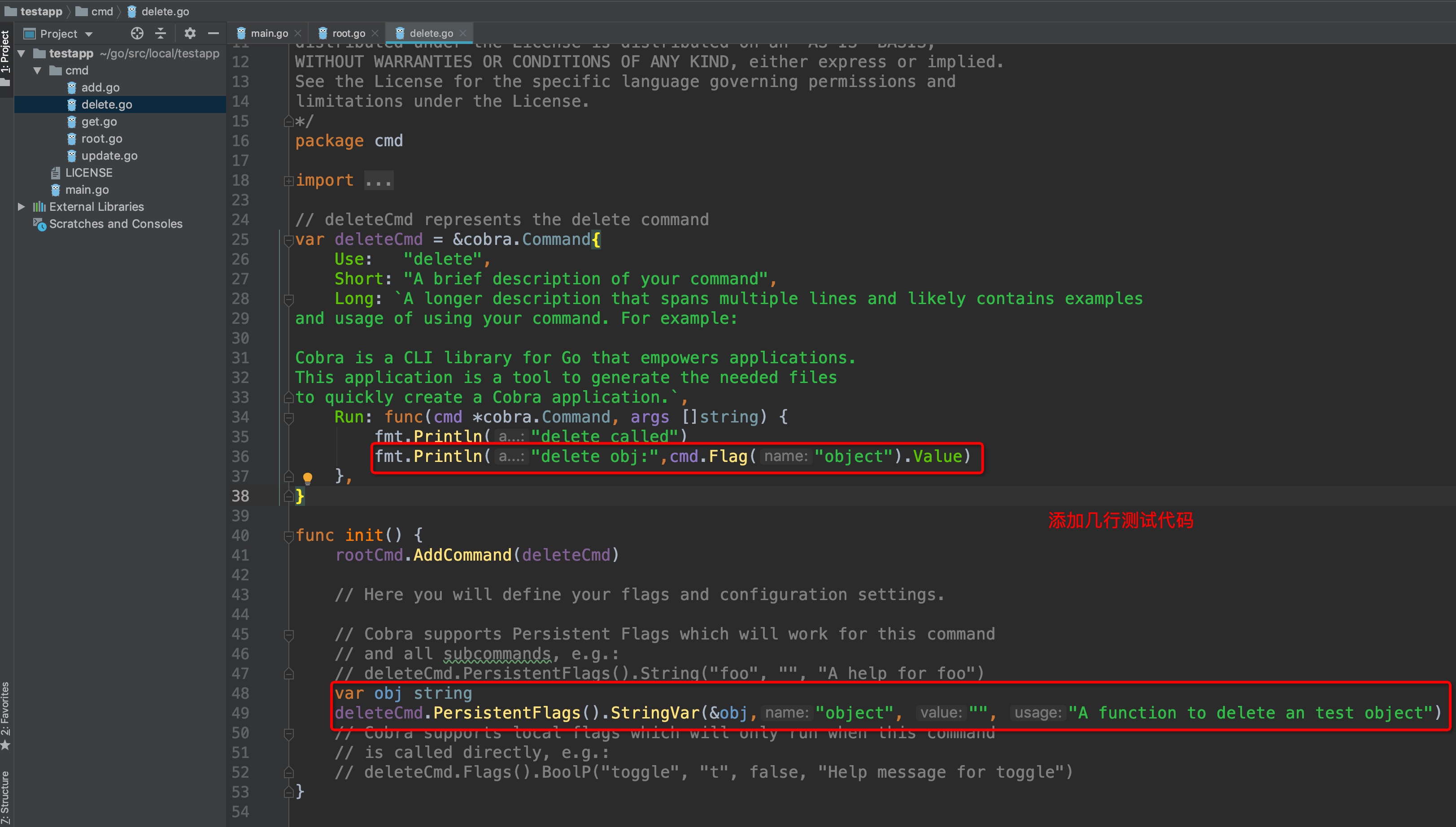
在`Run:func()`匿名函数中添加一行输出:
`fmt.Println("delete obj:",cmd.Flag("object").Value)`
-
+
运行结果:
@@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ delete obj: obj1
```
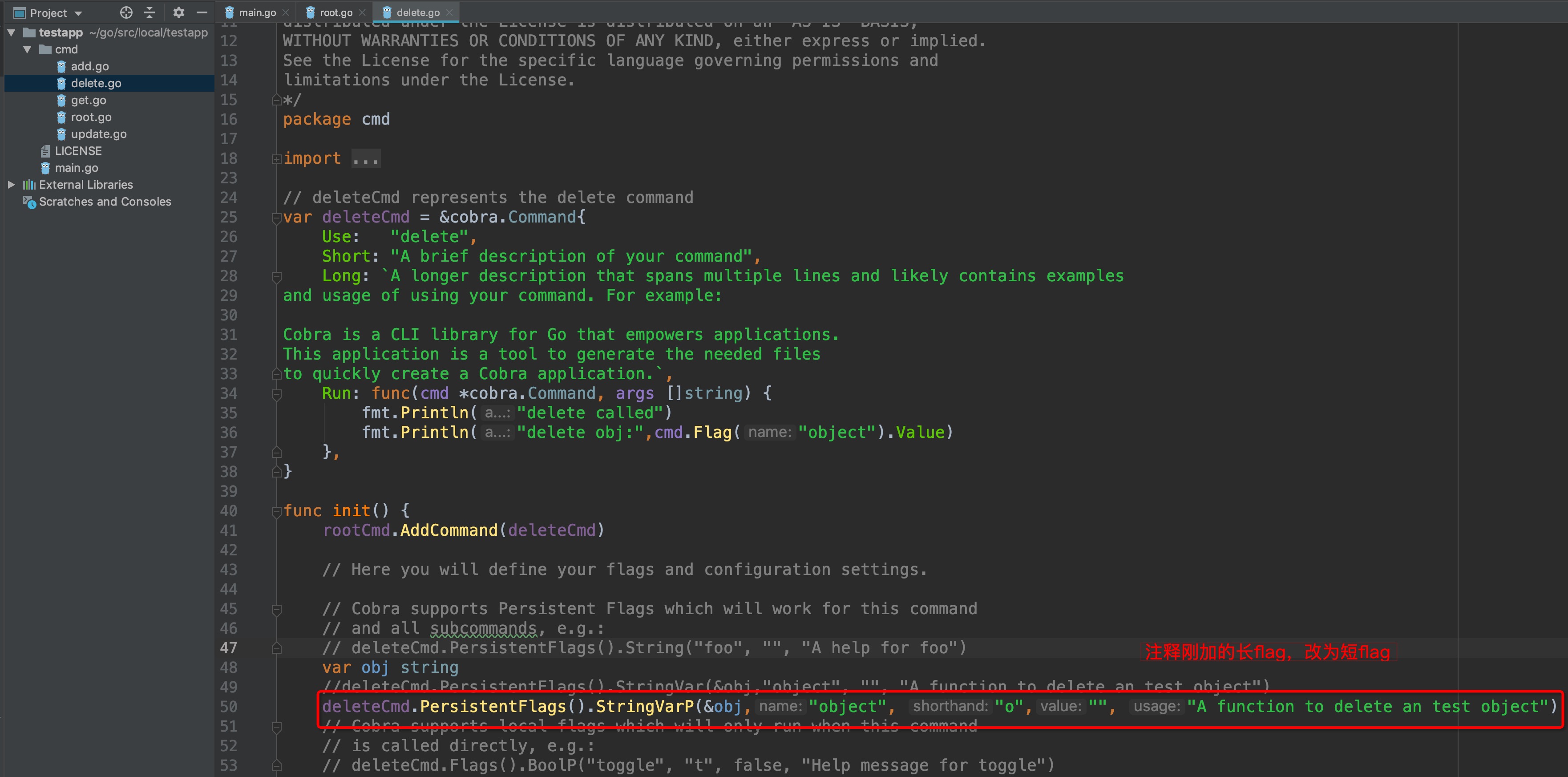
如果觉得`--`flag符号太麻烦,cobra同样支持短符号`-`flag缩写:
-
+
运行结果:
@@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ add.go delete.go get.go pods.go root.go
```
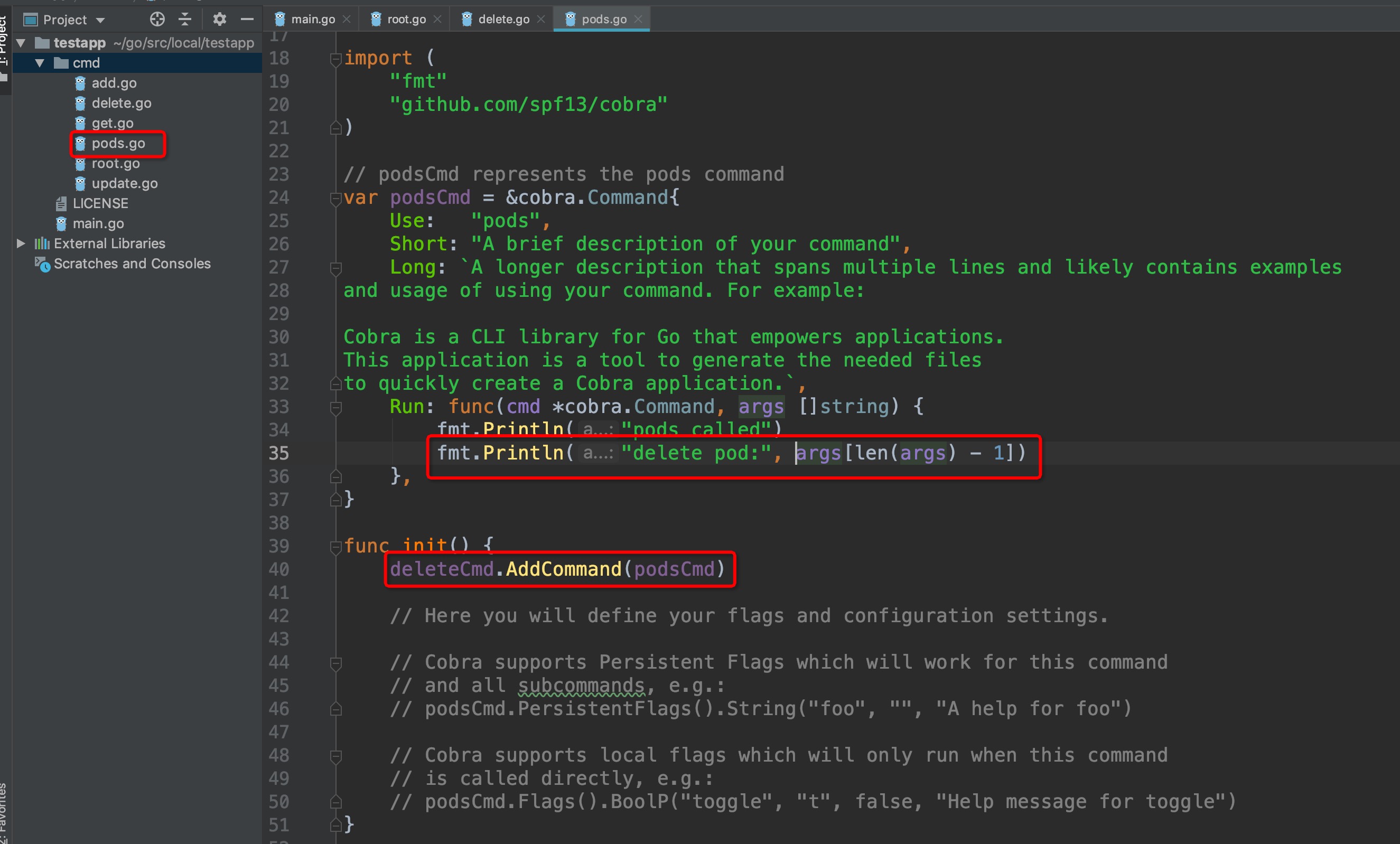
可以发现,cmd/目录下多了一个pods.go文件,我们来看看它是怎么关联上delete父级命令的,同时为它添加一行输出:
-
+
执行命令:
```
@@ -146,13 +146,13 @@ delete pods: pod1
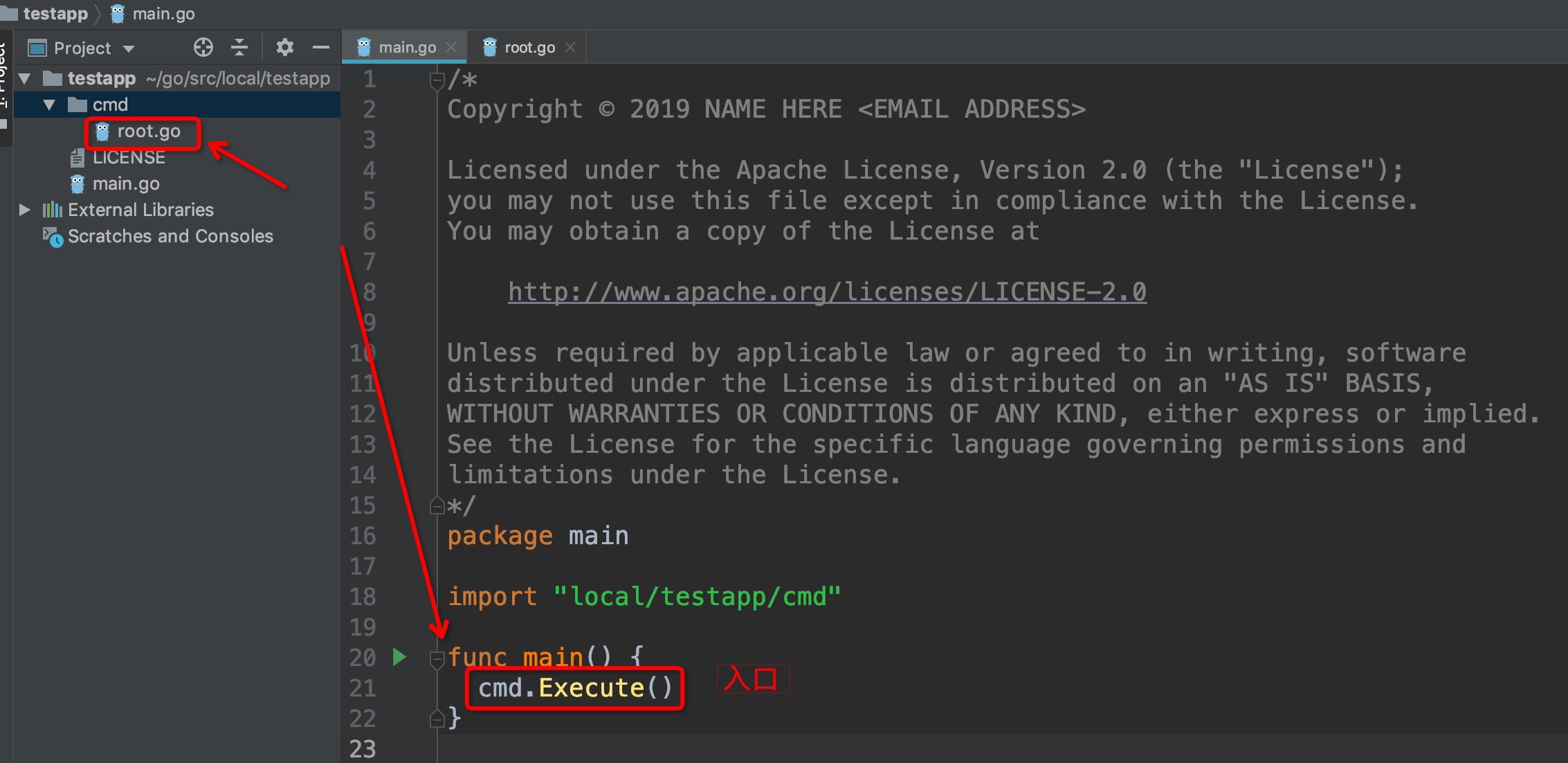
## 入口
通过对上方cobra的基本了解,我们不难知道,`cmd/kube-scheduler/scheduler.go`内的main()方法内部实际调用的是`cobra.Command.Run`内的匿名函数,我们可以进入`NewSchedulerCommand()`内部确认:
-
+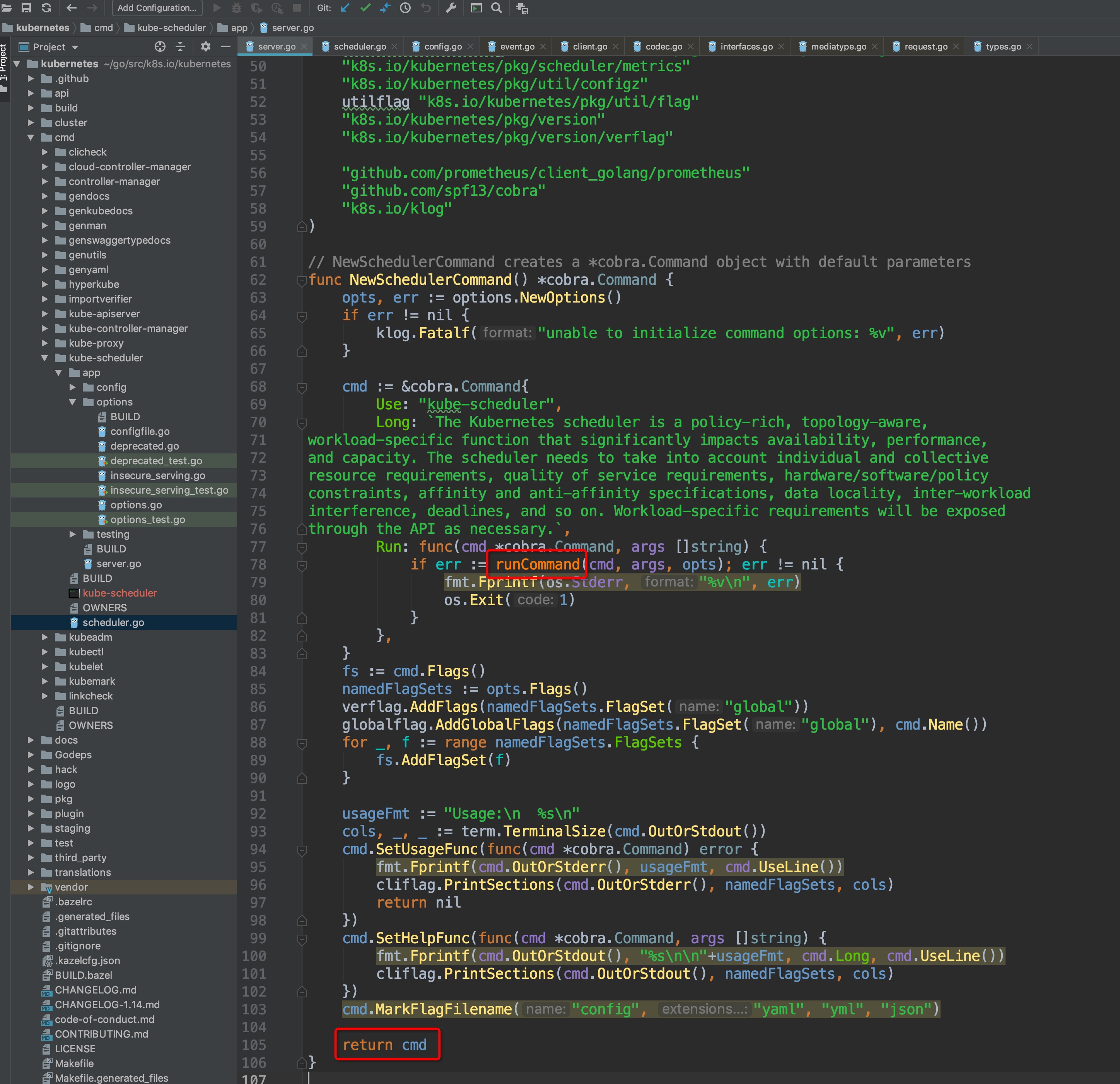
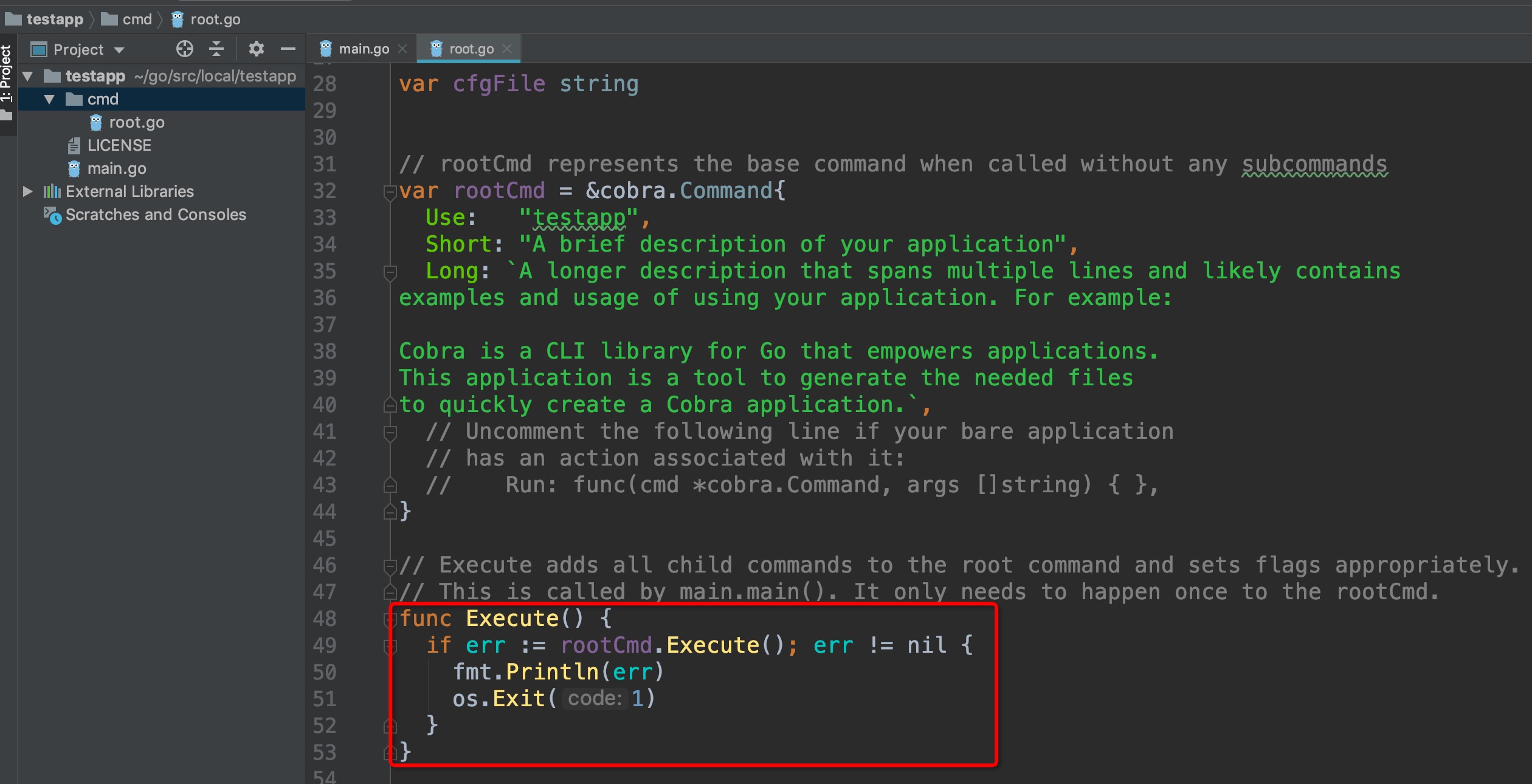
可以看到,调用了`Run`内部`runCommand`方法,再来看看Run方法内部需要重点关注的几个点:
-
+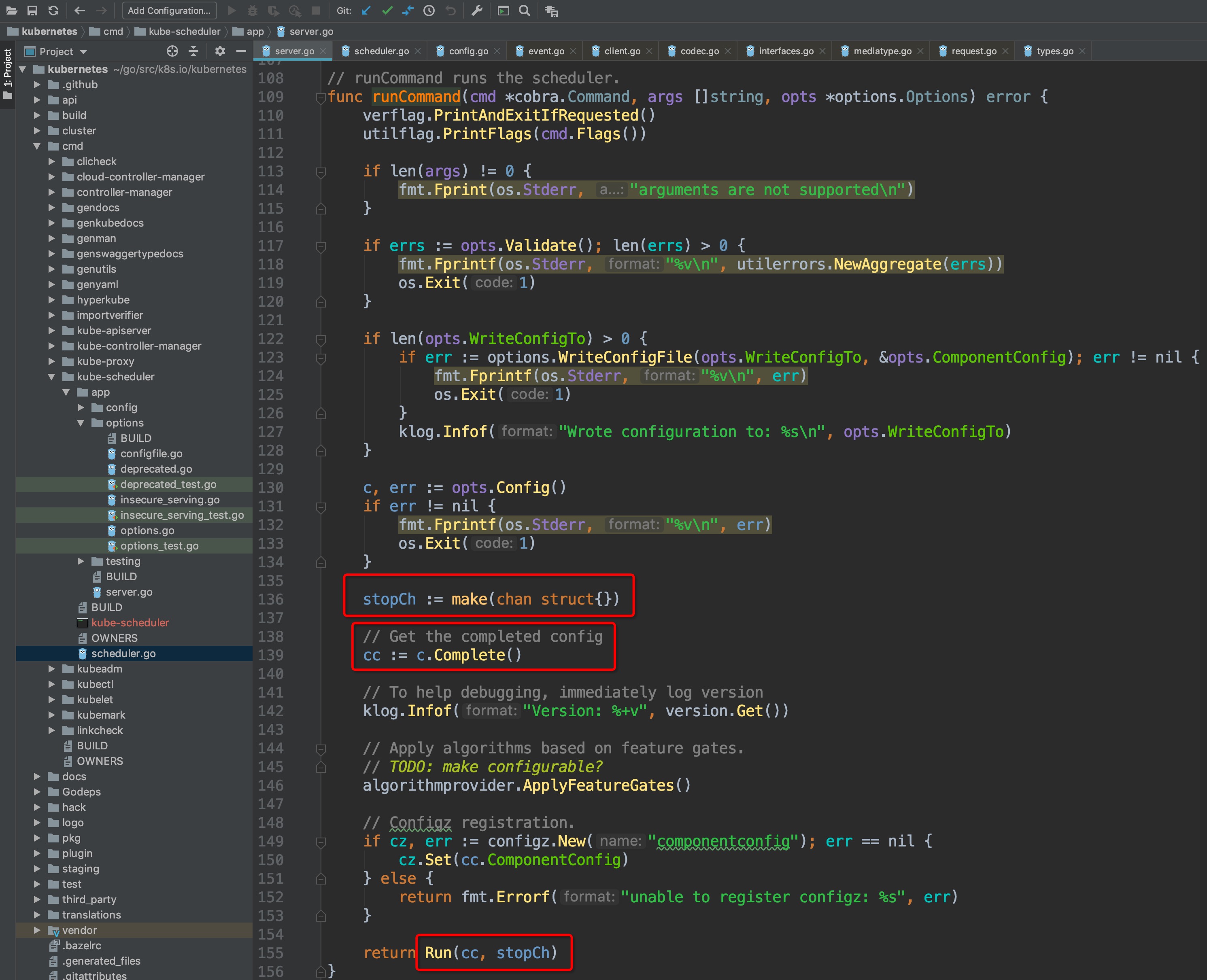
其中,上方是对命令行的参数、选项校验的步骤,跳过,重点关注两个变量:`cc和stopCh`,这两个变量会作为最后调用`Run()`方法的参数,其中`stopCh`作用是作为主程序退出的信号通知其他各协程进行相关的退出操作的,另外一个cc变量非常重要,可以点击`c.Complete()`方法,查看该方法的详情:
-
+
`Complete()`方法本质上返回的是一个Config结构体,该结构体内部的元素非常丰富,篇幅有限就不一一点开截图了,大家可以自行深入查看这些元素的作用,这里简单概括一下其中几个:
```
@@ -175,14 +175,14 @@ Recorder record.EventRecorder
Broadcaster record.EventBroadcaster
```
这里层级非常深,不便展示,Config这一个结构体非常重要,可以认真读一读代码。回到`cmd/kube-scheduler/app/server.go`.`runCommand`这里来,接着往下,进入其最后return调用的`Run()`函数中,函数中的前部分都是启动scheduler相关的组件,如event broadcaster、informers、healthz server、metric server等,重点看图中红框圈出的`sched.Run()`,这才是scheduler主程序的调用运行函数:
-
+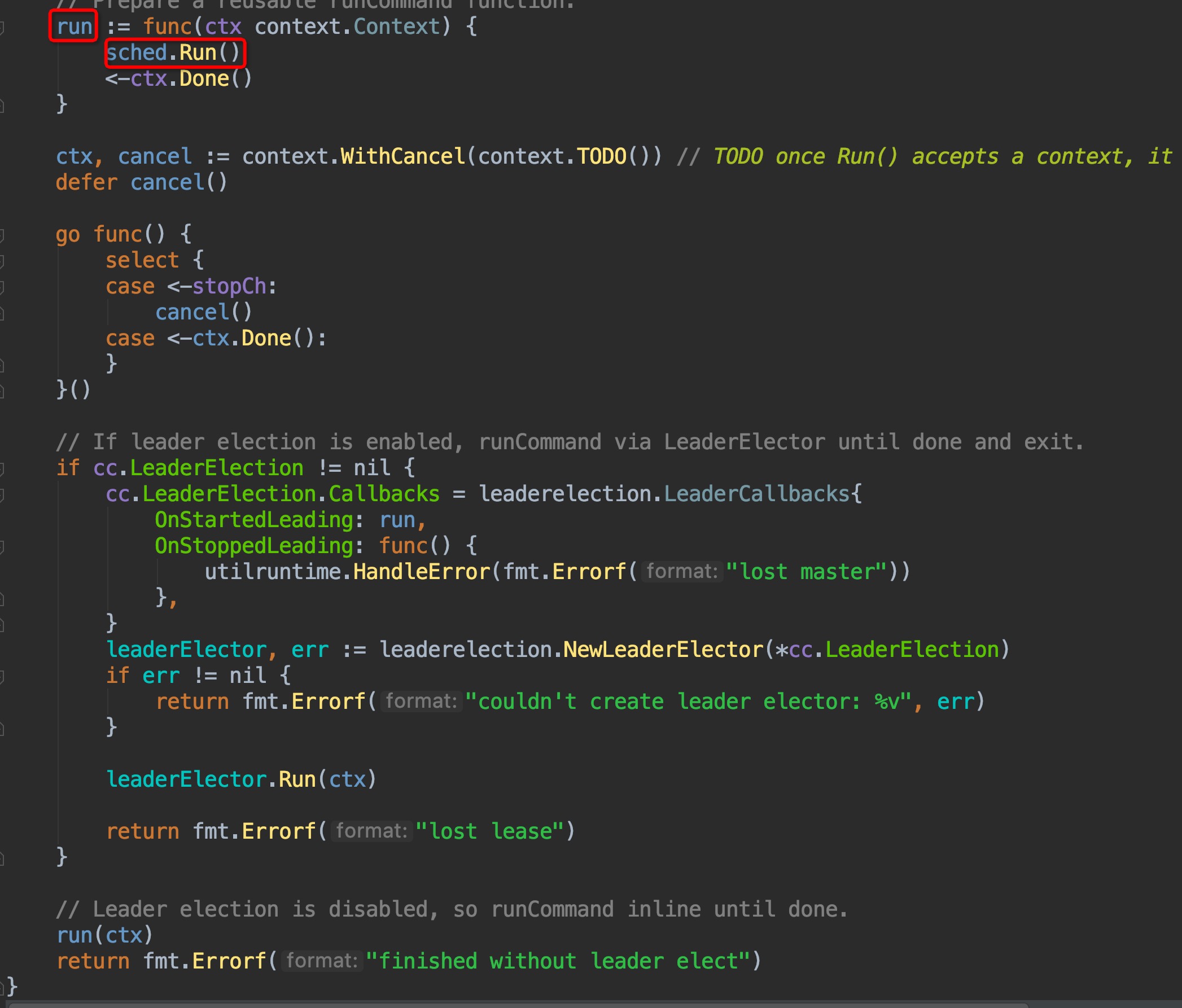
进入`sched.Run()`:
-
+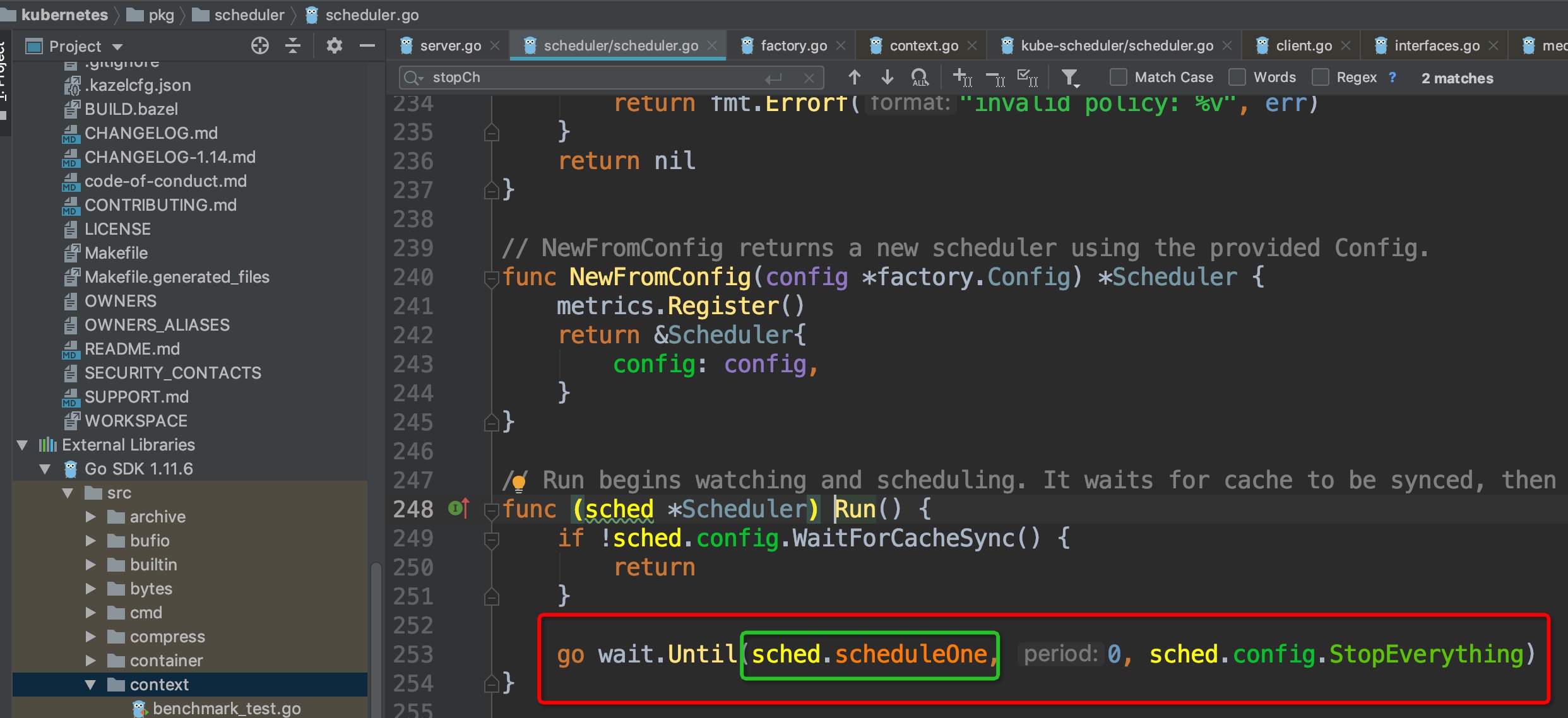
`wait.Until`这个调用的逻辑是,直到收到stop信号才终止,在此之前循环运行`sched.scheduleOne`。代码走到这里,终于找到启动入口最内部的主体啦:
-
+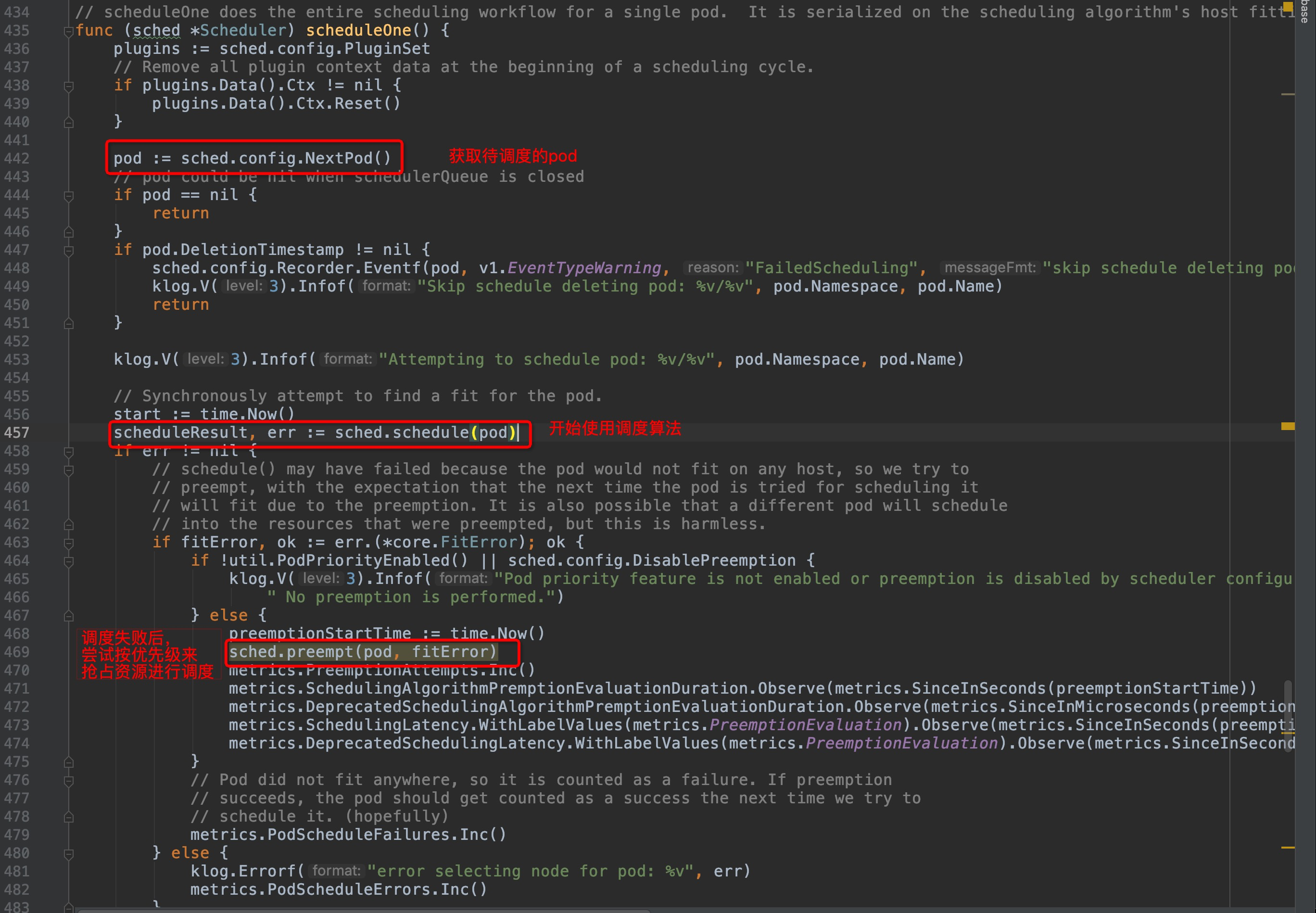
`sched.scheduleOne`这个函数有代码点长,整体的功能可以概括为:
diff --git a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P2-调度器框架.md b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P2-调度器框架.md
index d010094..fb3db33 100644
--- a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P2-调度器框架.md
+++ b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P2-调度器框架.md
@@ -12,15 +12,15 @@
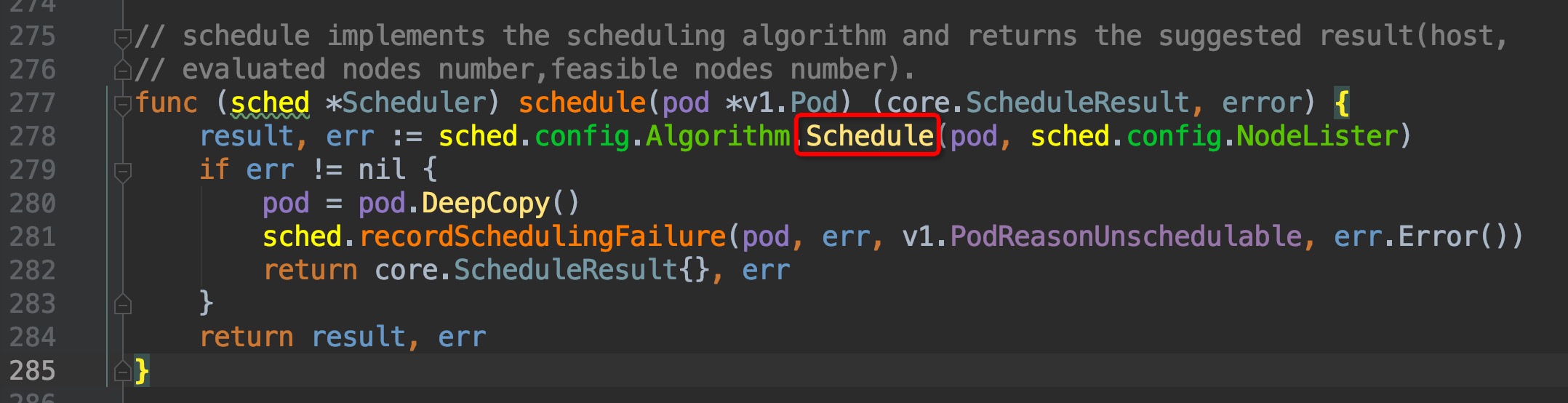
回顾上一篇篇末,我们找到了调度框架的实际调度工作逻辑的入口位置,`pkg/scheduler/scheduler.go:435`, `scheduleOne()`函数内部,定位在`pkg/scheduler/scheduler.go:457`位置,是通过这个`sched.schedule(pod)`方法来获取与pod匹配的node的,我们直接跳转2次,来到了这里`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:107`
-
+
-
+
-
+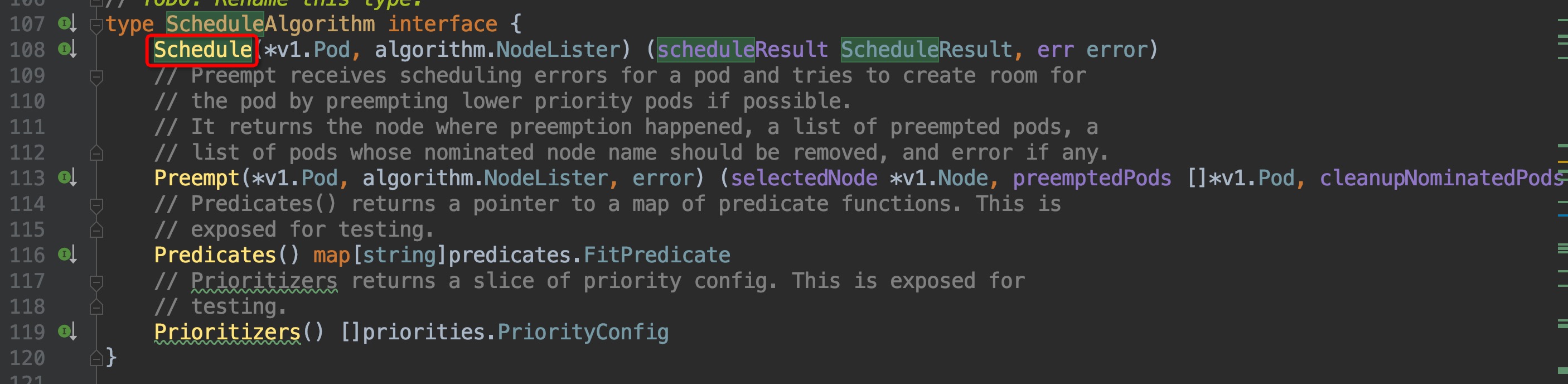
通过注释可以知道,ScheduleAlgorithm interface中的Schedule方法就是用来为pod筛选node的,但这是个接口方法,并不是实际调用的,我们稍微往下,在`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:162`这个位置,就可以找到实际调用的Schedule方法:
-
+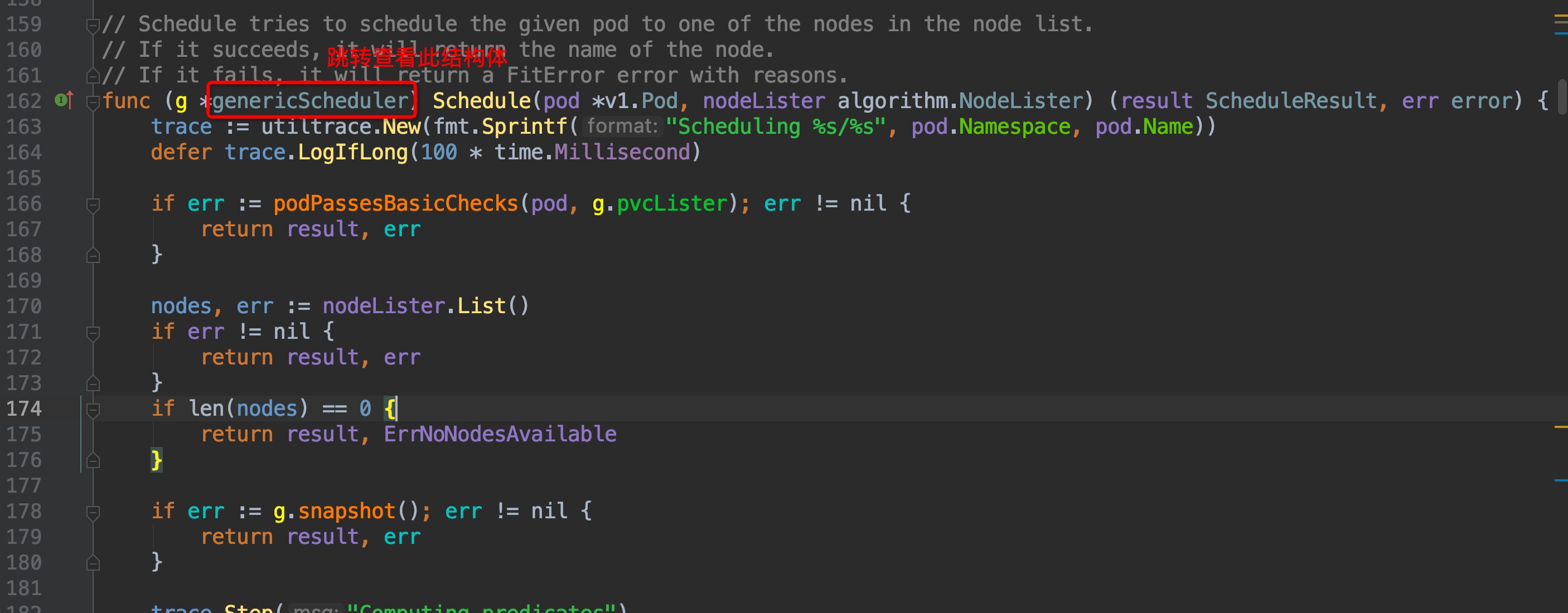
这个函数里面有4个重要的步骤:
@@ -46,41 +46,41 @@ g.selectHost(priorityList)
先来逆向回溯代码结构,找到哪里创建了scheduler,调度器的默认初始化配置,默认的调度算法来源等等框架相关的东西。`Schedule()`方法属于`genericScheduler`结构体,先查看`genericScheduler`结构体,再选中结构体名称,crtl + b组合键查看它在哪些地方被引用,找出创建结构体的位置:
-
+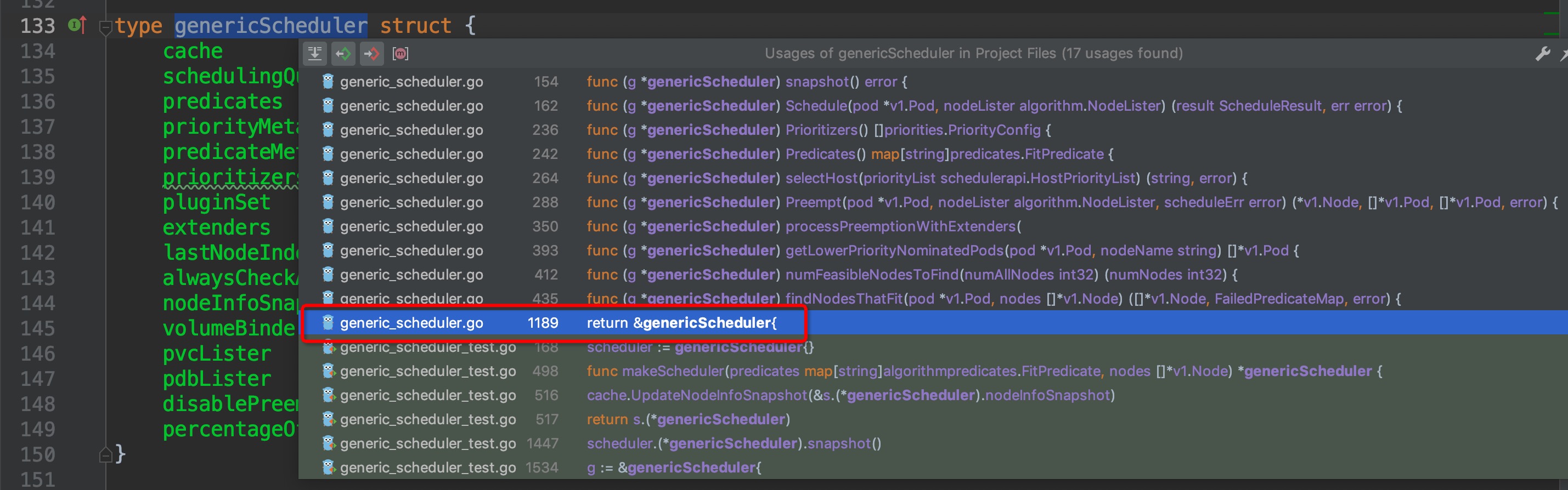
通过缩略代码框,排除test相关的测试文件,很容易找出创建结构体的地方位于`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:1189`,点击图中红框圈中位置,跳转过去,果然找到了`NewGenericScheduler()`方法,这个方法是用来创建一个`genericScheduler`对象的,那么我们再次crtl + b组合键查看`NewGenericScheduler`再什么地方被调用:
-
+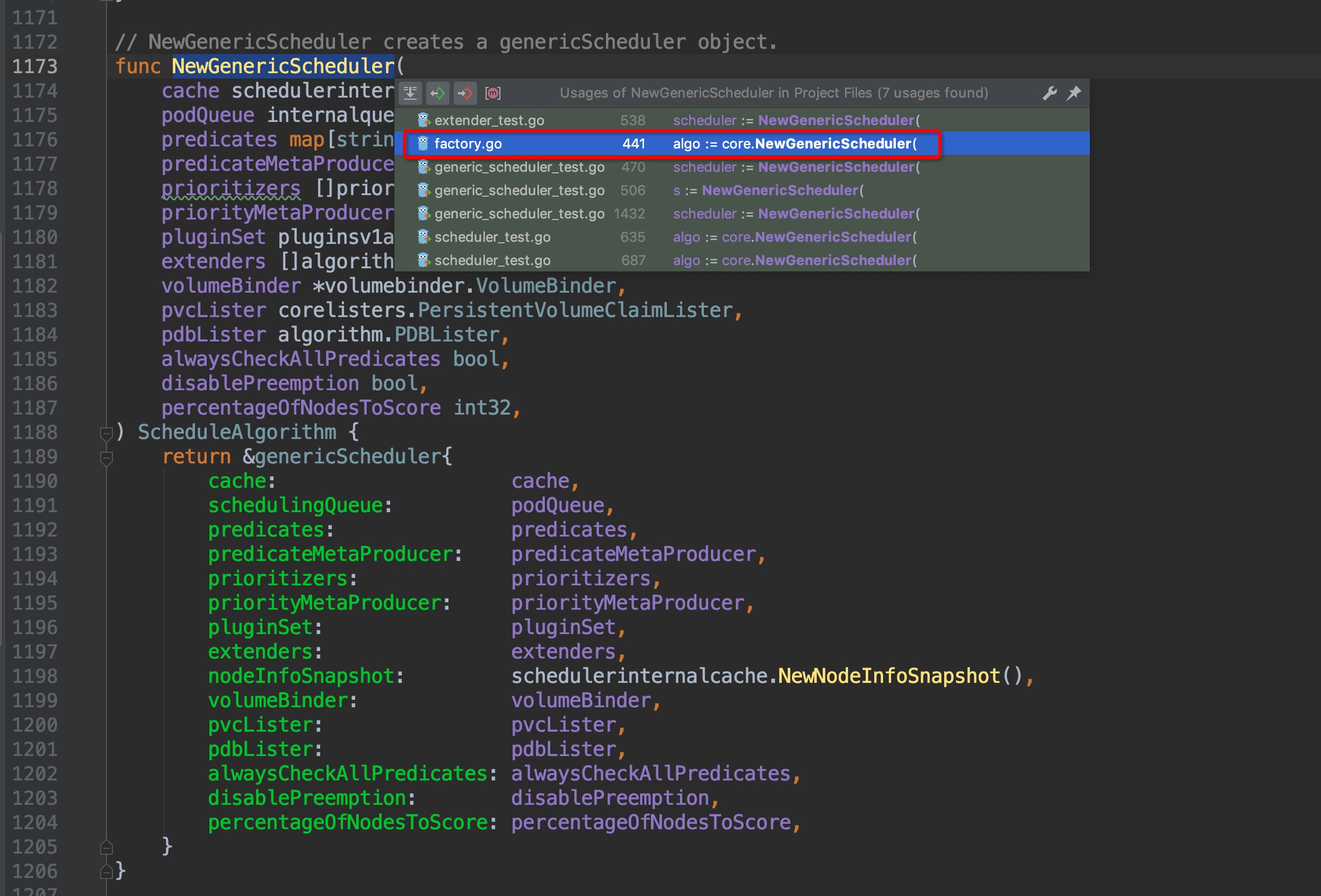
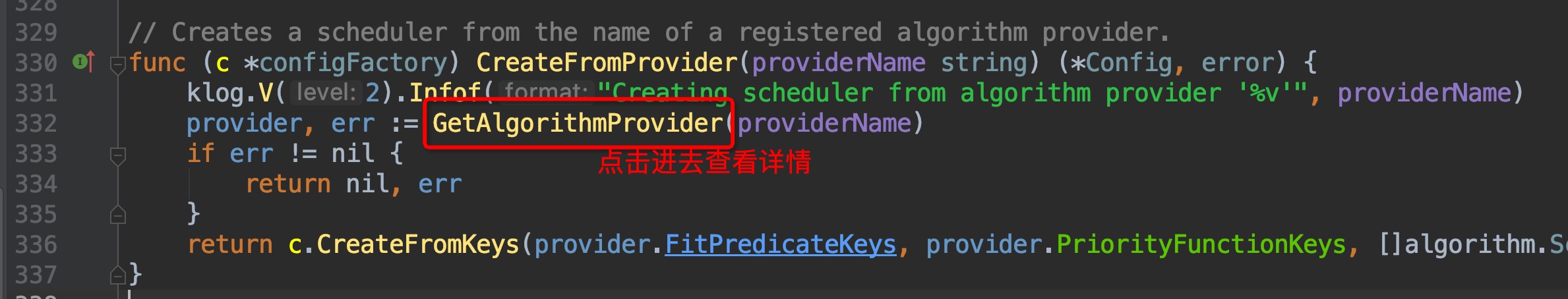
找出了在`pkg/scheduler/factory/factory.go:441`这个位置上找到了调用入口,这里位于`CreateFromKeys()`方法中,继续crtl + b查看它的引用,跳转到`pkg/scheduler/factory/factory.go:336`这个位置:
-
+
-
+
-
+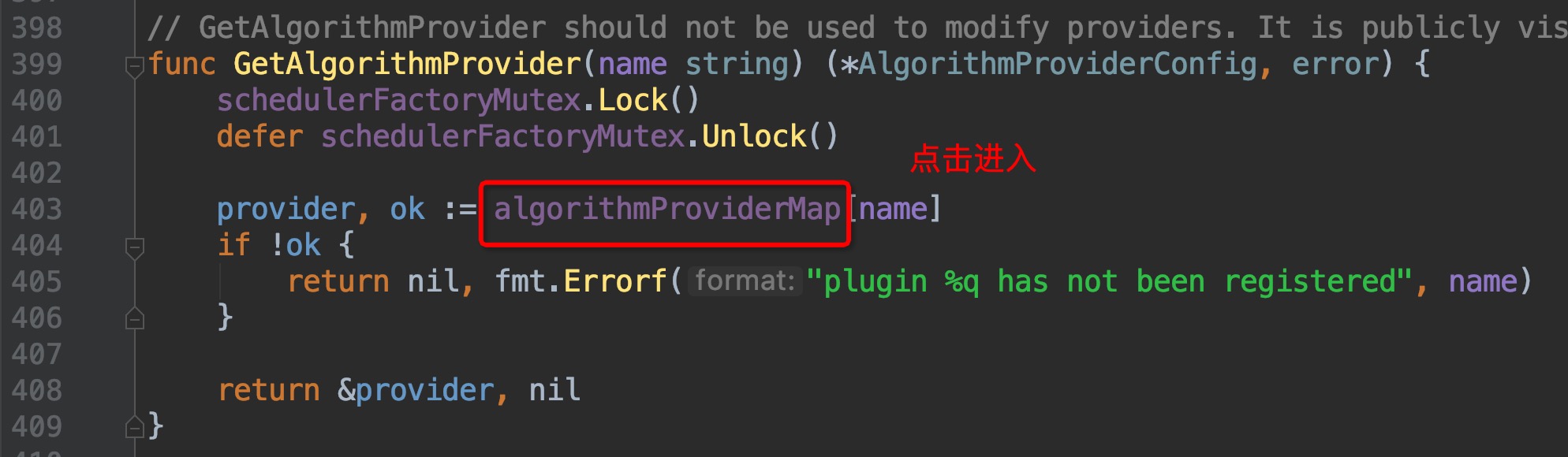
这里找到了`algorithmProviderMap`这个变量,顾名思义,这个变量里面包含的应该就是调度算法的来源,点击进去查看,跳转到了`pkg/scheduler/factory/plugins.go:86`这个位置,组合键查看引用,一眼就可以看出哪个引用为这个map添加了元素:
-
+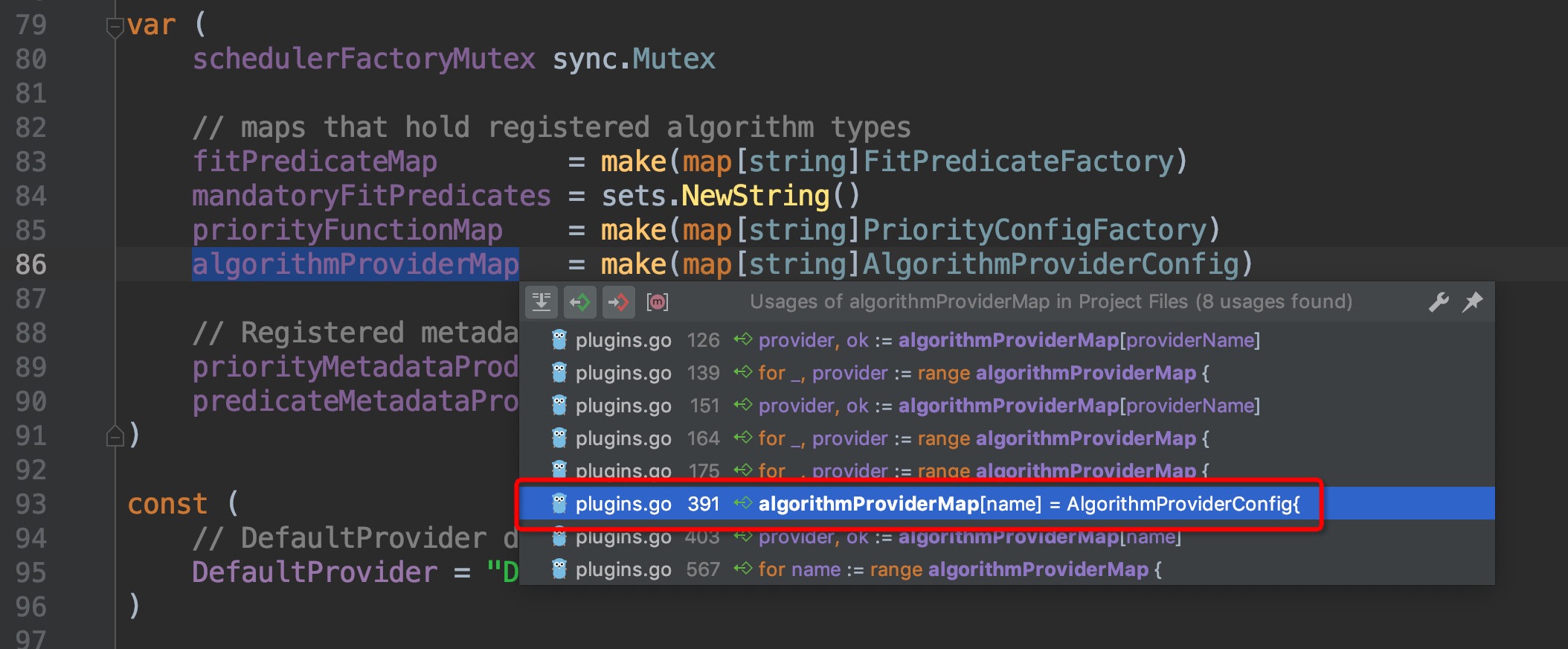
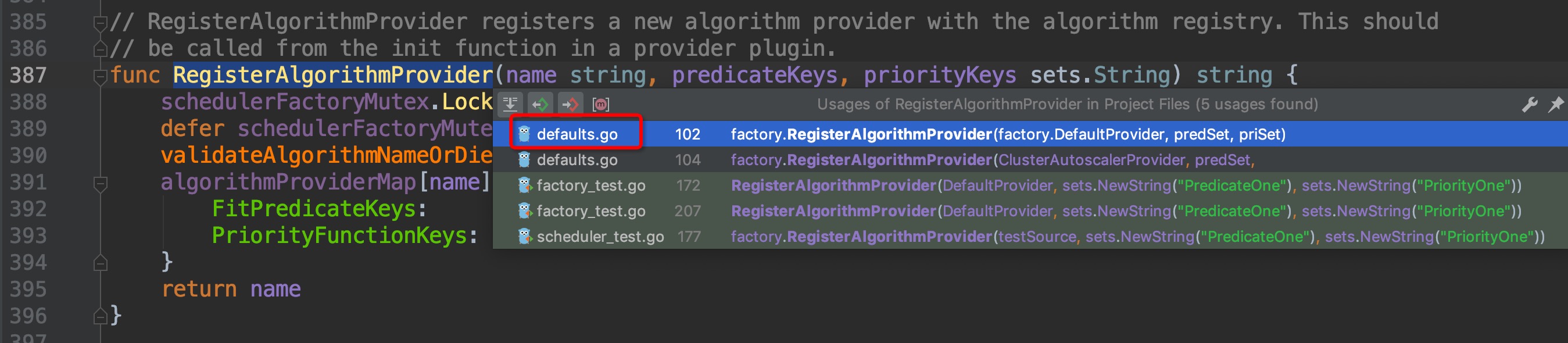
跳转过去,来到了`pkg/scheduler/factory/plugins.go:391`这个位置,这个函数的作用是为scheduler的配置指定调度算法,即`FitPredicate、Priority`这两个算法需要用到的metric或者方法,再次请出组合键,查找哪个地方调用了这个方法:
-
+
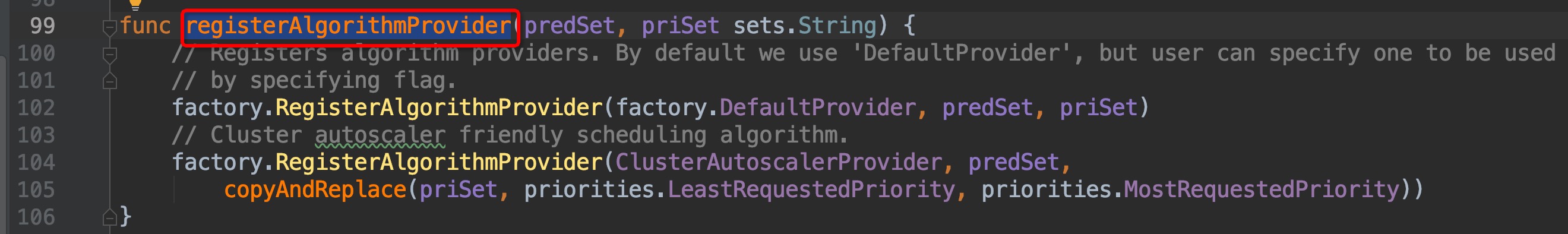
来到了`pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/defaults.go:99`,继续组合键向上查找引用,这次引用只有一个,没有弹窗直接跳转过去了`pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/defaults.go:36`:
-
+
-
+
我们来看看`defaultPredicates(), defaultPriorities()`这两个函数具体的内容:
-
+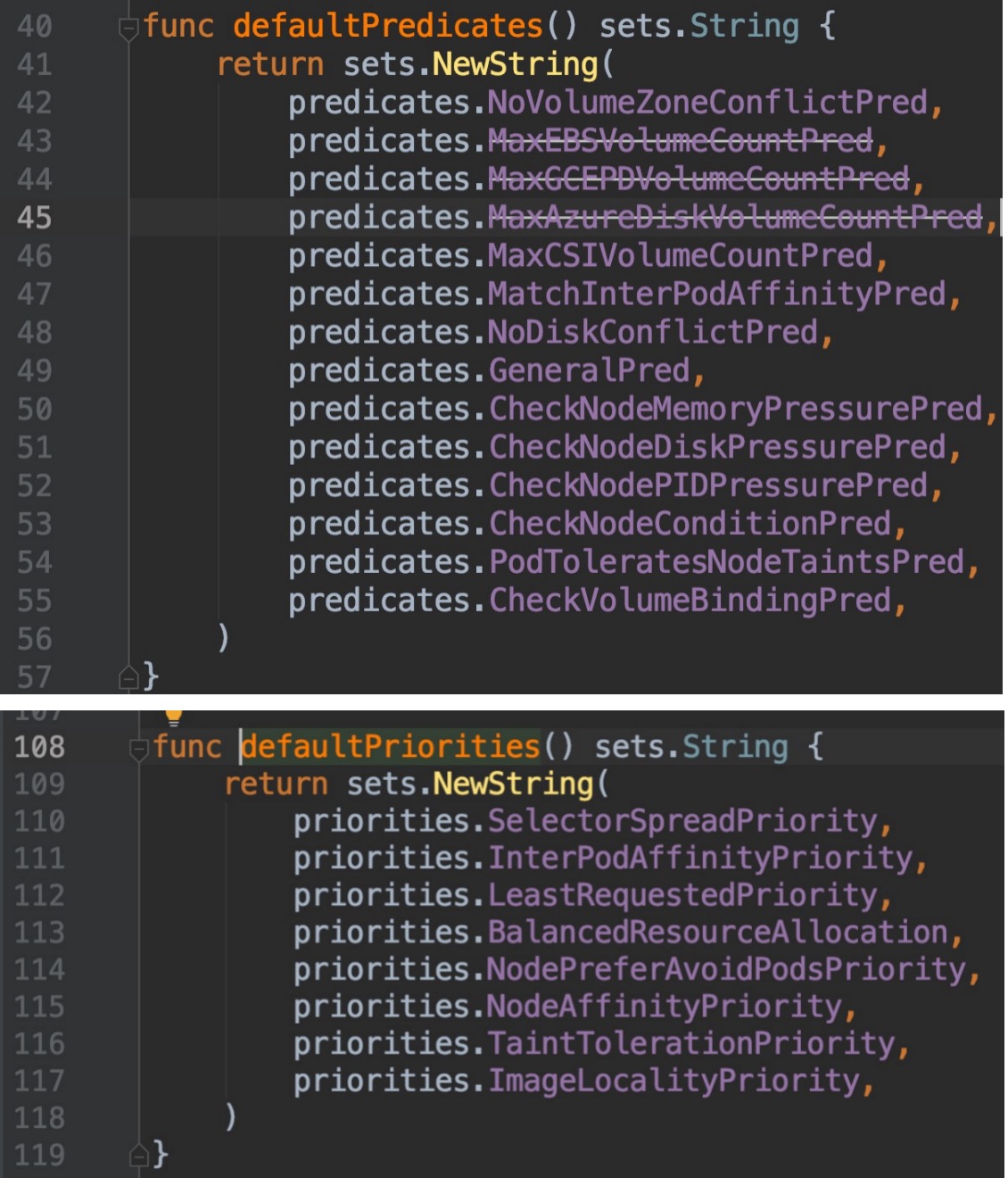
我们随便点击进去一个`predicates`选项查看其内容:
-
+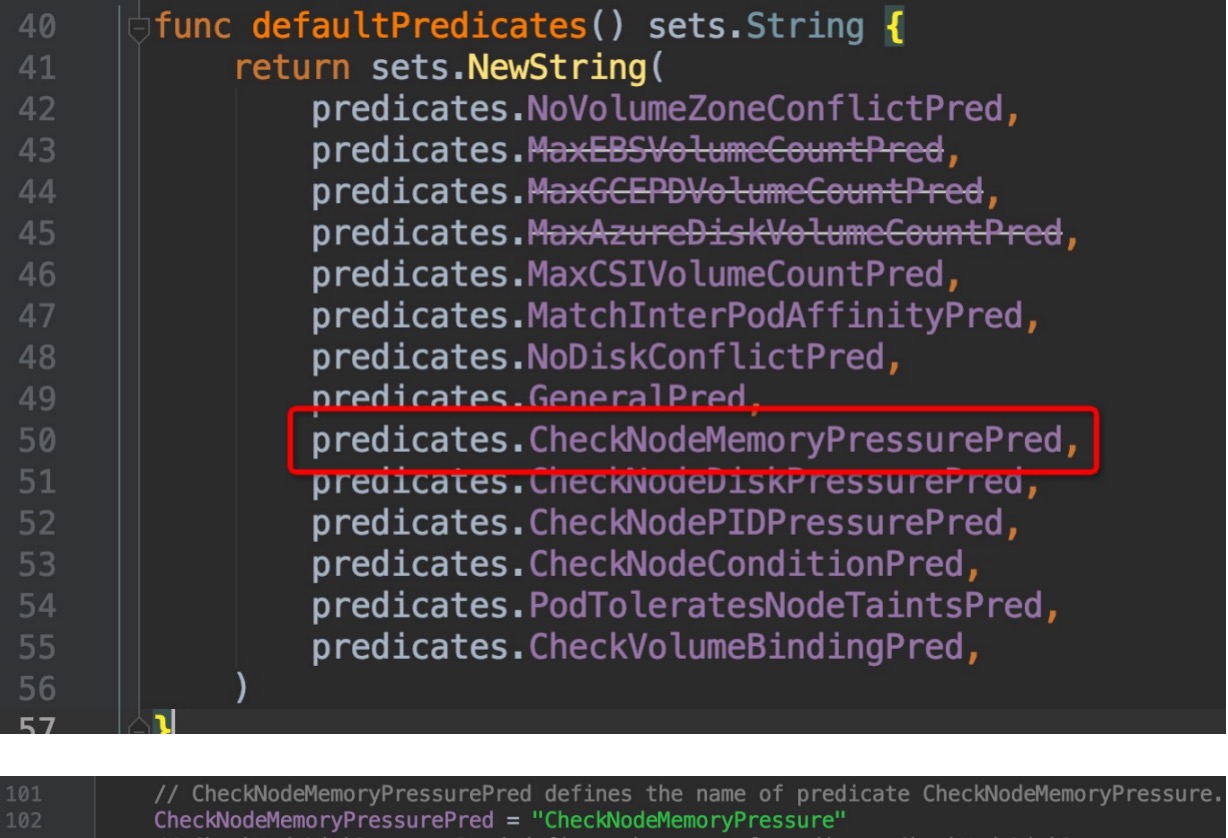
`CheckNodeMemoryPressure`这个词相应熟悉kubernetes 应用的朋友一定不会陌生,例如在node内存压力大无法调度的pod时,`kubectl describe pod xxx`就会在状态信息里面看到这个关键词。
@@ -103,7 +103,7 @@ func RegisterAlgorithmProvider(name string, predicateKeys, priorityKeys sets.Str
可以看到,这个方法为DefaultProvider绑定了配置:筛选算法和优先级排序算法的key集合,这些key只是字符串,那么是怎么具体落实到计算的方法过程上去的呢?让我们看看`pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/`目录下的`register_predicates.go,register_priorities.go`这两个文件:
-
+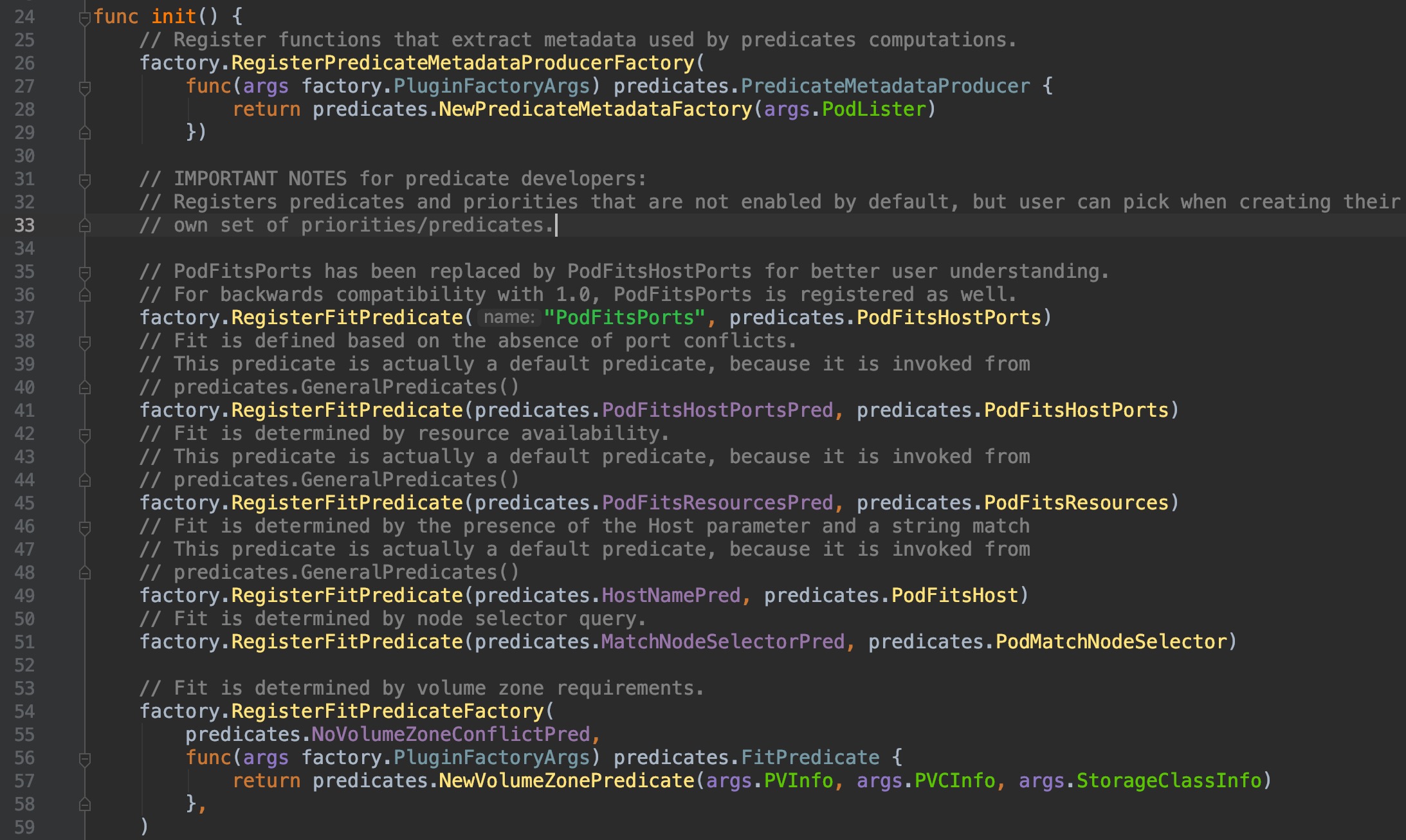
它们同样也在init()函数中初始化时使用`factory.RegisterFitPredicate()`方法做了一些注册操作,这个方法的两个参数,前一个是筛选/计算优先级 的关键key名,后一个是具体计算的功能实现方法,点击`factory.RegisterFitPredicate()`方法,深入一级,查看内部代码,
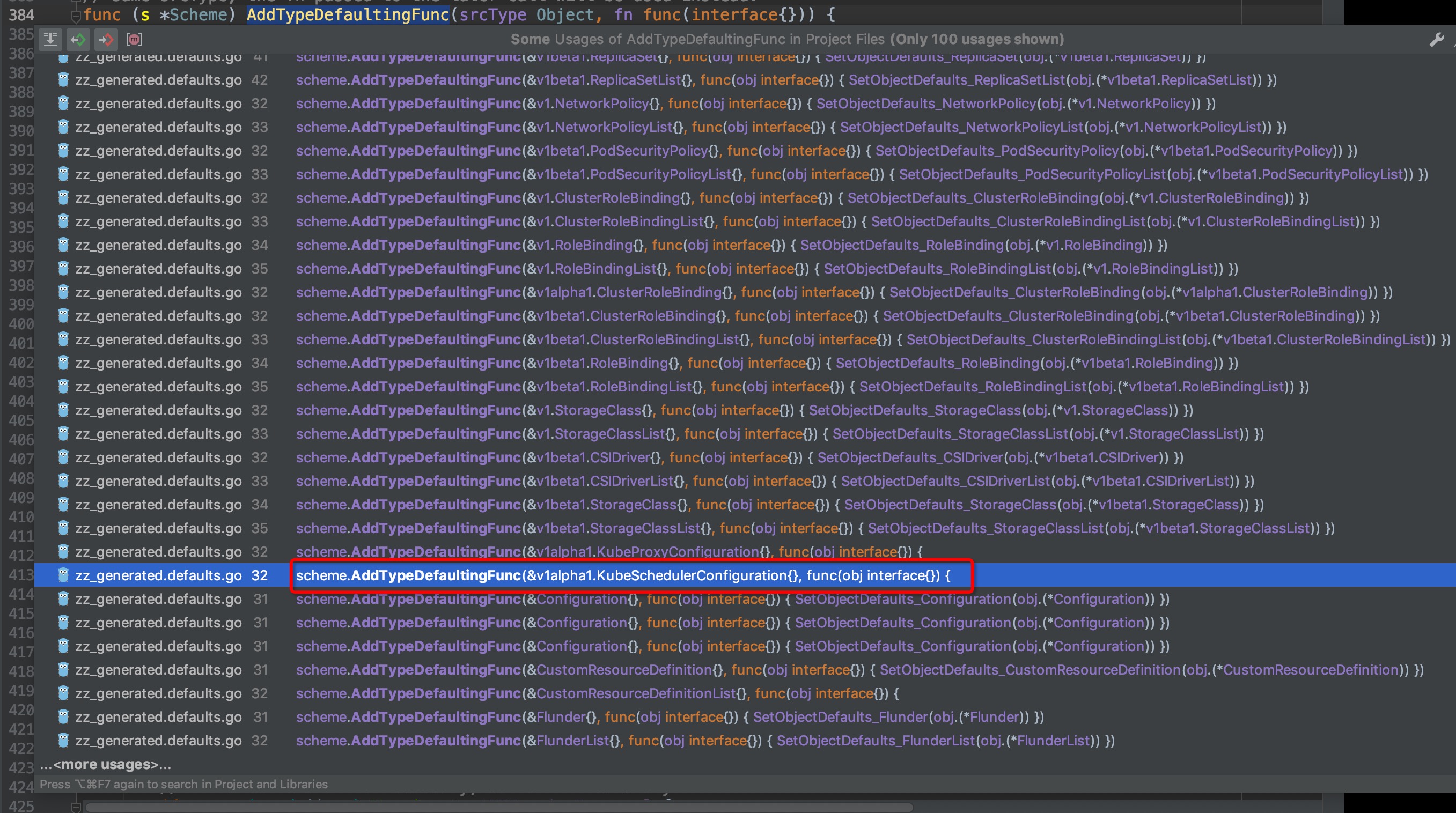
@@ -177,15 +177,15 @@ func (s *Scheme) AddTypeDefaultingFunc(srcType Object, fn func(interface{})) {
我们选中然后ctrl+b,查找AddTypeDefaultingFunc()的引用,弹窗中你可以看到有非常非常多的对象都引用了该方法,这些不同类型的对象相信无一例外都是通过Default()方法来生成默认配置的,我们找到其中的包含scheduler的方法:
-
+
跳转进去,来到了这个位置`pkg/scheduler/apis/config/v1alpha1/zz_generated.defaults.go:31`(原谅我的灵魂笔法):
-
+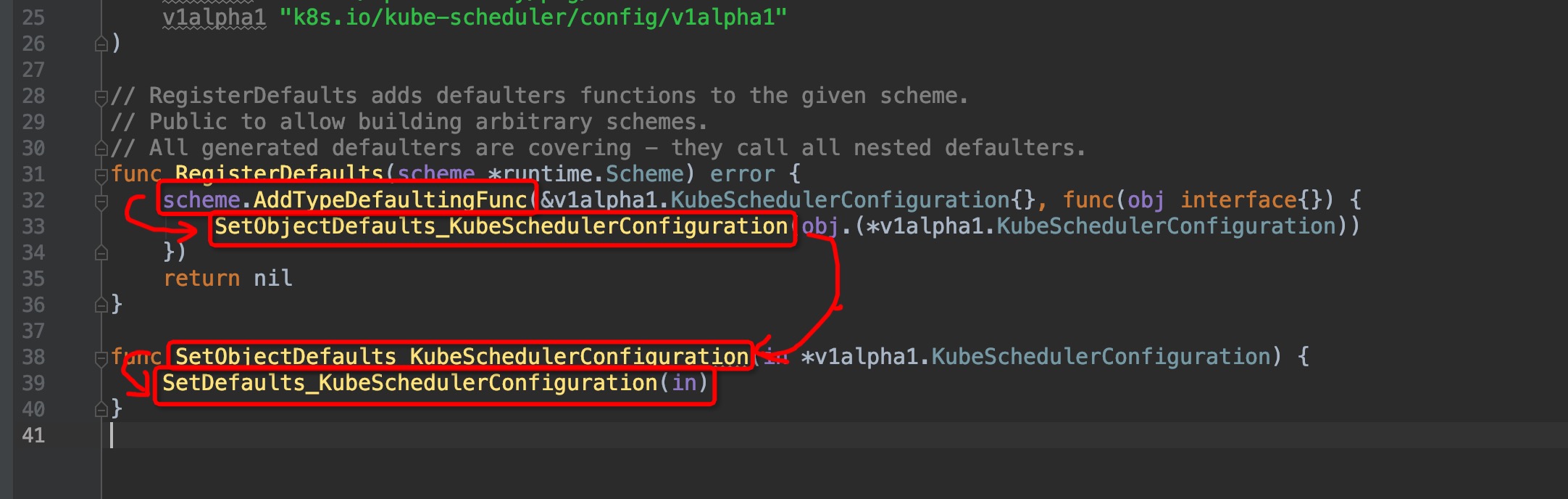
进入`SetDefaults_KubeSchedulerConfiguration()`,来到`pkg/scheduler/apis/config/v1alpha1/defaults.go:42`:
-
+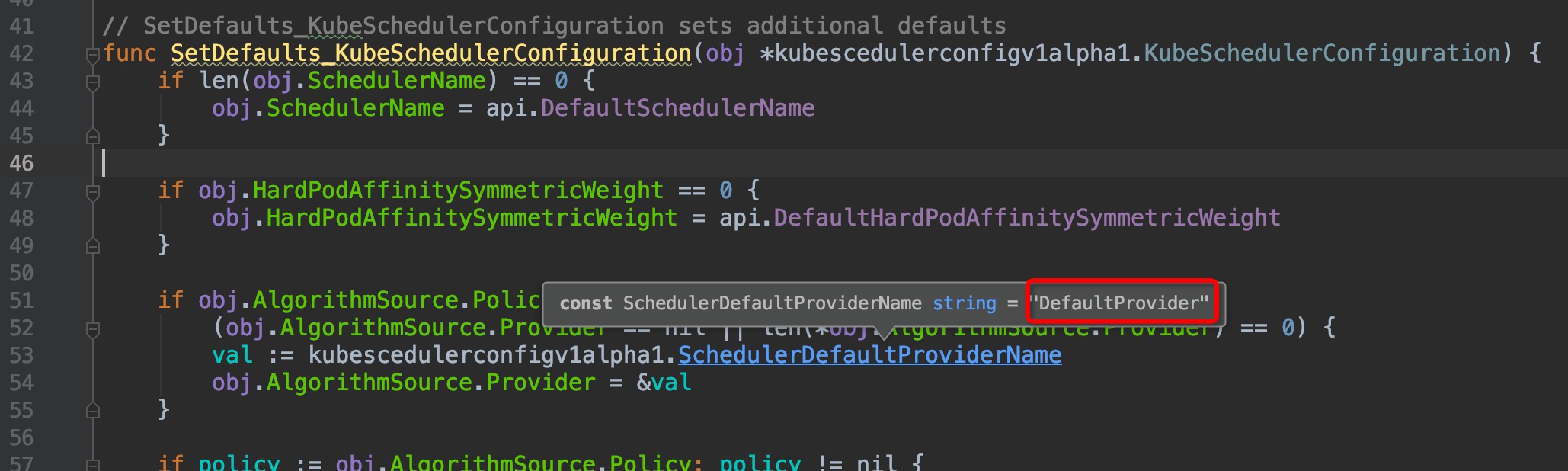
看到了`DefaultProvider`吗?是不是觉得瞬间豁然开朗,原来是在这里调用指定了scheduler配置的`AlgorithmSource.Provider`。
@@ -276,7 +276,7 @@ func podFitsOnNode(
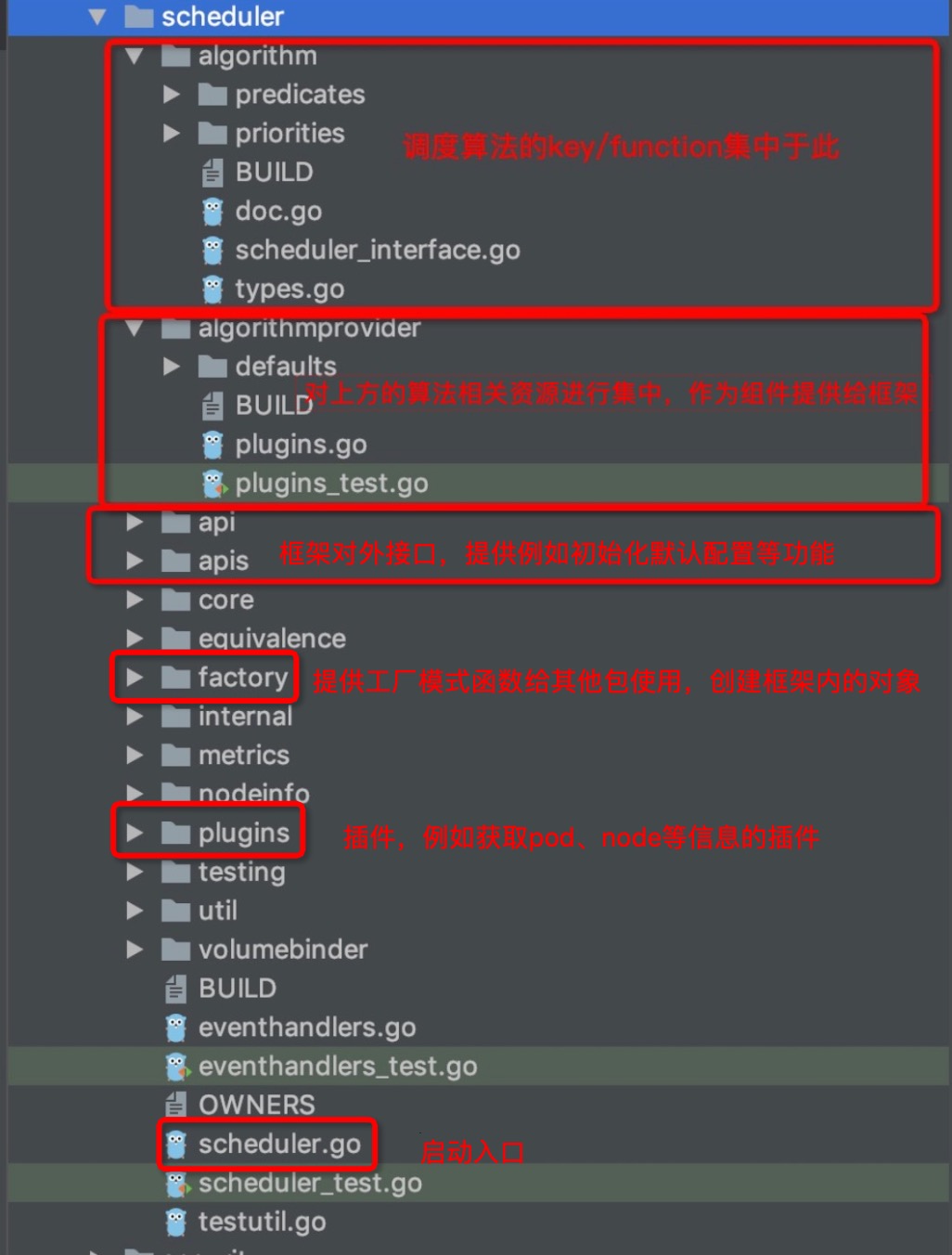
最后,对`pkg/scheduler`路径下的各子目录的功能来一个图文总结吧:
-
+
diff --git a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P3-Node筛选算法.md b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P3-Node筛选算法.md
index 59b9648..bfeed9e 100644
--- a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P3-Node筛选算法.md
+++ b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P3-Node筛选算法.md
@@ -145,7 +145,7 @@ ParallelizeUntil()的这种实现方式,可以很好地将并发实现和具
`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:460 --> pkg/scheduler/internal/cache/node_tree.go:161`
-
+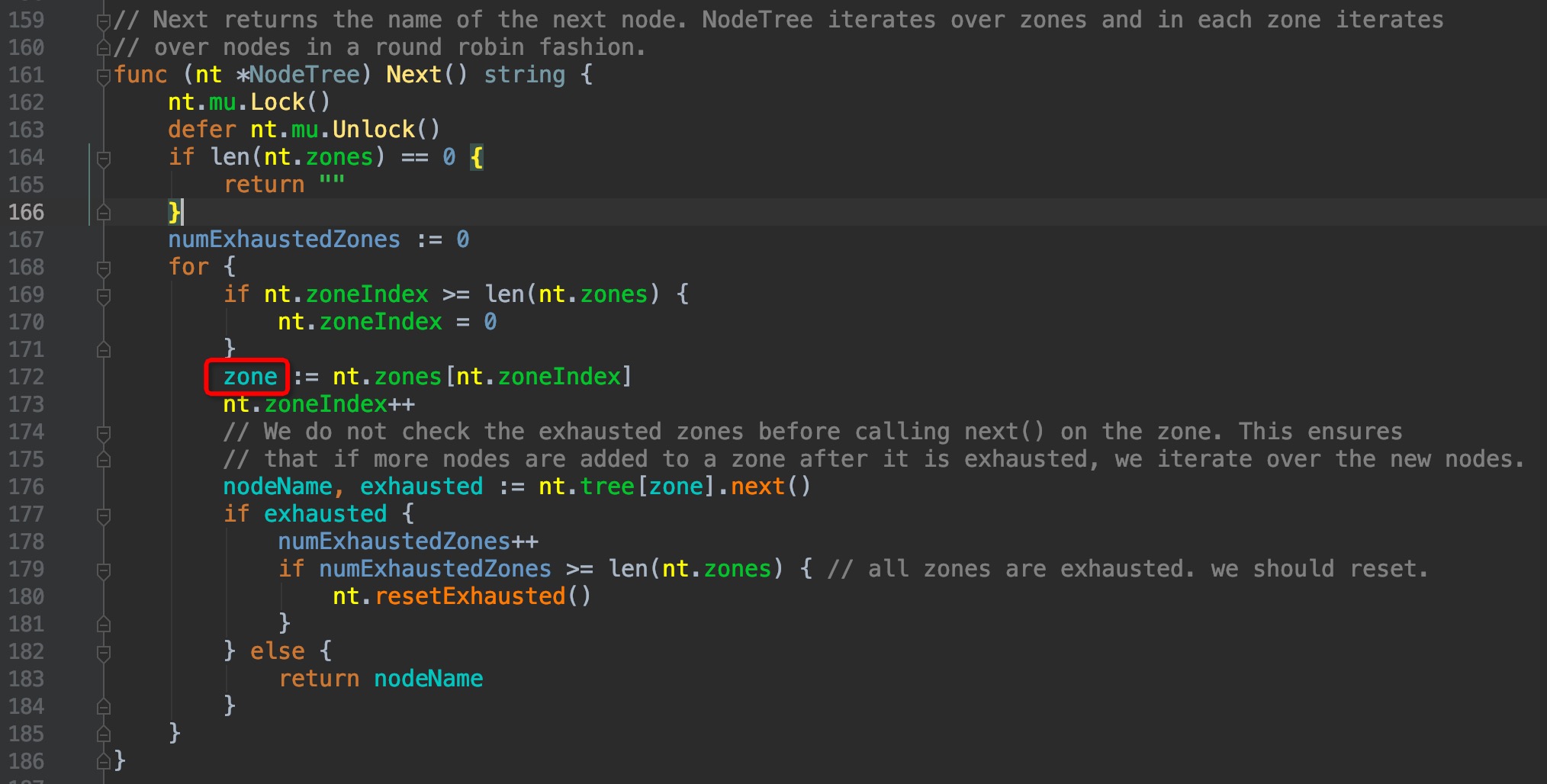
可以看到,这里有一个zone的逻辑层级,这个层级仿佛没有见过,google了一番才了解了这个颇为冷门的功能:这是一个轻量级的支持集群联邦特性的实现,单个cluster可以属于多个zone,但这个功能目前只有GCE和AWS支持,且绝大多数的使用场景也用不到,可以说是颇为冷门。默认情况下,cluster只属于一个zone,可以理解为cluster和zone是同层级,因此后面见到有关zone相关的层级,我们直接越过它。有兴趣的朋友可以了解一下zone的概念:
@@ -231,7 +231,7 @@ func podFitsOnNode(
有了以上理解,我们接着看代码,图中已注释:
-
+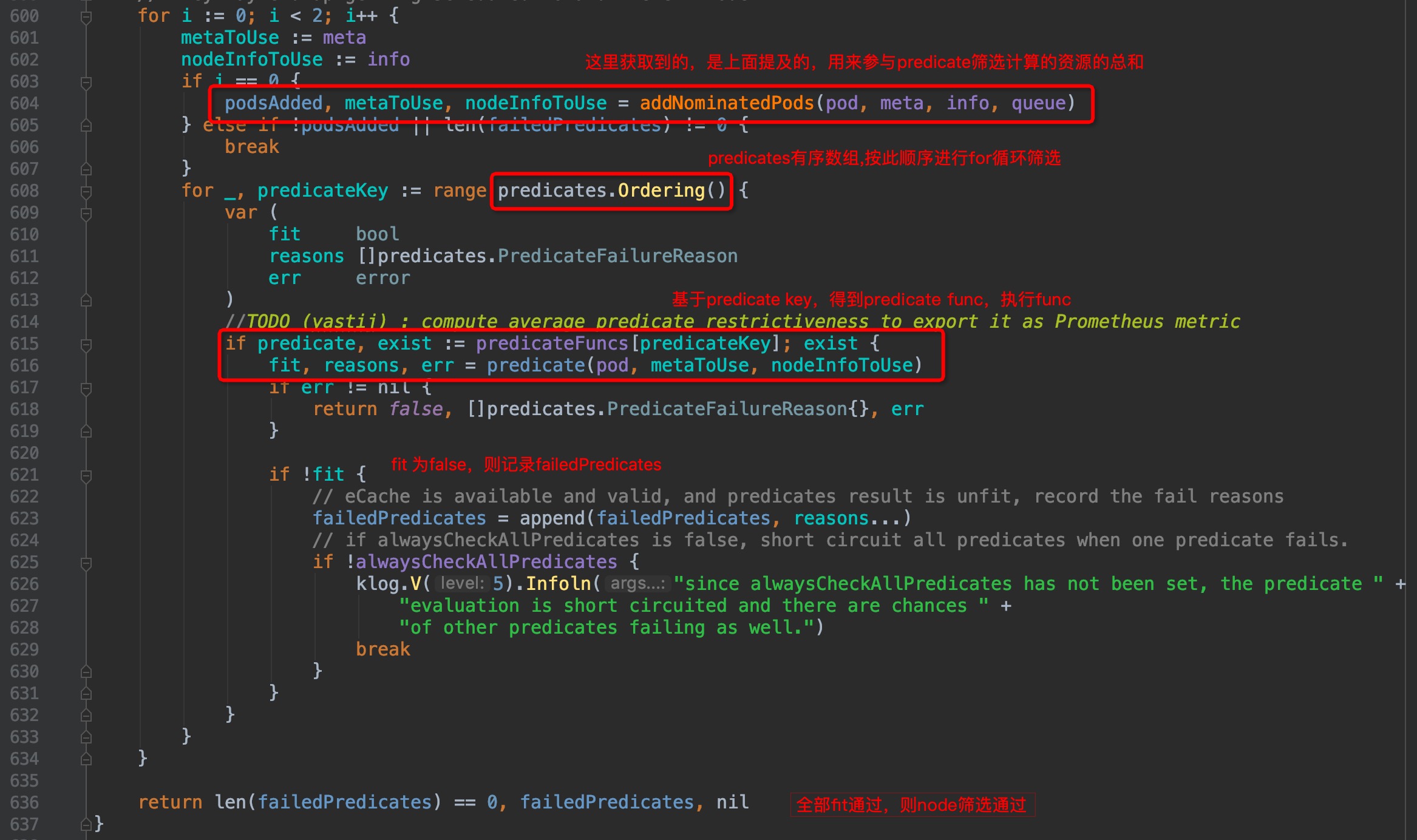
图中`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:608`位置正式开始了逐个计算筛选算法,那么筛选方法、筛选方法顺序在哪里呢?在上一篇[P2-框架篇]([https://github.com/yinwenqin/kubeSourceCodeNote/blob/master/scheduler/P2-%E8%B0%83%E5%BA%A6%E5%99%A8%E6%A1%86%E6%9E%B6.md](https://github.com/yinwenqin/kubeSourceCodeNote/blob/master/scheduler/P2-调度器框架.md))中已经有讲过,默认调度算法都在`pkg/scheduler/algorithm/`路径下,我们接着往下看.
@@ -260,7 +260,7 @@ var (
[链接](https://github.com/kubernetes/community/blob/master/contributors/design-proposals/scheduling/predicates-ordering.md)
-
+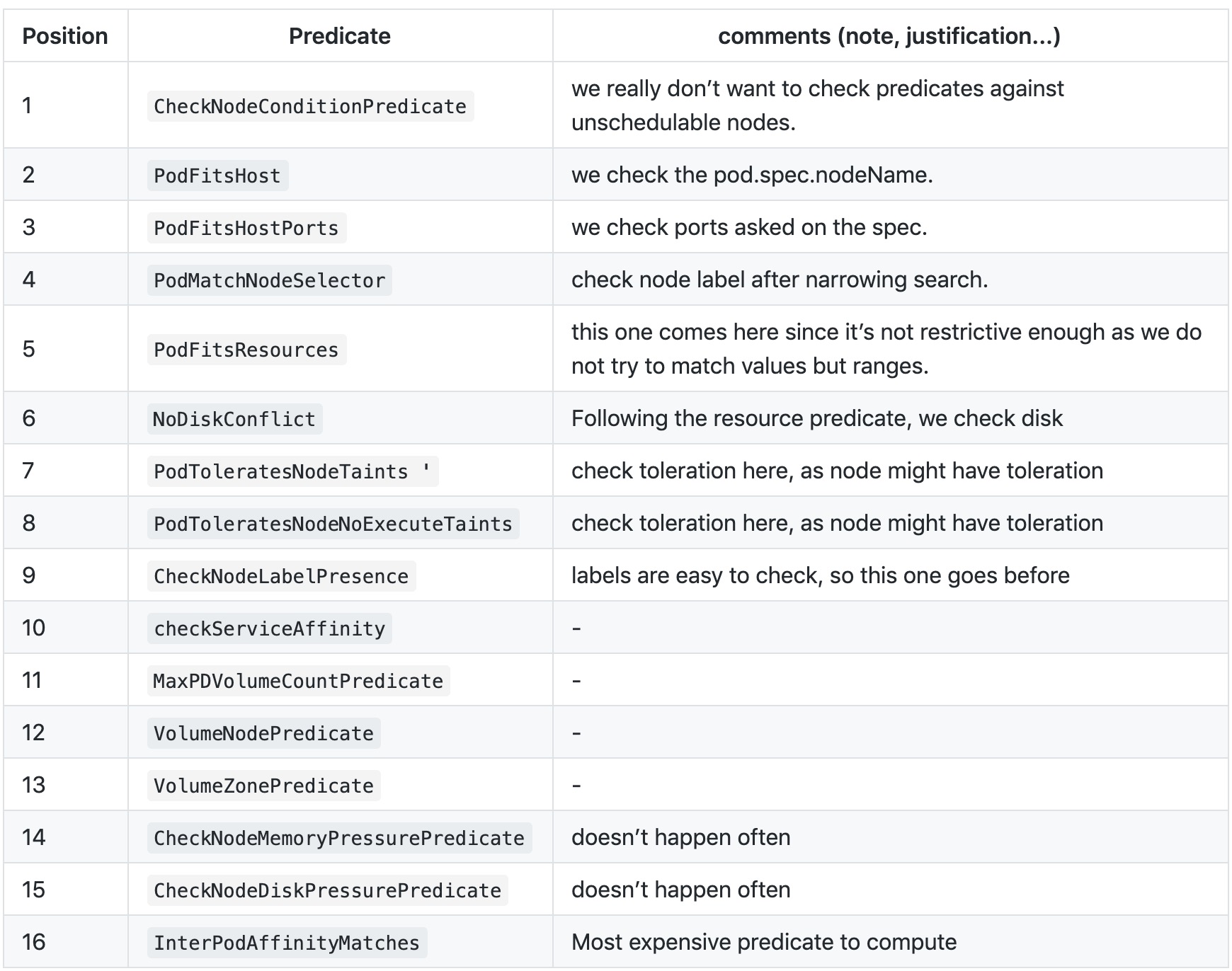
#### 筛选key
diff --git a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P4-Node优先级算法.md b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P4-Node优先级算法.md
index 7c7c8bd..e7e1acb 100644
--- a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P4-Node优先级算法.md
+++ b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P4-Node优先级算法.md
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ Tips: 本篇篇幅较长,因调度优选算法较为复杂,但请耐心结
同上一篇,回到`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go`中的`Schedule()`函数,`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:184`:
-
+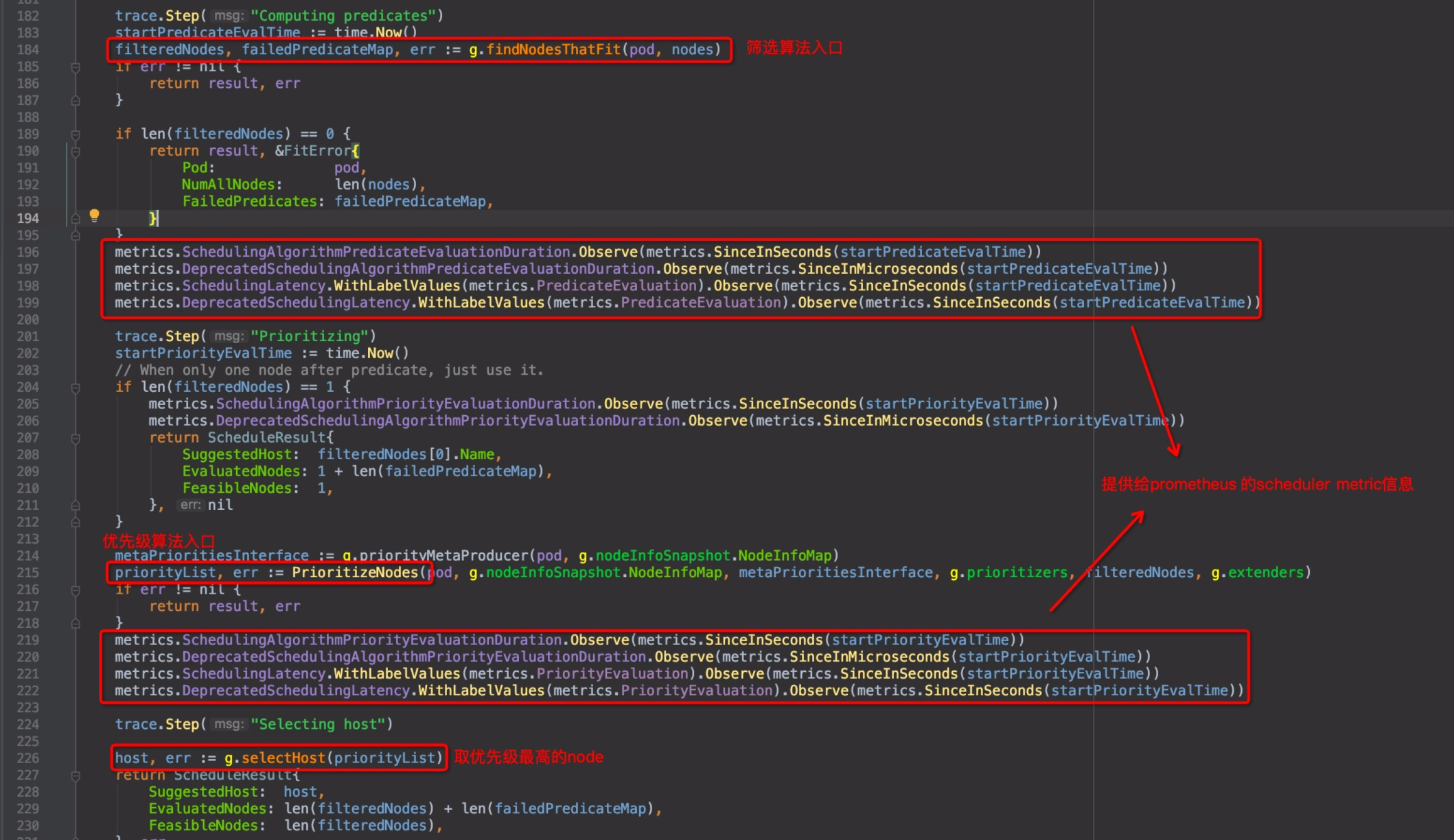
截图中有几处标注,metric相关的几行,是收集metric信息,用以提供给prometheus使用的,kubernetes的几个核心组件都有这个功能,以后如果读prometheus的源码,这个单独拎出来再讲。直接进入优先级函数`PrioritizeNodes()`内部`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:215`
@@ -201,7 +201,7 @@ func defaultPriorities() sets.String {
在注册的每一个计算维度,都有专属的维度描述关键字,即factory方法的第一个参数(str类型)。不难发现,这里的每一个关键字,`pkg/scheduler/algorithm/priorities`目录内都有与其对应的文件,图中圈出了几个例子(灵魂画笔请原谅):
-
+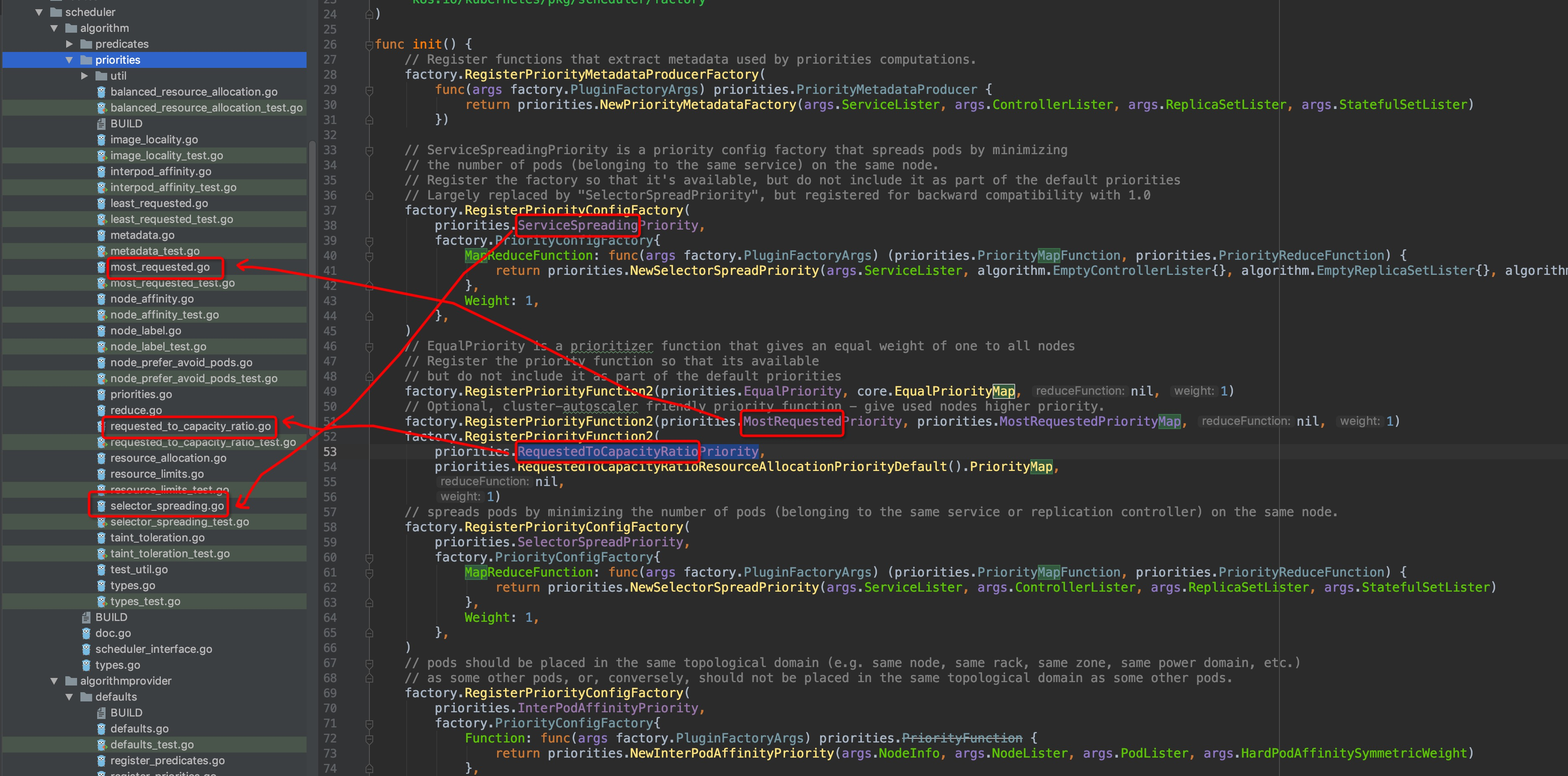
显而易见,维度计算的内容就在这些文件中,可以自行通过编辑器的跳转功能逐级查看进行验证.
@@ -239,7 +239,7 @@ func CalculateNodePreferAvoidPodsPriorityMap(pod *v1.Pod, meta interface{}, node
这也印证了前面说的当前仅剩pod亲和性这一个维度在使用传统的Function,虽然已经被DEPRECATED掉了,传统的Function是直接计算出结果,Map-Reduce是将这个过程解耦拆成了两个步骤,且我们可以看到所有的factory函数,很多形参`reduceFunction`接收到的实参实际是是`nil`:
-
+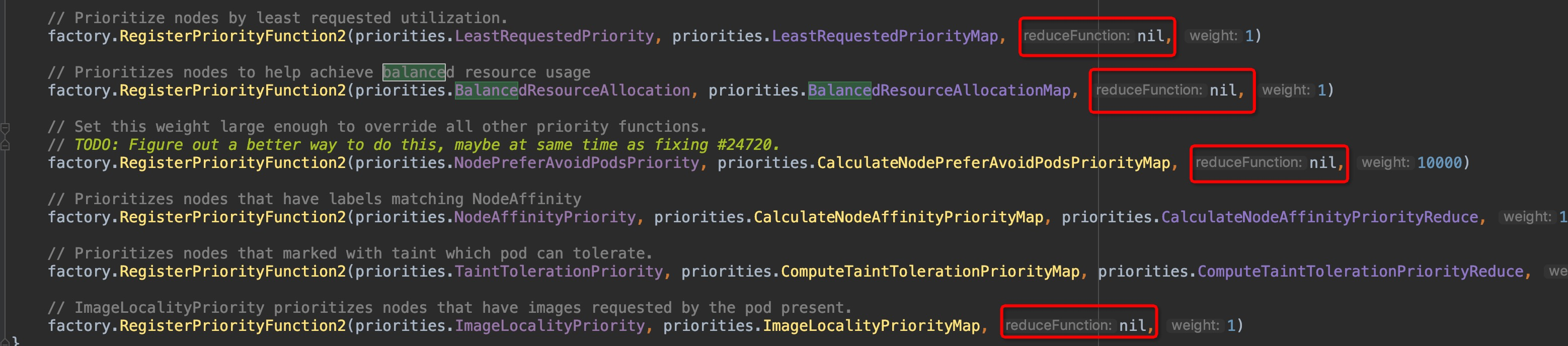
这就说明这些维度的计算工作在map函数里面已经执行完成了,不需要再执行reduce函数了。因此,传统的Function的计算过程同样值得参考,那么首先就来看看`InterPodAffinityPriority`维度是怎么计算的吧!
#### 总结
diff --git a/controller/README.md b/controller/README.md
index 83653e1..eeffe87 100644
--- a/controller/README.md
+++ b/controller/README.md
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ for {
kube-controller是一个控制组件,根据我们的使用经验,有多种经常使用的资源,都不是实际地直接进行任务计算的资源类型,而在申明之后由k8s自动发现并保证以达成申明语义状态的逻辑资源,例如deployment、statefulSet、pvc、endpoint等,这些资源都分别由对应的controller子组件,那么这样的controller子组件有多少呢?如下图:
-
+
可见controller的组件数量是非常之多的,因此在本部分中计划只抽选其中的deploymentController和statefulSetController这两种常见的对pod管理类型资源对应的controller来进行源码分析。
@@ -59,11 +59,11 @@ kube-controller是一个控制组件,根据我们的使用经验,有多种
`kubernetes/src/k8s.io/kubernetes/cmd/kube-controller-manager/controller-manager.go`
-
+
**功能模块**
`kubernetes/src/k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/controller`
-
+
diff --git a/kubelet/Kubernetes源码学习-Kubelet-P1-启动流程篇.md b/kubelet/Kubernetes源码学习-Kubelet-P1-启动流程篇.md
index adf0a47..766d974 100644
--- a/kubelet/Kubernetes源码学习-Kubelet-P1-启动流程篇.md
+++ b/kubelet/Kubernetes源码学习-Kubelet-P1-启动流程篇.md
@@ -768,7 +768,9 @@ func startKubelet(k kubelet.Bootstrap, podCfg *config.PodConfig, kubeCfg *kubele
}
```
-wait.Until()循环执行函数前面的文章中已经分析过多次了,不再赘述,来分析一下k.Run(podCfg.Updates())传的实参是什么:
+wait.Until()循环执行函数前面的文章中已经分析过多次了,不再过多赘述,这里传参是period是0,说明是无间隔死循环调用k.Run()方法,体现在实际环境中kubelet运行时的表现就是:无论运行中遇到什么报错,kubelet都会持续工作。
+
+来分析一下k.Run(podCfg.Updates())传的实参是什么:
--> `pkg/kubelet/config/config.go:105`
diff --git a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P1-调度器入口篇.md b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P1-调度器入口篇.md
index 6a6b3c9..d114afb 100644
--- a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P1-调度器入口篇.md
+++ b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P1-调度器入口篇.md
@@ -56,8 +56,8 @@ matebook-x-pro:local ywq$ go run main.go
# 因需要多次测试,这里所有的测试步骤就把build的步骤跳过,直接使用go run main.go进行测试
```
**我们打开IDE来查看一下testapp的代码结构:**
-
-
+
+
```
# 现在还未创建子命令,那么来创建几个试试:
@@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ add called
```
**来看看新增的子命令是怎么运行的呢?**
-
+
截图圈中部分可以看出,子命令是在init()函数里为root级添加了一个子命令,先不去管底层实现,接着往下.
**测试cobra的强大简洁的flag处理**
@@ -101,7 +101,7 @@ deleteCmd.PersistentFlags().StringVar(&obj,"object", "", "A function to delete a
```
在`Run:func()`匿名函数中添加一行输出:
`fmt.Println("delete obj:",cmd.Flag("object").Value)`
-
+
运行结果:
@@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ delete obj: obj1
```
如果觉得`--`flag符号太麻烦,cobra同样支持短符号`-`flag缩写:
-
+
运行结果:
@@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ add.go delete.go get.go pods.go root.go
```
可以发现,cmd/目录下多了一个pods.go文件,我们来看看它是怎么关联上delete父级命令的,同时为它添加一行输出:
-
+
执行命令:
```
@@ -146,13 +146,13 @@ delete pods: pod1
## 入口
通过对上方cobra的基本了解,我们不难知道,`cmd/kube-scheduler/scheduler.go`内的main()方法内部实际调用的是`cobra.Command.Run`内的匿名函数,我们可以进入`NewSchedulerCommand()`内部确认:
-
+
可以看到,调用了`Run`内部`runCommand`方法,再来看看Run方法内部需要重点关注的几个点:
-
+
其中,上方是对命令行的参数、选项校验的步骤,跳过,重点关注两个变量:`cc和stopCh`,这两个变量会作为最后调用`Run()`方法的参数,其中`stopCh`作用是作为主程序退出的信号通知其他各协程进行相关的退出操作的,另外一个cc变量非常重要,可以点击`c.Complete()`方法,查看该方法的详情:
-
+
`Complete()`方法本质上返回的是一个Config结构体,该结构体内部的元素非常丰富,篇幅有限就不一一点开截图了,大家可以自行深入查看这些元素的作用,这里简单概括一下其中几个:
```
@@ -175,14 +175,14 @@ Recorder record.EventRecorder
Broadcaster record.EventBroadcaster
```
这里层级非常深,不便展示,Config这一个结构体非常重要,可以认真读一读代码。回到`cmd/kube-scheduler/app/server.go`.`runCommand`这里来,接着往下,进入其最后return调用的`Run()`函数中,函数中的前部分都是启动scheduler相关的组件,如event broadcaster、informers、healthz server、metric server等,重点看图中红框圈出的`sched.Run()`,这才是scheduler主程序的调用运行函数:
-
+
进入`sched.Run()`:
-
+
`wait.Until`这个调用的逻辑是,直到收到stop信号才终止,在此之前循环运行`sched.scheduleOne`。代码走到这里,终于找到启动入口最内部的主体啦:
-
+
`sched.scheduleOne`这个函数有代码点长,整体的功能可以概括为:
diff --git a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P2-调度器框架.md b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P2-调度器框架.md
index d010094..fb3db33 100644
--- a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P2-调度器框架.md
+++ b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P2-调度器框架.md
@@ -12,15 +12,15 @@
回顾上一篇篇末,我们找到了调度框架的实际调度工作逻辑的入口位置,`pkg/scheduler/scheduler.go:435`, `scheduleOne()`函数内部,定位在`pkg/scheduler/scheduler.go:457`位置,是通过这个`sched.schedule(pod)`方法来获取与pod匹配的node的,我们直接跳转2次,来到了这里`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:107`
-
+
-
+
-
+
通过注释可以知道,ScheduleAlgorithm interface中的Schedule方法就是用来为pod筛选node的,但这是个接口方法,并不是实际调用的,我们稍微往下,在`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:162`这个位置,就可以找到实际调用的Schedule方法:
-
+
这个函数里面有4个重要的步骤:
@@ -46,41 +46,41 @@ g.selectHost(priorityList)
先来逆向回溯代码结构,找到哪里创建了scheduler,调度器的默认初始化配置,默认的调度算法来源等等框架相关的东西。`Schedule()`方法属于`genericScheduler`结构体,先查看`genericScheduler`结构体,再选中结构体名称,crtl + b组合键查看它在哪些地方被引用,找出创建结构体的位置:
-
+
通过缩略代码框,排除test相关的测试文件,很容易找出创建结构体的地方位于`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:1189`,点击图中红框圈中位置,跳转过去,果然找到了`NewGenericScheduler()`方法,这个方法是用来创建一个`genericScheduler`对象的,那么我们再次crtl + b组合键查看`NewGenericScheduler`再什么地方被调用:
-
+
找出了在`pkg/scheduler/factory/factory.go:441`这个位置上找到了调用入口,这里位于`CreateFromKeys()`方法中,继续crtl + b查看它的引用,跳转到`pkg/scheduler/factory/factory.go:336`这个位置:
-
+
-
+
-
+
这里找到了`algorithmProviderMap`这个变量,顾名思义,这个变量里面包含的应该就是调度算法的来源,点击进去查看,跳转到了`pkg/scheduler/factory/plugins.go:86`这个位置,组合键查看引用,一眼就可以看出哪个引用为这个map添加了元素:
-
+
跳转过去,来到了`pkg/scheduler/factory/plugins.go:391`这个位置,这个函数的作用是为scheduler的配置指定调度算法,即`FitPredicate、Priority`这两个算法需要用到的metric或者方法,再次请出组合键,查找哪个地方调用了这个方法:
-
+
来到了`pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/defaults.go:99`,继续组合键向上查找引用,这次引用只有一个,没有弹窗直接跳转过去了`pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/defaults.go:36`:
-
+
-
+
我们来看看`defaultPredicates(), defaultPriorities()`这两个函数具体的内容:
-
+
我们随便点击进去一个`predicates`选项查看其内容:
-
+
`CheckNodeMemoryPressure`这个词相应熟悉kubernetes 应用的朋友一定不会陌生,例如在node内存压力大无法调度的pod时,`kubectl describe pod xxx`就会在状态信息里面看到这个关键词。
@@ -103,7 +103,7 @@ func RegisterAlgorithmProvider(name string, predicateKeys, priorityKeys sets.Str
可以看到,这个方法为DefaultProvider绑定了配置:筛选算法和优先级排序算法的key集合,这些key只是字符串,那么是怎么具体落实到计算的方法过程上去的呢?让我们看看`pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/`目录下的`register_predicates.go,register_priorities.go`这两个文件:
-
+
它们同样也在init()函数中初始化时使用`factory.RegisterFitPredicate()`方法做了一些注册操作,这个方法的两个参数,前一个是筛选/计算优先级 的关键key名,后一个是具体计算的功能实现方法,点击`factory.RegisterFitPredicate()`方法,深入一级,查看内部代码,
@@ -177,15 +177,15 @@ func (s *Scheme) AddTypeDefaultingFunc(srcType Object, fn func(interface{})) {
我们选中然后ctrl+b,查找AddTypeDefaultingFunc()的引用,弹窗中你可以看到有非常非常多的对象都引用了该方法,这些不同类型的对象相信无一例外都是通过Default()方法来生成默认配置的,我们找到其中的包含scheduler的方法:
-
+
跳转进去,来到了这个位置`pkg/scheduler/apis/config/v1alpha1/zz_generated.defaults.go:31`(原谅我的灵魂笔法):
-
+
进入`SetDefaults_KubeSchedulerConfiguration()`,来到`pkg/scheduler/apis/config/v1alpha1/defaults.go:42`:
-
+
看到了`DefaultProvider`吗?是不是觉得瞬间豁然开朗,原来是在这里调用指定了scheduler配置的`AlgorithmSource.Provider`。
@@ -276,7 +276,7 @@ func podFitsOnNode(
最后,对`pkg/scheduler`路径下的各子目录的功能来一个图文总结吧:
-
+
diff --git a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P3-Node筛选算法.md b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P3-Node筛选算法.md
index 59b9648..bfeed9e 100644
--- a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P3-Node筛选算法.md
+++ b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P3-Node筛选算法.md
@@ -145,7 +145,7 @@ ParallelizeUntil()的这种实现方式,可以很好地将并发实现和具
`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:460 --> pkg/scheduler/internal/cache/node_tree.go:161`
-
+
可以看到,这里有一个zone的逻辑层级,这个层级仿佛没有见过,google了一番才了解了这个颇为冷门的功能:这是一个轻量级的支持集群联邦特性的实现,单个cluster可以属于多个zone,但这个功能目前只有GCE和AWS支持,且绝大多数的使用场景也用不到,可以说是颇为冷门。默认情况下,cluster只属于一个zone,可以理解为cluster和zone是同层级,因此后面见到有关zone相关的层级,我们直接越过它。有兴趣的朋友可以了解一下zone的概念:
@@ -231,7 +231,7 @@ func podFitsOnNode(
有了以上理解,我们接着看代码,图中已注释:
-
+
图中`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:608`位置正式开始了逐个计算筛选算法,那么筛选方法、筛选方法顺序在哪里呢?在上一篇[P2-框架篇]([https://github.com/yinwenqin/kubeSourceCodeNote/blob/master/scheduler/P2-%E8%B0%83%E5%BA%A6%E5%99%A8%E6%A1%86%E6%9E%B6.md](https://github.com/yinwenqin/kubeSourceCodeNote/blob/master/scheduler/P2-调度器框架.md))中已经有讲过,默认调度算法都在`pkg/scheduler/algorithm/`路径下,我们接着往下看.
@@ -260,7 +260,7 @@ var (
[链接](https://github.com/kubernetes/community/blob/master/contributors/design-proposals/scheduling/predicates-ordering.md)
-
+
#### 筛选key
diff --git a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P4-Node优先级算法.md b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P4-Node优先级算法.md
index 7c7c8bd..e7e1acb 100644
--- a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P4-Node优先级算法.md
+++ b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P4-Node优先级算法.md
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ Tips: 本篇篇幅较长,因调度优选算法较为复杂,但请耐心结
同上一篇,回到`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go`中的`Schedule()`函数,`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:184`:
-
+
截图中有几处标注,metric相关的几行,是收集metric信息,用以提供给prometheus使用的,kubernetes的几个核心组件都有这个功能,以后如果读prometheus的源码,这个单独拎出来再讲。直接进入优先级函数`PrioritizeNodes()`内部`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:215`
@@ -201,7 +201,7 @@ func defaultPriorities() sets.String {
在注册的每一个计算维度,都有专属的维度描述关键字,即factory方法的第一个参数(str类型)。不难发现,这里的每一个关键字,`pkg/scheduler/algorithm/priorities`目录内都有与其对应的文件,图中圈出了几个例子(灵魂画笔请原谅):
-
+
显而易见,维度计算的内容就在这些文件中,可以自行通过编辑器的跳转功能逐级查看进行验证.
@@ -239,7 +239,7 @@ func CalculateNodePreferAvoidPodsPriorityMap(pod *v1.Pod, meta interface{}, node
这也印证了前面说的当前仅剩pod亲和性这一个维度在使用传统的Function,虽然已经被DEPRECATED掉了,传统的Function是直接计算出结果,Map-Reduce是将这个过程解耦拆成了两个步骤,且我们可以看到所有的factory函数,很多形参`reduceFunction`接收到的实参实际是是`nil`:
-
+
这就说明这些维度的计算工作在map函数里面已经执行完成了,不需要再执行reduce函数了。因此,传统的Function的计算过程同样值得参考,那么首先就来看看`InterPodAffinityPriority`维度是怎么计算的吧!
 +
+ 那么依次逐个来看看每一种Authenticator对应的AuthenticateRequest方法。
@@ -192,7 +192,7 @@ extra:
使用kubeadm默认部署的集群,就启用了requestheader的配置:
-
+
来看看AuthenticateRequest方法的代码:
@@ -500,7 +500,7 @@ SA是一种面向集群内部应用需要调用APIServer的场景所设计的认
在集群上找一个例子,以kube-proxy举例:
-
+
看看代码层面:
diff --git a/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P4-APIServer的鉴权机制.md b/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P4-APIServer的鉴权机制.md
index 7b11785..9e6b3f4 100644
--- a/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P4-APIServer的鉴权机制.md
+++ b/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P4-APIServer的鉴权机制.md
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ Kubernetes 仅审查以下 API 请求属性:
来看看现有的kubeadm部署集群启用的鉴权策略:
-
+
可以看到,默认启用了Node授权和RBAC授权模块。
@@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ DefaultResourceRuleInfo{
### 鉴权流程图
-
+
@@ -218,7 +218,7 @@ RBAC 鉴权机制使用 `rbac.authorization.k8s.io` [API 组](https://kubernetes
RBAC模式的详细描述和使用样例请参考我之前的文章:
-[k8s(十四)、RBAC权限控制](https://blog.upweto.top/2018/12/06/k8s(%E5%8D%81%E5%9B%9B)%E3%80%81RBAC%E6%9D%83%E9%99%90%E6%8E%A7%E5%88%B6.html)
+[k8s(十四)、RBAC权限控制](https://blog.wqyin.cn/2018/12/06/k8s(%E5%8D%81%E5%9B%9B)%E3%80%81RBAC%E6%9D%83%E9%99%90%E6%8E%A7%E5%88%B6.html)
diff --git a/apiServer/README.md b/apiServer/README.md
index b138769..e96b456 100644
--- a/apiServer/README.md
+++ b/apiServer/README.md
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ APIServer提供了 k8s各类资源对象的CURD/watch、认证授权、准入控
如图所示,这是创建一个资源(Pod)实例过程中,控制层面所经过的调用过程:
-
+
在这个过程中,控制层面的每个组件、每一步骤,都需要与APIServer交互。
diff --git a/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.md b/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.md
index 20733ca..6e87fa4 100644
--- a/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.md
+++ b/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.md
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ watch依然比较麻烦,毕竟list获取的数据以及后续watch到的数据
#### 工作流程图
-
+
#### 流程图组件解释
diff --git a/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P3-Controller分类与Deployment Controller.md b/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P3-Controller分类与Deployment Controller.md
index 32934c6..c1c52e7 100644
--- a/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P3-Controller分类与Deployment Controller.md
+++ b/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P3-Controller分类与Deployment Controller.md
@@ -6,11 +6,11 @@
Controller部分的第一篇文章中,我们从cobra启动命令入口开始,进入到了多实例leader选举部分的代码,对leader选举流程做了详细地分析:
-[Controller-P1-多实例leader选举](https://blog.upweto.top/gitbooks/kubeSourceCodeNote/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P1-多实例leader选举.html)
+[Controller-P1-多实例leader选举](https://blog.wqyin.cn/gitbooks/kubeSourceCodeNote/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P1-多实例leader选举.html)
接着在第二篇中,文字和图解简单描述了controller是如何结合client-go模块中的informer工作的,为本篇及后面的几篇作铺垫:
-[Controller-P2-Controller与informer](https://blog.upweto.top/gitbooks/kubeSourceCodeNote/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.html)
+[Controller-P2-Controller与informer](https://blog.wqyin.cn/gitbooks/kubeSourceCodeNote/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.html)
那么本篇,就接着第一篇往下,继续看代码。
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ if err := StartControllers(controllerContext, saTokenControllerInitFunc, NewCont
==> `cmd/kube-controller-manager/app/controllermanager.go:343`
-
那么依次逐个来看看每一种Authenticator对应的AuthenticateRequest方法。
@@ -192,7 +192,7 @@ extra:
使用kubeadm默认部署的集群,就启用了requestheader的配置:
-
+
来看看AuthenticateRequest方法的代码:
@@ -500,7 +500,7 @@ SA是一种面向集群内部应用需要调用APIServer的场景所设计的认
在集群上找一个例子,以kube-proxy举例:
-
+
看看代码层面:
diff --git a/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P4-APIServer的鉴权机制.md b/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P4-APIServer的鉴权机制.md
index 7b11785..9e6b3f4 100644
--- a/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P4-APIServer的鉴权机制.md
+++ b/apiServer/Kubernetes源码学习-APIServer-P4-APIServer的鉴权机制.md
@@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ Kubernetes 仅审查以下 API 请求属性:
来看看现有的kubeadm部署集群启用的鉴权策略:
-
+
可以看到,默认启用了Node授权和RBAC授权模块。
@@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ DefaultResourceRuleInfo{
### 鉴权流程图
-
+
@@ -218,7 +218,7 @@ RBAC 鉴权机制使用 `rbac.authorization.k8s.io` [API 组](https://kubernetes
RBAC模式的详细描述和使用样例请参考我之前的文章:
-[k8s(十四)、RBAC权限控制](https://blog.upweto.top/2018/12/06/k8s(%E5%8D%81%E5%9B%9B)%E3%80%81RBAC%E6%9D%83%E9%99%90%E6%8E%A7%E5%88%B6.html)
+[k8s(十四)、RBAC权限控制](https://blog.wqyin.cn/2018/12/06/k8s(%E5%8D%81%E5%9B%9B)%E3%80%81RBAC%E6%9D%83%E9%99%90%E6%8E%A7%E5%88%B6.html)
diff --git a/apiServer/README.md b/apiServer/README.md
index b138769..e96b456 100644
--- a/apiServer/README.md
+++ b/apiServer/README.md
@@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ APIServer提供了 k8s各类资源对象的CURD/watch、认证授权、准入控
如图所示,这是创建一个资源(Pod)实例过程中,控制层面所经过的调用过程:
-
+
在这个过程中,控制层面的每个组件、每一步骤,都需要与APIServer交互。
diff --git a/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.md b/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.md
index 20733ca..6e87fa4 100644
--- a/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.md
+++ b/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.md
@@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ watch依然比较麻烦,毕竟list获取的数据以及后续watch到的数据
#### 工作流程图
-
+
#### 流程图组件解释
diff --git a/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P3-Controller分类与Deployment Controller.md b/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P3-Controller分类与Deployment Controller.md
index 32934c6..c1c52e7 100644
--- a/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P3-Controller分类与Deployment Controller.md
+++ b/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P3-Controller分类与Deployment Controller.md
@@ -6,11 +6,11 @@
Controller部分的第一篇文章中,我们从cobra启动命令入口开始,进入到了多实例leader选举部分的代码,对leader选举流程做了详细地分析:
-[Controller-P1-多实例leader选举](https://blog.upweto.top/gitbooks/kubeSourceCodeNote/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P1-多实例leader选举.html)
+[Controller-P1-多实例leader选举](https://blog.wqyin.cn/gitbooks/kubeSourceCodeNote/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P1-多实例leader选举.html)
接着在第二篇中,文字和图解简单描述了controller是如何结合client-go模块中的informer工作的,为本篇及后面的几篇作铺垫:
-[Controller-P2-Controller与informer](https://blog.upweto.top/gitbooks/kubeSourceCodeNote/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.html)
+[Controller-P2-Controller与informer](https://blog.wqyin.cn/gitbooks/kubeSourceCodeNote/controller/Kubernetes源码学习-Controller-P2-Controller与informer.html)
那么本篇,就接着第一篇往下,继续看代码。
@@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ if err := StartControllers(controllerContext, saTokenControllerInitFunc, NewCont
==> `cmd/kube-controller-manager/app/controllermanager.go:343`
- +
+ 可以看到,controller会对不同的资源,分别初始化相应的controller,包含我们常见的deployment、statefulset、endpoint、pvc等等资源,controller种类有多达30余个。因此,在controller整个章节中,不会对它们逐一分析,只会抽取几个常见有代表性地进行深入,本篇就来看看deployment controller吧。
@@ -745,7 +745,7 @@ func (dc *DeploymentController) syncRolloutStatus(allRSs []*apps.ReplicaSet, new
DeploymentCondition在这里面反复出现,便于理解,参照一个正常状态的deployment condition样例:
-
可以看到,controller会对不同的资源,分别初始化相应的controller,包含我们常见的deployment、statefulset、endpoint、pvc等等资源,controller种类有多达30余个。因此,在controller整个章节中,不会对它们逐一分析,只会抽取几个常见有代表性地进行深入,本篇就来看看deployment controller吧。
@@ -745,7 +745,7 @@ func (dc *DeploymentController) syncRolloutStatus(allRSs []*apps.ReplicaSet, new
DeploymentCondition在这里面反复出现,便于理解,参照一个正常状态的deployment condition样例:
- +
+ #### 总结
diff --git a/controller/README.md b/controller/README.md
index 83653e1..eeffe87 100644
--- a/controller/README.md
+++ b/controller/README.md
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ for {
kube-controller是一个控制组件,根据我们的使用经验,有多种经常使用的资源,都不是实际地直接进行任务计算的资源类型,而在申明之后由k8s自动发现并保证以达成申明语义状态的逻辑资源,例如deployment、statefulSet、pvc、endpoint等,这些资源都分别由对应的controller子组件,那么这样的controller子组件有多少呢?如下图:
-
+
可见controller的组件数量是非常之多的,因此在本部分中计划只抽选其中的deploymentController和statefulSetController这两种常见的对pod管理类型资源对应的controller来进行源码分析。
@@ -59,11 +59,11 @@ kube-controller是一个控制组件,根据我们的使用经验,有多种
`kubernetes/src/k8s.io/kubernetes/cmd/kube-controller-manager/controller-manager.go`
-
+
**功能模块**
`kubernetes/src/k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/controller`
-
+
diff --git a/kubelet/Kubernetes源码学习-Kubelet-P1-启动流程篇.md b/kubelet/Kubernetes源码学习-Kubelet-P1-启动流程篇.md
index adf0a47..766d974 100644
--- a/kubelet/Kubernetes源码学习-Kubelet-P1-启动流程篇.md
+++ b/kubelet/Kubernetes源码学习-Kubelet-P1-启动流程篇.md
@@ -768,7 +768,9 @@ func startKubelet(k kubelet.Bootstrap, podCfg *config.PodConfig, kubeCfg *kubele
}
```
-wait.Until()循环执行函数前面的文章中已经分析过多次了,不再赘述,来分析一下k.Run(podCfg.Updates())传的实参是什么:
+wait.Until()循环执行函数前面的文章中已经分析过多次了,不再过多赘述,这里传参是period是0,说明是无间隔死循环调用k.Run()方法,体现在实际环境中kubelet运行时的表现就是:无论运行中遇到什么报错,kubelet都会持续工作。
+
+来分析一下k.Run(podCfg.Updates())传的实参是什么:
--> `pkg/kubelet/config/config.go:105`
diff --git a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P1-调度器入口篇.md b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P1-调度器入口篇.md
index 6a6b3c9..d114afb 100644
--- a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P1-调度器入口篇.md
+++ b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P1-调度器入口篇.md
@@ -56,8 +56,8 @@ matebook-x-pro:local ywq$ go run main.go
# 因需要多次测试,这里所有的测试步骤就把build的步骤跳过,直接使用go run main.go进行测试
```
**我们打开IDE来查看一下testapp的代码结构:**
-
-
+
+
```
# 现在还未创建子命令,那么来创建几个试试:
@@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ add called
```
**来看看新增的子命令是怎么运行的呢?**
-
+
截图圈中部分可以看出,子命令是在init()函数里为root级添加了一个子命令,先不去管底层实现,接着往下.
**测试cobra的强大简洁的flag处理**
@@ -101,7 +101,7 @@ deleteCmd.PersistentFlags().StringVar(&obj,"object", "", "A function to delete a
```
在`Run:func()`匿名函数中添加一行输出:
`fmt.Println("delete obj:",cmd.Flag("object").Value)`
-
+
运行结果:
@@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ delete obj: obj1
```
如果觉得`--`flag符号太麻烦,cobra同样支持短符号`-`flag缩写:
-
+
运行结果:
@@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ add.go delete.go get.go pods.go root.go
```
可以发现,cmd/目录下多了一个pods.go文件,我们来看看它是怎么关联上delete父级命令的,同时为它添加一行输出:
-
+
执行命令:
```
@@ -146,13 +146,13 @@ delete pods: pod1
## 入口
通过对上方cobra的基本了解,我们不难知道,`cmd/kube-scheduler/scheduler.go`内的main()方法内部实际调用的是`cobra.Command.Run`内的匿名函数,我们可以进入`NewSchedulerCommand()`内部确认:
-
+
可以看到,调用了`Run`内部`runCommand`方法,再来看看Run方法内部需要重点关注的几个点:
-
+
其中,上方是对命令行的参数、选项校验的步骤,跳过,重点关注两个变量:`cc和stopCh`,这两个变量会作为最后调用`Run()`方法的参数,其中`stopCh`作用是作为主程序退出的信号通知其他各协程进行相关的退出操作的,另外一个cc变量非常重要,可以点击`c.Complete()`方法,查看该方法的详情:
-
+
`Complete()`方法本质上返回的是一个Config结构体,该结构体内部的元素非常丰富,篇幅有限就不一一点开截图了,大家可以自行深入查看这些元素的作用,这里简单概括一下其中几个:
```
@@ -175,14 +175,14 @@ Recorder record.EventRecorder
Broadcaster record.EventBroadcaster
```
这里层级非常深,不便展示,Config这一个结构体非常重要,可以认真读一读代码。回到`cmd/kube-scheduler/app/server.go`.`runCommand`这里来,接着往下,进入其最后return调用的`Run()`函数中,函数中的前部分都是启动scheduler相关的组件,如event broadcaster、informers、healthz server、metric server等,重点看图中红框圈出的`sched.Run()`,这才是scheduler主程序的调用运行函数:
-
+
进入`sched.Run()`:
-
+
`wait.Until`这个调用的逻辑是,直到收到stop信号才终止,在此之前循环运行`sched.scheduleOne`。代码走到这里,终于找到启动入口最内部的主体啦:
-
+
`sched.scheduleOne`这个函数有代码点长,整体的功能可以概括为:
diff --git a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P2-调度器框架.md b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P2-调度器框架.md
index d010094..fb3db33 100644
--- a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P2-调度器框架.md
+++ b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P2-调度器框架.md
@@ -12,15 +12,15 @@
回顾上一篇篇末,我们找到了调度框架的实际调度工作逻辑的入口位置,`pkg/scheduler/scheduler.go:435`, `scheduleOne()`函数内部,定位在`pkg/scheduler/scheduler.go:457`位置,是通过这个`sched.schedule(pod)`方法来获取与pod匹配的node的,我们直接跳转2次,来到了这里`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:107`
-
+
-
+
-
+
通过注释可以知道,ScheduleAlgorithm interface中的Schedule方法就是用来为pod筛选node的,但这是个接口方法,并不是实际调用的,我们稍微往下,在`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:162`这个位置,就可以找到实际调用的Schedule方法:
-
+
这个函数里面有4个重要的步骤:
@@ -46,41 +46,41 @@ g.selectHost(priorityList)
先来逆向回溯代码结构,找到哪里创建了scheduler,调度器的默认初始化配置,默认的调度算法来源等等框架相关的东西。`Schedule()`方法属于`genericScheduler`结构体,先查看`genericScheduler`结构体,再选中结构体名称,crtl + b组合键查看它在哪些地方被引用,找出创建结构体的位置:
-
+
通过缩略代码框,排除test相关的测试文件,很容易找出创建结构体的地方位于`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:1189`,点击图中红框圈中位置,跳转过去,果然找到了`NewGenericScheduler()`方法,这个方法是用来创建一个`genericScheduler`对象的,那么我们再次crtl + b组合键查看`NewGenericScheduler`再什么地方被调用:
-
+
找出了在`pkg/scheduler/factory/factory.go:441`这个位置上找到了调用入口,这里位于`CreateFromKeys()`方法中,继续crtl + b查看它的引用,跳转到`pkg/scheduler/factory/factory.go:336`这个位置:
-
+
-
+
-
+
这里找到了`algorithmProviderMap`这个变量,顾名思义,这个变量里面包含的应该就是调度算法的来源,点击进去查看,跳转到了`pkg/scheduler/factory/plugins.go:86`这个位置,组合键查看引用,一眼就可以看出哪个引用为这个map添加了元素:
-
+
跳转过去,来到了`pkg/scheduler/factory/plugins.go:391`这个位置,这个函数的作用是为scheduler的配置指定调度算法,即`FitPredicate、Priority`这两个算法需要用到的metric或者方法,再次请出组合键,查找哪个地方调用了这个方法:
-
+
来到了`pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/defaults.go:99`,继续组合键向上查找引用,这次引用只有一个,没有弹窗直接跳转过去了`pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/defaults.go:36`:
-
+
-
+
我们来看看`defaultPredicates(), defaultPriorities()`这两个函数具体的内容:
-
+
我们随便点击进去一个`predicates`选项查看其内容:
-
+
`CheckNodeMemoryPressure`这个词相应熟悉kubernetes 应用的朋友一定不会陌生,例如在node内存压力大无法调度的pod时,`kubectl describe pod xxx`就会在状态信息里面看到这个关键词。
@@ -103,7 +103,7 @@ func RegisterAlgorithmProvider(name string, predicateKeys, priorityKeys sets.Str
可以看到,这个方法为DefaultProvider绑定了配置:筛选算法和优先级排序算法的key集合,这些key只是字符串,那么是怎么具体落实到计算的方法过程上去的呢?让我们看看`pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/`目录下的`register_predicates.go,register_priorities.go`这两个文件:
-
+
它们同样也在init()函数中初始化时使用`factory.RegisterFitPredicate()`方法做了一些注册操作,这个方法的两个参数,前一个是筛选/计算优先级 的关键key名,后一个是具体计算的功能实现方法,点击`factory.RegisterFitPredicate()`方法,深入一级,查看内部代码,
@@ -177,15 +177,15 @@ func (s *Scheme) AddTypeDefaultingFunc(srcType Object, fn func(interface{})) {
我们选中然后ctrl+b,查找AddTypeDefaultingFunc()的引用,弹窗中你可以看到有非常非常多的对象都引用了该方法,这些不同类型的对象相信无一例外都是通过Default()方法来生成默认配置的,我们找到其中的包含scheduler的方法:
-
+
跳转进去,来到了这个位置`pkg/scheduler/apis/config/v1alpha1/zz_generated.defaults.go:31`(原谅我的灵魂笔法):
-
+
进入`SetDefaults_KubeSchedulerConfiguration()`,来到`pkg/scheduler/apis/config/v1alpha1/defaults.go:42`:
-
+
看到了`DefaultProvider`吗?是不是觉得瞬间豁然开朗,原来是在这里调用指定了scheduler配置的`AlgorithmSource.Provider`。
@@ -276,7 +276,7 @@ func podFitsOnNode(
最后,对`pkg/scheduler`路径下的各子目录的功能来一个图文总结吧:
-
+
diff --git a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P3-Node筛选算法.md b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P3-Node筛选算法.md
index 59b9648..bfeed9e 100644
--- a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P3-Node筛选算法.md
+++ b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P3-Node筛选算法.md
@@ -145,7 +145,7 @@ ParallelizeUntil()的这种实现方式,可以很好地将并发实现和具
`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:460 --> pkg/scheduler/internal/cache/node_tree.go:161`
-
+
可以看到,这里有一个zone的逻辑层级,这个层级仿佛没有见过,google了一番才了解了这个颇为冷门的功能:这是一个轻量级的支持集群联邦特性的实现,单个cluster可以属于多个zone,但这个功能目前只有GCE和AWS支持,且绝大多数的使用场景也用不到,可以说是颇为冷门。默认情况下,cluster只属于一个zone,可以理解为cluster和zone是同层级,因此后面见到有关zone相关的层级,我们直接越过它。有兴趣的朋友可以了解一下zone的概念:
@@ -231,7 +231,7 @@ func podFitsOnNode(
有了以上理解,我们接着看代码,图中已注释:
-
+
图中`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:608`位置正式开始了逐个计算筛选算法,那么筛选方法、筛选方法顺序在哪里呢?在上一篇[P2-框架篇]([https://github.com/yinwenqin/kubeSourceCodeNote/blob/master/scheduler/P2-%E8%B0%83%E5%BA%A6%E5%99%A8%E6%A1%86%E6%9E%B6.md](https://github.com/yinwenqin/kubeSourceCodeNote/blob/master/scheduler/P2-调度器框架.md))中已经有讲过,默认调度算法都在`pkg/scheduler/algorithm/`路径下,我们接着往下看.
@@ -260,7 +260,7 @@ var (
[链接](https://github.com/kubernetes/community/blob/master/contributors/design-proposals/scheduling/predicates-ordering.md)
-
+
#### 筛选key
diff --git a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P4-Node优先级算法.md b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P4-Node优先级算法.md
index 7c7c8bd..e7e1acb 100644
--- a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P4-Node优先级算法.md
+++ b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P4-Node优先级算法.md
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ Tips: 本篇篇幅较长,因调度优选算法较为复杂,但请耐心结
同上一篇,回到`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go`中的`Schedule()`函数,`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:184`:
-
+
截图中有几处标注,metric相关的几行,是收集metric信息,用以提供给prometheus使用的,kubernetes的几个核心组件都有这个功能,以后如果读prometheus的源码,这个单独拎出来再讲。直接进入优先级函数`PrioritizeNodes()`内部`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:215`
@@ -201,7 +201,7 @@ func defaultPriorities() sets.String {
在注册的每一个计算维度,都有专属的维度描述关键字,即factory方法的第一个参数(str类型)。不难发现,这里的每一个关键字,`pkg/scheduler/algorithm/priorities`目录内都有与其对应的文件,图中圈出了几个例子(灵魂画笔请原谅):
-
+
显而易见,维度计算的内容就在这些文件中,可以自行通过编辑器的跳转功能逐级查看进行验证.
@@ -239,7 +239,7 @@ func CalculateNodePreferAvoidPodsPriorityMap(pod *v1.Pod, meta interface{}, node
这也印证了前面说的当前仅剩pod亲和性这一个维度在使用传统的Function,虽然已经被DEPRECATED掉了,传统的Function是直接计算出结果,Map-Reduce是将这个过程解耦拆成了两个步骤,且我们可以看到所有的factory函数,很多形参`reduceFunction`接收到的实参实际是是`nil`:
-
+
这就说明这些维度的计算工作在map函数里面已经执行完成了,不需要再执行reduce函数了。因此,传统的Function的计算过程同样值得参考,那么首先就来看看`InterPodAffinityPriority`维度是怎么计算的吧!
#### 总结
diff --git a/controller/README.md b/controller/README.md
index 83653e1..eeffe87 100644
--- a/controller/README.md
+++ b/controller/README.md
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ for {
kube-controller是一个控制组件,根据我们的使用经验,有多种经常使用的资源,都不是实际地直接进行任务计算的资源类型,而在申明之后由k8s自动发现并保证以达成申明语义状态的逻辑资源,例如deployment、statefulSet、pvc、endpoint等,这些资源都分别由对应的controller子组件,那么这样的controller子组件有多少呢?如下图:
-
+
可见controller的组件数量是非常之多的,因此在本部分中计划只抽选其中的deploymentController和statefulSetController这两种常见的对pod管理类型资源对应的controller来进行源码分析。
@@ -59,11 +59,11 @@ kube-controller是一个控制组件,根据我们的使用经验,有多种
`kubernetes/src/k8s.io/kubernetes/cmd/kube-controller-manager/controller-manager.go`
-
+
**功能模块**
`kubernetes/src/k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/controller`
-
+
diff --git a/kubelet/Kubernetes源码学习-Kubelet-P1-启动流程篇.md b/kubelet/Kubernetes源码学习-Kubelet-P1-启动流程篇.md
index adf0a47..766d974 100644
--- a/kubelet/Kubernetes源码学习-Kubelet-P1-启动流程篇.md
+++ b/kubelet/Kubernetes源码学习-Kubelet-P1-启动流程篇.md
@@ -768,7 +768,9 @@ func startKubelet(k kubelet.Bootstrap, podCfg *config.PodConfig, kubeCfg *kubele
}
```
-wait.Until()循环执行函数前面的文章中已经分析过多次了,不再赘述,来分析一下k.Run(podCfg.Updates())传的实参是什么:
+wait.Until()循环执行函数前面的文章中已经分析过多次了,不再过多赘述,这里传参是period是0,说明是无间隔死循环调用k.Run()方法,体现在实际环境中kubelet运行时的表现就是:无论运行中遇到什么报错,kubelet都会持续工作。
+
+来分析一下k.Run(podCfg.Updates())传的实参是什么:
--> `pkg/kubelet/config/config.go:105`
diff --git a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P1-调度器入口篇.md b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P1-调度器入口篇.md
index 6a6b3c9..d114afb 100644
--- a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P1-调度器入口篇.md
+++ b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P1-调度器入口篇.md
@@ -56,8 +56,8 @@ matebook-x-pro:local ywq$ go run main.go
# 因需要多次测试,这里所有的测试步骤就把build的步骤跳过,直接使用go run main.go进行测试
```
**我们打开IDE来查看一下testapp的代码结构:**
-
-
+
+
```
# 现在还未创建子命令,那么来创建几个试试:
@@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ add called
```
**来看看新增的子命令是怎么运行的呢?**
-
+
截图圈中部分可以看出,子命令是在init()函数里为root级添加了一个子命令,先不去管底层实现,接着往下.
**测试cobra的强大简洁的flag处理**
@@ -101,7 +101,7 @@ deleteCmd.PersistentFlags().StringVar(&obj,"object", "", "A function to delete a
```
在`Run:func()`匿名函数中添加一行输出:
`fmt.Println("delete obj:",cmd.Flag("object").Value)`
-
+
运行结果:
@@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ delete obj: obj1
```
如果觉得`--`flag符号太麻烦,cobra同样支持短符号`-`flag缩写:
-
+
运行结果:
@@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ add.go delete.go get.go pods.go root.go
```
可以发现,cmd/目录下多了一个pods.go文件,我们来看看它是怎么关联上delete父级命令的,同时为它添加一行输出:
-
+
执行命令:
```
@@ -146,13 +146,13 @@ delete pods: pod1
## 入口
通过对上方cobra的基本了解,我们不难知道,`cmd/kube-scheduler/scheduler.go`内的main()方法内部实际调用的是`cobra.Command.Run`内的匿名函数,我们可以进入`NewSchedulerCommand()`内部确认:
-
+
可以看到,调用了`Run`内部`runCommand`方法,再来看看Run方法内部需要重点关注的几个点:
-
+
其中,上方是对命令行的参数、选项校验的步骤,跳过,重点关注两个变量:`cc和stopCh`,这两个变量会作为最后调用`Run()`方法的参数,其中`stopCh`作用是作为主程序退出的信号通知其他各协程进行相关的退出操作的,另外一个cc变量非常重要,可以点击`c.Complete()`方法,查看该方法的详情:
-
+
`Complete()`方法本质上返回的是一个Config结构体,该结构体内部的元素非常丰富,篇幅有限就不一一点开截图了,大家可以自行深入查看这些元素的作用,这里简单概括一下其中几个:
```
@@ -175,14 +175,14 @@ Recorder record.EventRecorder
Broadcaster record.EventBroadcaster
```
这里层级非常深,不便展示,Config这一个结构体非常重要,可以认真读一读代码。回到`cmd/kube-scheduler/app/server.go`.`runCommand`这里来,接着往下,进入其最后return调用的`Run()`函数中,函数中的前部分都是启动scheduler相关的组件,如event broadcaster、informers、healthz server、metric server等,重点看图中红框圈出的`sched.Run()`,这才是scheduler主程序的调用运行函数:
-
+
进入`sched.Run()`:
-
+
`wait.Until`这个调用的逻辑是,直到收到stop信号才终止,在此之前循环运行`sched.scheduleOne`。代码走到这里,终于找到启动入口最内部的主体啦:
-
+
`sched.scheduleOne`这个函数有代码点长,整体的功能可以概括为:
diff --git a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P2-调度器框架.md b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P2-调度器框架.md
index d010094..fb3db33 100644
--- a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P2-调度器框架.md
+++ b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P2-调度器框架.md
@@ -12,15 +12,15 @@
回顾上一篇篇末,我们找到了调度框架的实际调度工作逻辑的入口位置,`pkg/scheduler/scheduler.go:435`, `scheduleOne()`函数内部,定位在`pkg/scheduler/scheduler.go:457`位置,是通过这个`sched.schedule(pod)`方法来获取与pod匹配的node的,我们直接跳转2次,来到了这里`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:107`
-
+
-
+
-
+
通过注释可以知道,ScheduleAlgorithm interface中的Schedule方法就是用来为pod筛选node的,但这是个接口方法,并不是实际调用的,我们稍微往下,在`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:162`这个位置,就可以找到实际调用的Schedule方法:
-
+
这个函数里面有4个重要的步骤:
@@ -46,41 +46,41 @@ g.selectHost(priorityList)
先来逆向回溯代码结构,找到哪里创建了scheduler,调度器的默认初始化配置,默认的调度算法来源等等框架相关的东西。`Schedule()`方法属于`genericScheduler`结构体,先查看`genericScheduler`结构体,再选中结构体名称,crtl + b组合键查看它在哪些地方被引用,找出创建结构体的位置:
-
+
通过缩略代码框,排除test相关的测试文件,很容易找出创建结构体的地方位于`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:1189`,点击图中红框圈中位置,跳转过去,果然找到了`NewGenericScheduler()`方法,这个方法是用来创建一个`genericScheduler`对象的,那么我们再次crtl + b组合键查看`NewGenericScheduler`再什么地方被调用:
-
+
找出了在`pkg/scheduler/factory/factory.go:441`这个位置上找到了调用入口,这里位于`CreateFromKeys()`方法中,继续crtl + b查看它的引用,跳转到`pkg/scheduler/factory/factory.go:336`这个位置:
-
+
-
+
-
+
这里找到了`algorithmProviderMap`这个变量,顾名思义,这个变量里面包含的应该就是调度算法的来源,点击进去查看,跳转到了`pkg/scheduler/factory/plugins.go:86`这个位置,组合键查看引用,一眼就可以看出哪个引用为这个map添加了元素:
-
+
跳转过去,来到了`pkg/scheduler/factory/plugins.go:391`这个位置,这个函数的作用是为scheduler的配置指定调度算法,即`FitPredicate、Priority`这两个算法需要用到的metric或者方法,再次请出组合键,查找哪个地方调用了这个方法:
-
+
来到了`pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/defaults.go:99`,继续组合键向上查找引用,这次引用只有一个,没有弹窗直接跳转过去了`pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/defaults.go:36`:
-
+
-
+
我们来看看`defaultPredicates(), defaultPriorities()`这两个函数具体的内容:
-
+
我们随便点击进去一个`predicates`选项查看其内容:
-
+
`CheckNodeMemoryPressure`这个词相应熟悉kubernetes 应用的朋友一定不会陌生,例如在node内存压力大无法调度的pod时,`kubectl describe pod xxx`就会在状态信息里面看到这个关键词。
@@ -103,7 +103,7 @@ func RegisterAlgorithmProvider(name string, predicateKeys, priorityKeys sets.Str
可以看到,这个方法为DefaultProvider绑定了配置:筛选算法和优先级排序算法的key集合,这些key只是字符串,那么是怎么具体落实到计算的方法过程上去的呢?让我们看看`pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/`目录下的`register_predicates.go,register_priorities.go`这两个文件:
-
+
它们同样也在init()函数中初始化时使用`factory.RegisterFitPredicate()`方法做了一些注册操作,这个方法的两个参数,前一个是筛选/计算优先级 的关键key名,后一个是具体计算的功能实现方法,点击`factory.RegisterFitPredicate()`方法,深入一级,查看内部代码,
@@ -177,15 +177,15 @@ func (s *Scheme) AddTypeDefaultingFunc(srcType Object, fn func(interface{})) {
我们选中然后ctrl+b,查找AddTypeDefaultingFunc()的引用,弹窗中你可以看到有非常非常多的对象都引用了该方法,这些不同类型的对象相信无一例外都是通过Default()方法来生成默认配置的,我们找到其中的包含scheduler的方法:
-
+
跳转进去,来到了这个位置`pkg/scheduler/apis/config/v1alpha1/zz_generated.defaults.go:31`(原谅我的灵魂笔法):
-
+
进入`SetDefaults_KubeSchedulerConfiguration()`,来到`pkg/scheduler/apis/config/v1alpha1/defaults.go:42`:
-
+
看到了`DefaultProvider`吗?是不是觉得瞬间豁然开朗,原来是在这里调用指定了scheduler配置的`AlgorithmSource.Provider`。
@@ -276,7 +276,7 @@ func podFitsOnNode(
最后,对`pkg/scheduler`路径下的各子目录的功能来一个图文总结吧:
-
+
diff --git a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P3-Node筛选算法.md b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P3-Node筛选算法.md
index 59b9648..bfeed9e 100644
--- a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P3-Node筛选算法.md
+++ b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P3-Node筛选算法.md
@@ -145,7 +145,7 @@ ParallelizeUntil()的这种实现方式,可以很好地将并发实现和具
`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:460 --> pkg/scheduler/internal/cache/node_tree.go:161`
-
+
可以看到,这里有一个zone的逻辑层级,这个层级仿佛没有见过,google了一番才了解了这个颇为冷门的功能:这是一个轻量级的支持集群联邦特性的实现,单个cluster可以属于多个zone,但这个功能目前只有GCE和AWS支持,且绝大多数的使用场景也用不到,可以说是颇为冷门。默认情况下,cluster只属于一个zone,可以理解为cluster和zone是同层级,因此后面见到有关zone相关的层级,我们直接越过它。有兴趣的朋友可以了解一下zone的概念:
@@ -231,7 +231,7 @@ func podFitsOnNode(
有了以上理解,我们接着看代码,图中已注释:
-
+
图中`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:608`位置正式开始了逐个计算筛选算法,那么筛选方法、筛选方法顺序在哪里呢?在上一篇[P2-框架篇]([https://github.com/yinwenqin/kubeSourceCodeNote/blob/master/scheduler/P2-%E8%B0%83%E5%BA%A6%E5%99%A8%E6%A1%86%E6%9E%B6.md](https://github.com/yinwenqin/kubeSourceCodeNote/blob/master/scheduler/P2-调度器框架.md))中已经有讲过,默认调度算法都在`pkg/scheduler/algorithm/`路径下,我们接着往下看.
@@ -260,7 +260,7 @@ var (
[链接](https://github.com/kubernetes/community/blob/master/contributors/design-proposals/scheduling/predicates-ordering.md)
-
+
#### 筛选key
diff --git a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P4-Node优先级算法.md b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P4-Node优先级算法.md
index 7c7c8bd..e7e1acb 100644
--- a/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P4-Node优先级算法.md
+++ b/scheduler/Kubernetes源码学习-Scheduler-P4-Node优先级算法.md
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ Tips: 本篇篇幅较长,因调度优选算法较为复杂,但请耐心结
同上一篇,回到`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go`中的`Schedule()`函数,`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:184`:
-
+
截图中有几处标注,metric相关的几行,是收集metric信息,用以提供给prometheus使用的,kubernetes的几个核心组件都有这个功能,以后如果读prometheus的源码,这个单独拎出来再讲。直接进入优先级函数`PrioritizeNodes()`内部`pkg/scheduler/core/generic_scheduler.go:215`
@@ -201,7 +201,7 @@ func defaultPriorities() sets.String {
在注册的每一个计算维度,都有专属的维度描述关键字,即factory方法的第一个参数(str类型)。不难发现,这里的每一个关键字,`pkg/scheduler/algorithm/priorities`目录内都有与其对应的文件,图中圈出了几个例子(灵魂画笔请原谅):
-
+
显而易见,维度计算的内容就在这些文件中,可以自行通过编辑器的跳转功能逐级查看进行验证.
@@ -239,7 +239,7 @@ func CalculateNodePreferAvoidPodsPriorityMap(pod *v1.Pod, meta interface{}, node
这也印证了前面说的当前仅剩pod亲和性这一个维度在使用传统的Function,虽然已经被DEPRECATED掉了,传统的Function是直接计算出结果,Map-Reduce是将这个过程解耦拆成了两个步骤,且我们可以看到所有的factory函数,很多形参`reduceFunction`接收到的实参实际是是`nil`:
-
+
这就说明这些维度的计算工作在map函数里面已经执行完成了,不需要再执行reduce函数了。因此,传统的Function的计算过程同样值得参考,那么首先就来看看`InterPodAffinityPriority`维度是怎么计算的吧!